You have been interested in blockchain for some time now and are wondering if you could use it in your business model? Undoubtedly it is a technology which has recently gained popularity and which usability in the real estate and entertainment has been found pretty quickly. Among the companies present on the AngelList around 3 thousand use Blockchain. On our Nextrope blog we are trying to explain the most effective ways in which it can be used in business. In this article we compared the 4 most popular protocols- Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, Corda and Quorum.
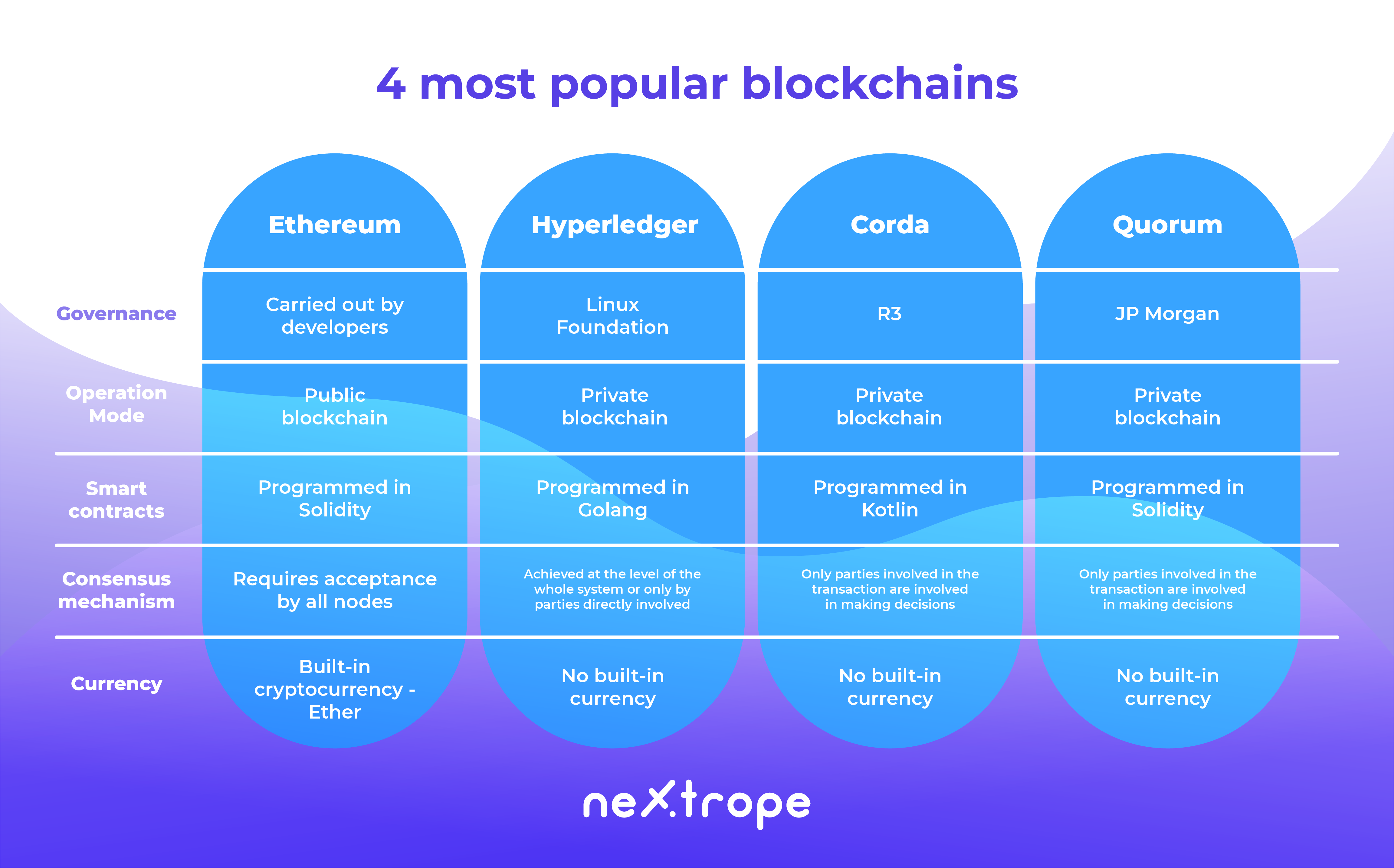
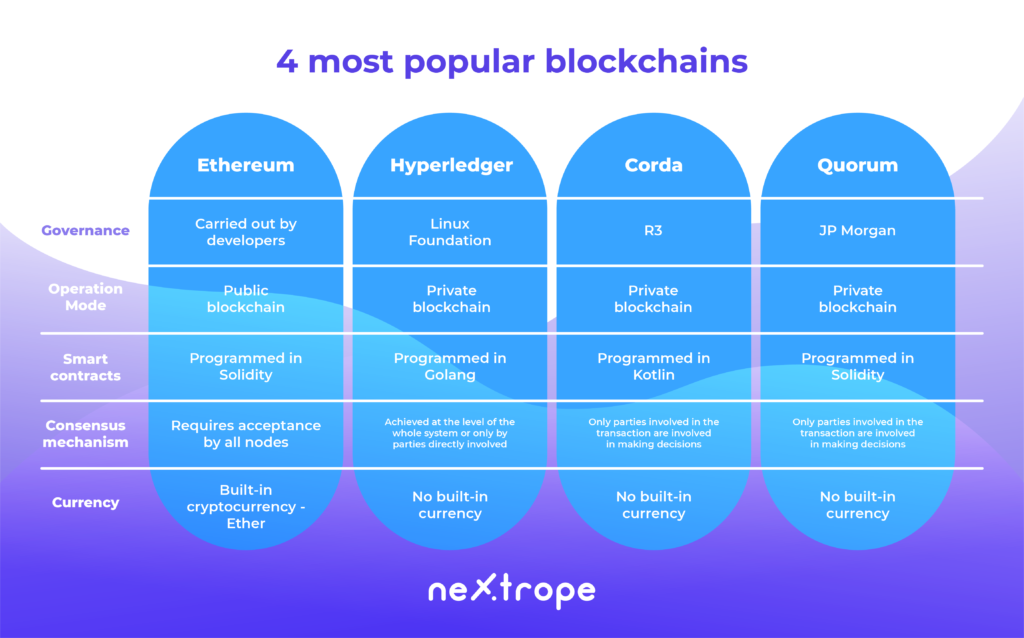
Ethereum

Ethereum is a developer platform based on the blockchain technology which was founded in 2015 by Vitalik Buterin. It allows the creation of decentralised applications which use the smart contracts.
Ethereum was the first blockchain which started to use smart contracts- fragments of Solidity code. Those contracts are called out by EVM, which is the core of Ethereum. Those contracts cannot interact with the surroundings and cant be activated without an input, they must be called out externally. If their function is called out by one of the chains, it automatically carries out the rest. The effects can be seen by the entire network. Thanks to that it is possible for Ethereum to create decentralised applications.
Because the code of established contract cannot be influenced, it is only available for read-only. In order to change it a complete overhaul would be required by establishing a new, completely different code of a different address and the initial state of the variables. The contract cannot be stopped after its execution unless it has been written in its code. Any of the operations on the record of the smart contract are openly logged and can be read through many available blockchain explorers. That way it is guaranteed that the coded information, value or function shall be constant. It is sometimes called „law by code”-creating the law with the usage of the source code.
Ethereum guarantees the constancy of the data and consequently its reliability in the processes of blockchain and smart contracts. That way the need of engaging the third party disappears. It brings many advantages as it grants its users the ability to make transactions directly with the clients, quickens the process of entering into the contract and lowers the costs of increasing the reliability of data.
