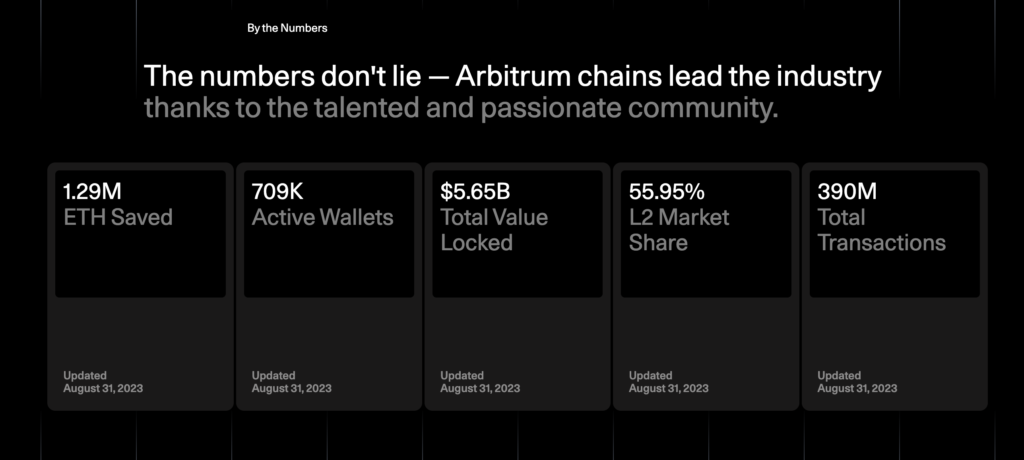
As the blockchain technology landscape continues to expand and evolve, two major challenges remain prominent, particularly within the Ethereum network: scalability and transaction cost. In response to these issues, we find Arbitrum as a promising solution. So, what is Arbitrum?
Arbitrum is a Layer 2 scaling solution designed exclusively for the Ethereum network. Its core function involves processing the majority of transactions off the primary Ethereum chain (off-chain) and submitting a summarized version, or 'rollup,' of these transactions to the main chain. This approach significantly alleviates the burden on the main Ethereum chain, leading to faster transaction times and considerably reduced gas fees.

Analysis of Arbitrum
In today's dynamic blockchain environment, continuous development and growth are imperative. As platforms like Ethereum become increasingly popular, scalability emerges as a considerable challenge. This is where Arbitrum comes into play - a Layer 2 scaling solution aimed at addressing many of the limitations Ethereum currently experiences. So, what is Arbitrum, and why is it garnering such attention within the blockchain sphere?
The Origin Story
Arbitrum, created by Offchain Labs, emerged due to the rising need for a more efficient transaction process on the Ethereum blockchain. As user adoption and decentralized applications on Ethereum began to surge, it became evident that the existing network structure could not efficiently manage high volumes without exorbitant transaction fees or delayed transaction times.
Fundamental Idea and Methodology
At its foundation, Arbitrum employs something referred to as "Optimistic Rollups." What does this entail? Generally, rollups involve consolidating or "rolling up" numerous transactions into one which gets recorded on the main chain. This translates to less on-chain data, leading to faster and more affordable transactions.
The "Optimistic" component of Optimistic Rollups stems from its mechanism. Rather than verifying every individual transaction (a burdensome and time-consuming effort), Optimistic Rollups operate based on trust by presuming each transaction is legitimate. There's a catch though - if any transaction is discovered to be invalid, mechanisms exist to penalize those involved. This approach effectively maintains a balance between trust and validation while enabling faster transaction times without sacrificing security.

