As the blockchain space evolves, the complexity of creating sustainable, efficient, and fair systems increases. Token Engineering provides a structured framework to address these challenges. It ensures that tokenomics is designed with a clear understanding of its potential impact on user behavior and system dynamics. This is particularly important in decentralized projects, where traditional control mechanisms are replaced by algorithmic governance.
Understanding Token Engineering
Token Engineering is an emerging field that addresses the systematic design and engineering of blockchain-based tokens. It applies rigorous mathematical methods from the Complex Systems Engineering discipline to tokenomics design.
The Basis of Token Engineering
The foundation of Token Engineering lies in the realization that tokens are not merely digital assets but pivotal elements that facilitate governance, incentivize desired behaviors, and enable new forms of economic interactions. The discipline draws upon:
- Complex Systems Science: Understanding the behavior of complex systems is essential for designing token economies that are resilient and adaptable. This involves studying network effects, feedback loops, and emergent behaviors within token ecosystems.
- Behavioral Economics: Integrating insights from behavioral economics allows for the creation of token models that align with human behaviors and motivations, ensuring that token mechanisms encourage beneficial actions within the network.
- Cryptoeconomic Protocols: These protocols are the backbone of decentralized networks, securing transactions and interactions without the need for centralized authorities. Token Engineering involves designing these protocols to ensure they are robust against attacks and manipulations.
The Objectives of Token Engineering
The primary objectives of Token Engineering include:
- Sustainability: Ensuring that the token economy can sustain itself over the long term, through mechanisms that promote balance, reduce volatility, and encourage growth.
- Security: Designing token systems that are secure against speculative attacks, protecting the integrity of the network and its participants.
- Efficiency: Creating token economies that facilitate efficient transactions, interactions, and governance processes, minimizing costs and maximizing benefits for all participants.
The Process of Token Engineering
The process of Token Engineering is a methodical approach to designing, implementing, and refining token-based systems. It involves several stages, from the initial conceptualization of a token economy to its deployment and ongoing management. Each stage requires careful consideration of the economic, technical, and social aspects of the system.
Ideation and Objective Setting
The first step in the Token Engineering process is to clearly define the goals and objectives of the token system. This involves identifying the specific behaviors the tokens are meant to incentivize, the roles they will play within the ecosystem, and the values they represent. Objectives might include creating a more efficient payment system, facilitating decentralized governance, or incentivizing certain behaviors among network participants.
Model Development and Simulation
Once the objectives are set, the next step is to develop a model of the token economy. This model should include the mechanisms by which tokens will be issued, distributed, and exchanged, as well as how they will interact with other elements of the ecosystem. The model also needs to account for potential external influences and the behavior of participants. Simulations are then run to test the model under various conditions, allowing engineers to identify potential issues and make adjustments.
Testing and Refinement
After modeling and simulation, the proposed token system enters the testing phase. This can involve both virtual testing environments and real-world pilots or beta tests. During this phase, the focus is on identifying and fixing bugs, assessing the system's resilience to attacks, and ensuring that it behaves as intended under a wide range of conditions. Feedback from these tests is used to refine the model and improve the system's design.
Deployment and Monitoring
With testing and refinement complete, the token system is ready for deployment. This involves launching the token within the intended environment, whether it be a blockchain network, a specific platform, or a broader ecosystem. After deployment, continuous monitoring is crucial to ensure the system operates as expected, to manage any unforeseen issues, and to make necessary adjustments based on evolving conditions and objectives.
Iterative Improvement
Token Engineering is an iterative process. Even after deployment, the system is continually analyzed and improved based on real-world performance and changing conditions. This might involve adjusting token issuance rates, changing incentive mechanisms, or introducing new features to adapt to users' needs and market dynamics.