“We live in the era in which there is no trust, which is why we are creating the third parties which we give our trust to. We send them our data, information, wealth or identity because we want to carry out some common interest and create a positive value. Blockchain will have its use the moment we will be able to fully embrace the cheap, trustful method it can give us”
Maciej Jędrzejczyk IBM Blockchain Leader interview with Nextrope
Dapps also allow us the reduction of the need of administrative control, for example the business entity which establishes the platform, over the entire network. Very often it finds its use in the b2c relationship. We recently had an occasion to present the examples on how OPUS (which is based on Ethereum) can change the entertainment market.
Thanks to the decentralization, the safety of data is no more dependant on the single server. If it is destroyed in one of the chains, they still will exist in all the other ones. We already talked about the superiority of the decentralization when it came to land registers which, at the moment, are held in a centralised way which makes them vulnerable towards the random events such as the natural catastrophes or fires. The constant nature of the source code also makes the data invulnerable towards the hackers.
Another advantage behind Ethereum is the tokenisation layer. Token is a smart contract which has a standardised form which stands for a unit of value. Companies create it to make it possible for the users to interact with their products and to make the distribution of prizes and benefits easier. Tokens can be used for accounting the property rights, pay checks or to give the bonuses to old-time clients. Their usage is as broad as the company needs it to be.
Ethereum is the only blockchain in this article that has its own cryptocurrency- Ether. In order to send the data, the user must give the pay- gas for saving it. In order to do this the user must have his own e-wallet key. Smart contract alone will not be enough to carry out the transaction unless its carried out through the e-wallet.
