Technology can be a great solution for many businesses and companies. Unfortunately, one of the unfortunate side effects is the amount of various technical jargon, which may be unintelligible to the average person. For the end-user, NFT often means little more than a decentralized collectors’ item or a work of digital art. You can enjoy this industry without understanding how it works. But the trends in blockchain technology can be fascinating even for those who are not involved with creating it. Why are ERC721 and ERC721A so important in NFT? What makes it special and why should we learn about this technology? We’re writing about this below!
- What is ERC721?
- What makes ERC721 compliant tokens useful?
- What is ERC721A?
- How does ERC721A work?
- Why is ERC721A so important?
- What risks are involved with using ERC721A contracts for generating multiple NFT transactions?
- How to minimize the cost of transferring an entire batch of NFT?
- Are ERC721A contracts still considered to be NFT transactions?

What is ERC721?
Although blockchain technology is decentralized, we need a common language which will allow us to understand the data contained within it. As such, token standards like ERC721 become essential. It is a standard which works in a similar way to how all ports or plugs on various devices work. It is worth noting, for example, that formats such as PNG i JPEG, which are commonly associated with NFT, are by themselves image standards.
ERC721 is an extremely popular token standard for creating non-fungible tokens – NFT – on blockchains, such as Ethereum and Polygon. The letter ‘E’ in ‘ERC721’ stands for ‘Ethereum’ and is not the NFT standard that runs on blockchains that are incompatible with Ethereum portfolios such as Solana and Tezos.
What makes ERC721 compliant tokens useful?
Below we outline some of the advantages of this solution:
- Each token is unique (previously mentioned non-fungibility)
- Each token can be transferred or sold
- Owners can authorize other smart contracts to manage tokens
In addition, each of them is crucial to ensuring that NFT markets, such as OpenSea and LooksRare, can operate as intended. It should be pointed out that smart contracts are simply applications that live within blockchain technology. Seems complicated? It can be described in an even simpler way: ERC721 is a standardized way of creating unique blockchain tokens, which can be traded at markets.

What is ERC721A?
Software developers in crypto typically use existing code libraries to simplify the development process of a project. When you write a code that’s in the blockchain, there’s even more pressure to use a battle-proven, existing code wherever possible, because blockchain technology prevents any code editing! In the NFT sector, a single open source code was widely accepted in order to enable the use of ERC721. Then there was the “Azuki” project, which quickly gained recognition in the NFT sector. In addition to the NFT issue itself, the project has created a new implementation of ERC721A.
The implementation of ERC721A is not meant to change the token standard. Its main purpose is to fit the token perfectly, but this task requires a number of other standards to be met, as opposed to ERC721 which has been used to date.
This has led to the reduction of the amount of gas needed to mint new NFT (especially those that are minted in batches).
The gas costs incurred in transferring NFT based on ERC721A to other persons at the original owner’s prices are slightly higher. Overall, the gas savings that ERC721A can provide compared to ERC721 are excellent, but this solution cannot be implemented everywhere. For example, entities that do not mint NFT in bulk will still spend a significant amount of gas if we consider the transfer costs.
Let us remember that NFT provides many limitless possibilities not only for art, music, or sports. It is important to know and understand ERC721 and ERC721A, as this allows us to understand what NFT really is from its very basics. This makes us more aware of the direction in which this sector is developing. It is worth noting that while both implementations are important, they are neither the first nor last elements of NFT. They are the benchmark to follow.
How does ERC721A work?
ERC721A adopts specific conditions which then affect the smart contract project. This impact makes the following things happen:
- Token IDs should always grow steadily – starting from zero. Currently, many NFT projects fulfill this condition.
- The reduction of the gas costs related to minting NFT is the most important part of NFT production.
With these assumptions, ERC721A makes the following optimization of contracts:
- Reduces the unused space, which is used to store metadata from tokens.
- Limits ownership to one coin from the entire NFT batch.
Why is ERC721A so important?
Because it allows us to understand how high the gas charges really are, and what they result from! Reducing your work to sending transactions saves energy. At this point, we should emphasize that blockchain generates 2 types of transactions – reads and writes.
- Write – occurs when we are doing something in a blockchain and its condition changes (for example, we sell NFT).
- Read – it can be said that this is a review of the transaction file.
Users who use blockchain technology incur higher write costs than read costs. Therefore, if we reduce the pool of write information or transaction transfer requirements, we will reduce the cost of minting NFT.