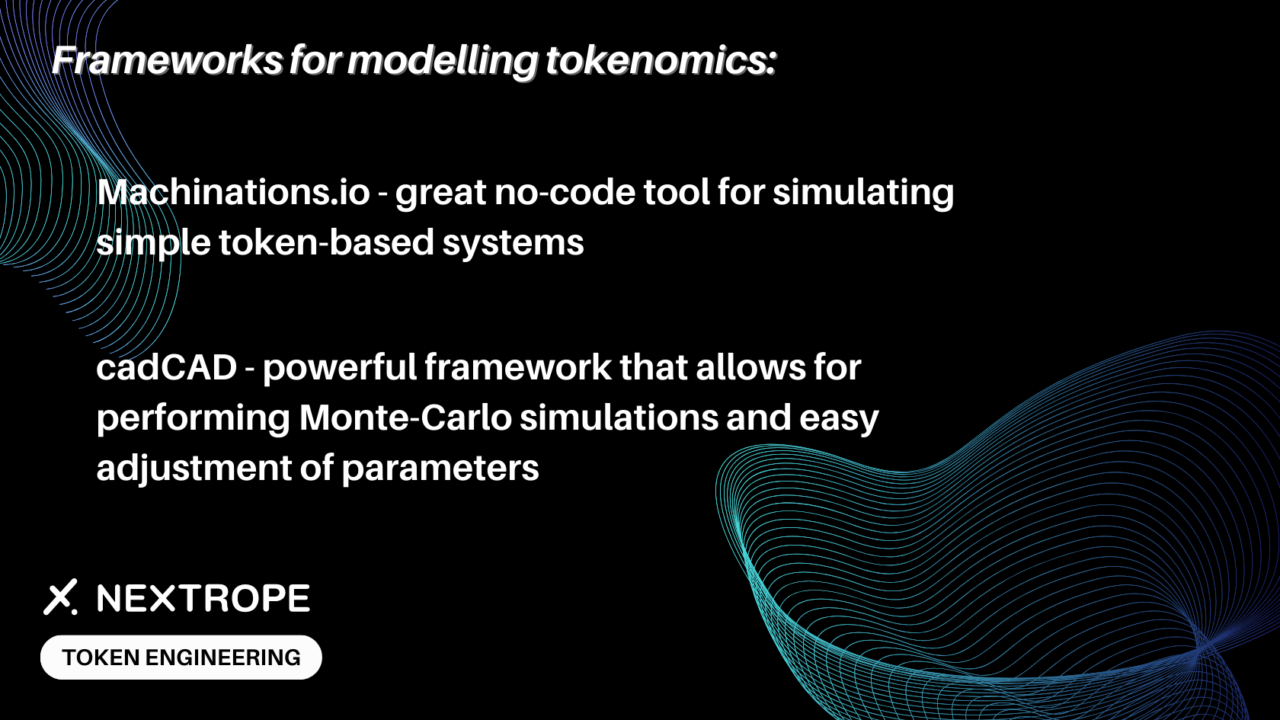
Different Approaches to Modelling
In the realm of Token Engineering, various modeling techniques are employed to analyze and predict the behavior of the protocol under a multitude of scenarios. Two of the most common models utilized are Monte Carlo simulations and agent-based simulations. These models serve as critical tools for engineers and researchers aiming to design efficient, resilient, and sustainable token-based systems.
Monte Carlo Simulations in Token Engineering
Monte Carlo simulations are a class of computational algorithms that rely on repeated random sampling to obtain numerical results. Within the context of Token Engineering, these simulations are used to model the probability of different outcomes in a token economy. The approach is particularly useful for assessing risk and uncertainty in complex systems where analytical solutions may be unattainable.
Token engineers run thousands or even millions of scenarios, each with a set of randomly generated variables. This allows them to study where all the extreme outputs come from and makes them aware of all unwanted interactions.
Agent-Based Simulations in Token Engineering
Agent-based simulations represent another powerful modeling technique, focusing on the interactions of individual agents within a token economy. These agents, which can represent users, smart contracts, or other entities, operate based on a set of rules and can adapt their behavior in response to the changing state of the system.
This type of simulation is particularly adept at capturing the emergent properties of decentralized systems. By simulating the interactions of multiple agents, token engineers can observe how local behaviors scale up to global system dynamics. Agent-based models are invaluable for studying phenomena related to spreading information. For example, the spread of adoption of new token functionalities, or the resilience of the system against coordinated attacks

Conclusion
Token Engineering is pivotal for the advancement of blockchain and decentralized systems, blending disciplines like economics, game theory, and complex systems science to design robust token economies. Through a detailed process from conception to deployment and beyond, it ensures these economies are adaptable and sustainable amidst the dynamic blockchain landscape.
Rigorous testing holds the promise of making decentralized systems more transparent and secure. As regulations roll out, it might be fundamental in proving the long-term viability of crypto projects to the general public.
If you're looking to design a sustainable tokenomics model for your DeFi project, please reach out to contact@nextrope.com. Our team is ready to help you create a tokenomics structure that aligns with your project's long-term growth and market resilience.
FAQ
What is Token Engineering?
- It's a field focused on the systematic design and analysis of token-based systems. It integrates engineering principles to ensure that token economies are sustainable and secure.
How does Token Engineering contribute to sustainability and security in token economies?
- Through modelling and simulations, it makes sure that a project is resilient even to the toughest conditions.
What are the stages involved in the Token Engineering process?
- The process includes ideation and objective setting, model development and simulation, testing and refinement, deployment and monitoring, and iterative improvement.
 en
en  pl
pl