Hyperledger Fabric

As it turns out, it is not optimal for each user to keep a decentralised registry. Having the privacy of data in mind, in 2018 the Linux foundation has founded the Hyperledger Project which is currently supported by IBM, Intel or SAP Ariba which develops a number of solutions, which also includes the most frequently used Hyperledger Fabric.
Thanks to its modularity, it can be used as a private blockchain which means that only the registered users will be capable of accessing the data which is held by it. It is a key factor when it comes to many companies which are keen on the exchange of data about the transactions between the trusted sides.
The difference in practice
For the purpose of explanation of how Hyperledger works lets imagine a regular Jan who has his own blockchain based shop in Warsaw. Recently he found a Chilean producer of avocado- Emilia. They manage to negotiate a special prize, but Emilia wants to keep this a secret, she wants her clients to still pay the full prize for her prized avocados.
This would be impossible if their transaction was registered in the public domain of blockchain. The other clients would be immediately alarmed of this situation. The transaction would not be even carried out because all of the parties would have to agree on the price.
Hyperledger allows us to solve this problem. The application based on it will check the identity of Jan and then it will send the data about the transaction to Emilia. After agreeing to the established terms, she would send the data back to Jan, and so the transaction could be saved on their registry. In such a situation only two sides of transaction must receive the results. When there is more of them, after the terms are accepted, the transaction deal will be sent to the cloud server where they will be able to accept the transaction after reaching consensus. Then the transaction is saved in the registry.
However, just delivering the avocado to Jans shop engages not only him, but also its producer and many other parties. For the fruit to be delivered to Warsaw the engagement of the shipping agent, the custom and harbour department and the insurance company which will ensure that the transaction will be secured. The majority of those parties do not need the information about the special prize of avocados. Thanks to Hyperledger, such a transaction can be carried out without the need to use all of the information.
Thats why it finds its use everywhere where privacy and flow of information without the need to share it with all the sides of the transaction is needed. Hyperledger Fabric has its use in the number of different industries, including the financial, logistic and even the food one.
Corda

Another solution which extends the topic of private blockchain networks is Corda, founded by the R3 corporation. The goal of its creation was to create a global registry which would allow the economic operators to interact with each other and manage their contracts. In order to make this possible the platforms architecture must be based on the following principles:
- Only parties which have justified interests should have access to the registries on the platform
- The contracts are sustained through the system which is made with the usage of the computer code which makes it so that they are used in accordance to law
- The consensus is reached out by the people who carry out the transactions, not the entire system
Platforms like Hyperledger and Ethereum are using smart contracts, however in case of Corda the leading language of their encryption is Kotlin, and the smart contract terminology is replaced by just “contract”. Such contracts use both logic and business data with the judicial process which allows for rooting of the contracts in the existing judicial system.
Corda has two types of consensus: validity of the transaction and the uniqueness of the transaction. In order to acquire the first one, the sides must reach the certainty by checking the entire code behind the contract and by delivering all of the required signs. As far as the second one is concerned, they verify if the transaction is a unique consumer of all of the information.
Quorum
The finance world in mind sees blockchain as both a chance and a risk. The stability and ease of verification of data is conflicted by the model of public transparency which is opposed by some institutions. Quorum is the platform created by JP Morgan. It is an Ethereum which was improved by the layer of privacy which allows the use of blockchain without the need of making your data public to all of the users.
Just like Corda, it’s a private blockchain, which is created only by the users which were verified by the special program. Quorum can differentiate the private and public transactions in the chain and allow them to appear in one blockchain network. Public ones act like transactions based on Ethereum, however, the private ones are operated by the system called Constellation. It’s a mechanism which doesn’t use the blockchain technology. It is based on encryption of the messages on the communication mechanism called enclave – which is the record of the previous transactions, authentications and verifications. Thanks to this, Constellation Quorum is able to process several hundred transactions per minute, much faster than Ethereum or Bitcoin.
Thanks to its reliability and privacy it provides, it’s the perfect solution for the financial sector. Even today it has been recognized by the National Bank of Canada, Central Bank of Brazil or the commercial projects like Adhara or Skeps. It can also be seen that many international companies like Starbucks see the potential behind this technology and are eager to experiment with it.
What is the best blockchain for your business?
The key advantage of every one of aforementioned blockchain solutions is the way in which they solve the problem of a distrust. The companies could possibly save money by investing at the decentralised apps which would allow to save time and give an ability to verify the relations between the parties remotely.
The choice of the platform should be dictated by your current needs. Most b2c companies like facebook ebay or amazon use ethereum which they used to create their own cryptotokens. Hyperledger is chosen mostly by b2b companies which seek to improve their relations. And finally, Corda and Quorum are chosen by financial sector and are used by institutions such as the National Bank of Canada.