In the dynamic realm of blockchain technology, two terms are increasingly gaining traction: cryptoeconomics and token engineering. As the blockchain landscape evolves, these concepts are becoming crucial for the development of robust and efficient decentralized systems. While they are often used interchangeably, cryptoeconomics and token engineering actually have different meanings. Cryptoeconomics lays the theoretical groundwork, posing the vital questions that guide the creation of decentralized networks. Token engineering, on the other hand, is the practical application, the methodology used to answer these questions and solve the problems that arise. This article aims to explore the relationship between the two.
Understanding Cryptoeconomics
Cryptoeconomics: The ‘Why’ Behind Decentralized Systems
Cryptoeconomics is not just a branch of economics; it is a multidisciplinary field that blends cryptographic techniques with economic incentives. At its core, cryptoeconomics is about understanding and designing the incentives and economic mechanisms that encourage desired behaviors in decentralized networks. It is a theoretical science that delves deep into the ‘why’ – why participants in a decentralized system will act in a way that ensures the network’s functionality, security, and prosperity.
- Economic Models and Incentive Structures: The economic models in cryptoeconomics are designed to align the interests of diverse network participants. By leveraging token incentives and penalties, these models ensure that every participant, from miners to end-users, acts in a way that is beneficial to the network’s overall health and security.
- Security and Trust: Cryptoeconomics is crucial for establishing trust in a trustless environment – the blockchain. It underpins the security models that protect decentralized networks from malicious actors. The economic cost of attacking the network is designed to be so high that it becomes infeasible.
- Governance and Network Maintenance: It also involves the governance of decentralized systems, determining how decisions are made and how the network can evolve over time. This includes the creation of policies for the distribution of new tokens, transaction validation processes, and consensus mechanisms.
In conclusion, cryptoeconomics serves as the backbone of blockchain technology, posing fundamental questions about the structure and sustainability of decentralized systems. By understanding what needs to be optimized and why, cryptoeconomics provides a guiding light for the entire blockchain industry. However, identifying the optimal economic model is just the beginning. The implementation of these models – the ‘how’ – is where token engineering comes into play, bridging the gap between theory and practice.
Delving into Token Engineering
Token Engineering: Crafting the ‘How’ of Tokenized Ecosystems
While cryptoeconomics provides the theoretical scaffolding, token engineering is the discipline that brings theory to life through design and implementation. It is the engineering of digital tokens, applying systematic tools and methods to create functional and resilient token-based systems. Token engineering focuses on the ‘how’, utilizing a methodological toolkit to construct the mechanisms that guide interactions within the system.
- Design and Functionality: At the heart of token engineering is the design process. It involves defining the token’s purpose, features, and utility within the ecosystem. It’s a meticulous process that requires a profound understanding of the desired outcomes and behaviors that need to be incentivized.
- System Analysis and Modeling: Token engineers employ various models to predict how tokens will perform in different scenarios. This includes simulating economic models, stress-testing the system, and ensuring that the token behaves as intended under various conditions.
- Interdisciplinary Approach: The field of token engineering is inherently interdisciplinary, drawing from areas such as game theory, computer science, and behavioral economics. This convergence of knowledge is essential to address the complex challenges that arise in token economies.
Token engineering is thus a comprehensive approach to ensuring that the ‘what’ identified by cryptoeconomics is achieved efficiently in practice. With the right tools and methodologies, token engineers strive to optimize tokenized systems, ensuring their functionality, scalability, and security.
Comparing and Contrasting
While cryptoeconomics and token engineering are interdependent, they have distinct roles and methodologies within the broader blockchain landscape.
Common Grounds
Both disciplines share a common goal: to optimize and ensure the integrity of decentralized systems. Cryptoeconomics and token engineering converge in their reliance on economic theory and principles to design systems that can operate securely.
- Interdisciplinary Foundations: They both draw from a similar pool of interdisciplinary knowledge, integrating insights from behavioral economics, game theory, and computer science.
- Focus on Optimization: Optimization is a shared objective, whether it’s about determining the optimal incentive structure in cryptoeconomics or fine-tuning the individual components within a token system in token engineering.
Key Differences
Despite these similarities, cryptoeconomics and token engineering diverge in their focus and application.