Arbitrum's Enhancement of Ethereum
Ethereum boasts a strong and groundbreaking foundation; however, its shortcomings in scalability are apparent. This is where Arbitrum steps in. By processing the bulk of transactions off-chain and only submitting crucial data to Ethereum's main chain, it substantially eases the burden on Ethereum in the following ways:
- Faster Transactions: No more lengthy waits for transaction confirmations.
- Lower Fees: Reduced on-chain data processing leads to substantially lower transaction costs.
- Improved Scalability: this layer 2 solution can accommodate a greater volume of transactions simultaneously, making it suitable for extensive dApps and platforms.
Essentially, Arbitrum serves as a connection point, maximizing Ethereum's advantages while concurrently offering solutions to its limitations. As the cryptocurrency community progresses and expands, innovative technologies like Arbitrum will take center stage in shaping the decentralized landscape of the future.
Features and Advantages of Arbitrum

Promising Layer 2 solution introduces a suite of features that cater to the prevailing issues of blockchain scalability and cost. Here’s a closer look at its main features and inherent advantages:
Enhanced Scalability
Higher Transaction Throughput: this layer 2 solution can process a multitude of transactions simultaneously, considerably enhancing the speed of operations.
Parallel Execution: With the ability to handle multiple transactions in tandem, Arbitrum reduces the backlog that's often witnessed on Ethereum’s main chain.
Cost Efficiency
Lower Gas Fees: Transactions on it are processed off-chain, resulting in significantly reduced gas fees on Ethereum.
Optimized Data Storage: With only essential data being recorded on the main chain, Arbitrum optimizes storage and, consequently, costs.
Compatibility
Seamless Ethereum Integration: Arbitrum is designed to be fully compatible with Ethereum's smart contracts, requiring little to no changes for developers to migrate their dApps.
Interoperable Tooling: Developers can employ familiar Ethereum tools and frameworks when working with Arbitrum.
Security Measures
Secure Consensus Mechanism: Leveraging Ethereum's security, Arbitrum benefits from the same trust and decentralization.
Fraud Proofs: The Optimistic Rollup design ensures that any fraudulent activity can be quickly detected and penalized.
Potential Use Cases for Arbitrum

Arbitrum’s unique feature set positions it as a sought-after Layer 2 solution for various applications.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
High-frequency Trading: With reduced transaction costs and faster speeds, Arbitrum can enable efficient high-frequency trading platforms in the DeFi space.
Yield Farming: Users and protocols can achieve better operational efficiency, making yield farming strategies more effective and lucrative.
Gaming
Real-time Gameplay: it can facilitate real-time, on-chain gaming experiences.
In-game Asset Trading: Speedier and cheaper transactions could revolutionize how in-game assets are traded and monetized.
NFT Marketplaces
Cost-efficient Trades: Reduced transaction fees can potentially lower the barriers for trading NFTs, encouraging a more vibrant marketplace.
Fast Auctions: Quicker transaction times can facilitate real-time bidding wars and instantaneous auction results.
The Future of Arbitrum

Recent Developments
Strategic Partnerships: Many projects and platforms are beginning to integrate to leverage its advantages. Highlighting some key partnerships can showcase its growing influence.
Tech Upgrades: As with any technology, this layer 2 solution continues to evolve. Future updates might introduce even more optimizations and features.
Expected Growth and Adoption
Mainstreaming Layer 2: As more entities recognize the importance of Layer 2 solutions, Arbitrum's adoption is poised to grow exponentially.
Potential Beyond Ethereum: While currently focused on Ethereum, the technology behind this layer 2 solution has the potential to be adapted for other blockchains, broadening its horizons and influence.
As the blockchain ecosystem continues its march towards mainstream adoption, solutions like Arbitrum will be pivotal in addressing the challenges of today and shaping the decentralized platforms of tomorrow.
Conclusion - What is Arbitrum?
Arbitrum's introduction into the blockchain domain stands as a testament to the industry's drive towards innovation and optimization. As Ethereum continues to serve as a foundational layer for countless decentralized applications, the need for solutions like Arbitrum becomes ever more apparent. With its ability to drastically improve transaction speeds while concurrently slashing costs, Arbitrum not only addresses some of Ethereum's current limitations but also paves the way for a more scalable and cost-effective decentralized future. As we continue to push the boundaries of what's possible in the blockchain sphere, tools like Arbitrum will undeniably play a central role in shaping that journey.
 en
en  pl
pl