What risks are involved with using ERC721A contracts for generating multiple NFT transactions?
TransferFrom and safeTransferFrom transactions cost more gas, which means that NFT can cost more from the moment of its minting. We should emphasize that using ERC721A leads to an increase in performance without the need to set owners of particular token ID.
For example, in the picture below there are two calls to mint a batch, one by Marcus to mint chips #100, #101, and #102 in one call, and the other by Brutus to mint chips #103 and #104
The above diagram shows that ERC721A must set up the property metadata twice, instead of 5 times – once for the Marcus package and once for the Brutus package. This is not so easy because by transferring a tokenID that does not have an owner address, the contract must create actions that include all tokenID’s in order to verify the original NFT owner. This is because the original owner has the right to move the token and set it to a new entity. Below we present a graph associated with this:
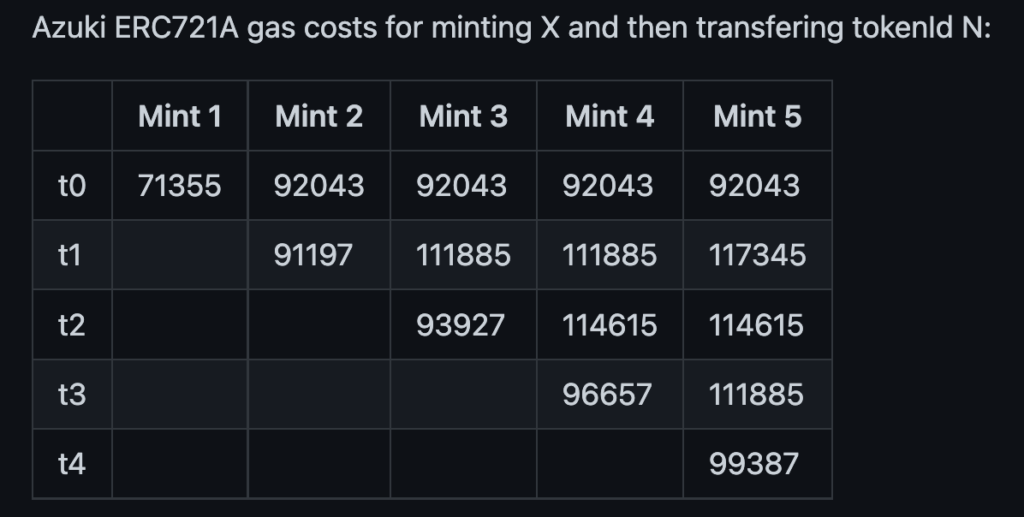
The method of reading this chart is as follows: first move to the x-axis and then to the y-axis, for example:
- „Mint a batch of 1 NFT, and then transfer tokenID 0”,
- „Mint a batch 3 of NFT, and then transfer tokenID 1”
- „Mint a batch 5 of NFT, and then transfer tokenID 4”
The above results indicate that moving token IDs in the middle of a larger mint batch (i.e. t1, t2) costs more than moving token IDs at the end of the batch (i.e. t0, t4).
How to minimize the cost of transferring an entire batch of NFT?
You can minimize costs if you are always minting the maximum allowed number of NFT when releasing an entire batch. In addition – when moving a batch, it is important to start a cycle with tokens of an ODD number in an ascending manner.
Examples of NFT projects using the ERC721A contract
Here is a list of projects, which are currently using the ERC721A contract:
- @AzukiZen
- @cerealclubnft
- @TheLostGlitches
- @standardweb3
- @KittyCryptoGang
- @XRabbitsClub
- @WhaleTogether
- @pixelpiracynft
- @dastardlyducks
- @MissMetaNFT
- @StarcatchersNFT
- @LivesOfAsuna
- @richsadcatnft
- @themonkeypoly
- @womenofcrypto_
- @TravelToucans
- @HuhuNFT
Are ERC721A contracts still considered to be NFT transactions?
Of course. ERC721A contracts are NFT. Any contract that implements the ERC721 token standard, or the ERC1155 interfaces is seen as non-fungible or semi-fungible tokens. To put it simply, ERC721A is an extension and optimization of the previous version, the ERC721. The ERC721A contract is a very good idea which allows for saving money on gas in a given community, while at the same time protecting the Ethereum network from unnecessary workload.