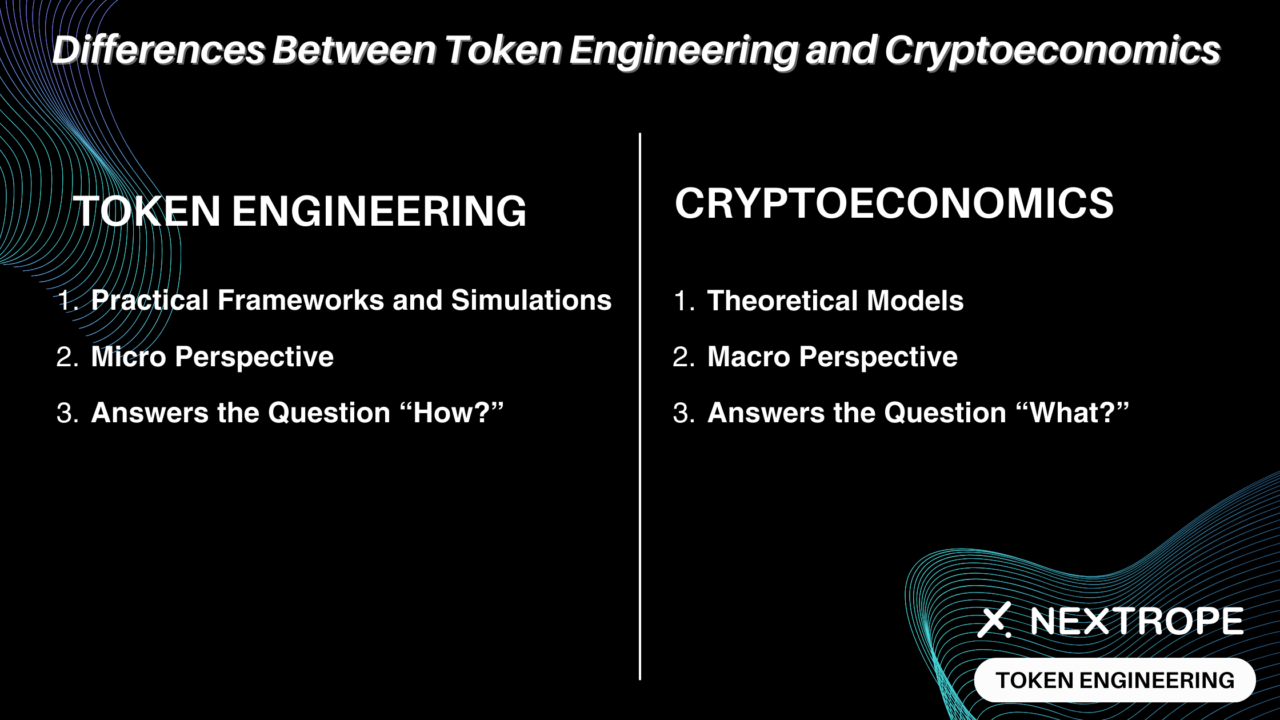
- Macro vs. Micro Perspective: Cryptoeconomics tends to address the broader, macroeconomic questions of blockchain ecosystems, such as overall network incentives and system security. Token engineering, conversely, zooms in on the micro-level details, focusing on the specific design and functionality of individual tokens.
- Theory vs. Application: Cryptoeconomics is theoretical, concerned with the ‘why’ behind the economic strategies that govern decentralized systems. Token engineering is practical, addressing the ‘how’ with a hands-on approach to creating and implementing token systems.
- Methodological Tools: The methodologies of the two fields also differ. Cryptoeconomics is often concerned with abstract reasoning and theoretical models. Token engineering uses concrete tools and simulations to test and refine token functionality.
Understanding the nuanced differences and connections between cryptoeconomics and token engineering is vital. It ensures that both the theoretical and practical aspects are aligned to create harmonious, resilient, and efficient decentralized ecosystems.
The Future Landscape
The future of blockchain is inextricably linked to the advancements in both cryptoeconomics and token engineering. As these fields mature, their evolution will play a role in the entire digital economy.
- Advancements in Token Engineering: We can expect to see more sophisticated tools and frameworks emerging within token engineering. They will be aimed at simplifying the design process while enhancing the robustness of tokenized systems. This will likely include the integration of artificial intelligence to automate certain aspects of the engineering process.
- Cryptoeconomic Research: Research in cryptoeconomics will continue to expand to new economic models that better account for the complexities of decentralized networks. These models will be essential in addressing scalability, privacy, and interoperability challenges.
- Cross-disciplinary Innovation: The intersection of cryptoeconomics and token engineering with other technological advancements like IoT is expected to generate novel use cases.
- Policy and Governance: As these disciplines develop, they will also influence policy-making and governance structures within the digital economy. Regulators may begin to adopt more nuanced and informed approaches to overseeing the token engineering process.
The trajectory of cryptoeconomics and token engineering points towards an era where decentralized systems are more integrated into mainstream applications. The synergy between these fields’ theoretical and practical elements will likely fuel the next wave of innovation in blockchain technology.
Conclusion
Cryptoeconomics lays down the theoretical questions of ‘why’ and ‘what to optimize,’ setting the stage for the necessary incentive structures and governance models. Token engineering, with its methodological toolkit, addresses the ‘how’ and ‘how to optimize,’ turning theory into practical, functioning systems.
Understanding both disciplines’ individual contributions and their interplay is crucial for anyone involved in blockchain development. As we move forward, the line between cryptoeconomics and token engineering may blur even further. That’s because each discipline continuously informs and refines the other.
If you’re looking to design a sustainable tokenomics model for your DeFi project, please reach out to contact@nextrope.com. Our team is ready to help you create a tokenomics structure that aligns with your project’s long-term growth and market resilience.
FAQ
What distinguishes cryptoeconomics from token engineering?
- Cryptoeconomics is the theoretical framework focused on incentives in decentralized systems. Token engineering applies these theories to build resilient token systems.
How do both fields contribute to blockchain development?
- Cryptoeconomics provides the incentive models, while token engineering designs and implements these models in real-world applications.
What role do economic models play in cryptoeconomics?
- They align participant incentives to ensure network health and security.
Does technological advancement affect their interplay?
- Technological progress shapes the evolution and integration of both fields in the digital economy.


