As the world of blockchain technology quickly progresses, the issue of scalability is among the greatest hurdles yet. With the expansion and popularity of decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts, finding effective and economical solutions is crucial. Two leading contenders tackling these challenges are Arbitrum and Polygon, each offering distinct Layer 2 scaling solutions and features. This article delves into the complexities of "Arbitrum vs Polygon" to help readers make well-informed choices for their blockchain requirements.
Understanding Layer 2 Scaling
Blockchain technology fundamentally consists of interconnected blocks which create a transparent and unchangeable ledger. However, as this technology gained widespread adoption, particularly through Ethereum's smart contracts and dApps, it was evident that Layer 1—the base layer—had limitations concerning transaction throughput and speed.
Often referred to as "L2," Layer 2 scaling presents a suite of solutions constructed atop existing Layer 1 blockchains. These solutions do not intend to supplant the main chain but rather augment its capabilities. By relocating certain operations from the main chain (such as calculations or storage) and subsequently consolidating them back, L2 solutions can significantly boost transactions per second, minimize fees, and enhance overall user experience.
Numerous L2 techniques exist, including state channels, Plasma, sidechains, and rollups. Each provides a unique scalability approach accompanied by individual advantages and trade-offs. Arbitrum and Polygon have risen as top solutions among these techniques, attracting both developers and investors.
Arbitrum

Read our post 'What is Arbitrum?'
Developed by Offchain Labs, Arbitrum is a Layer 2 scaling solution employing Optimistic Rollups that enhance the efficacy of Ethereum-based applications. Here's an in-depth examination:
Origin and Development
Arbitrum was devised to tackle Ethereum's scalability issues without jeopardizing security. The developers at Offchain Labs concentrated on crafting a user-friendly solution that lowers fees and expedites transactions for users.
Technical Insights
Arbitrum's central technology is Optimistic Rollup. Instead of performing each transaction on the main Ethereum chain, Arbitrum conducts the majority of transactions off-chain. These are periodically amalgamated into a single group and sent to Ethereum, significantly reducing data stored on the main chain and improving efficiency.
The "optimistic" aspect relates to how transaction validity disputes are managed. Arbitrum presumes transactions are valid unless contested, circumventing validation for each transaction. An on-chain mechanism is in place to resolve any disputes that may surface.
Adoption and Use Cases
Numerous applications and projects have started integrating with Arbitrum due to its advantages. Its ability to preserve Ethereum's security guarantees while bolstering its capabilities makes it an attractive option for many in the industry.
Polygon

Previously known as Matic Network, Polygon has emerged as a leading multi-chain scaling solution for blockchain networks compatible with Ethereum. It strives to offer a means for building a more interconnected and scalable decentralized web.
Foundations and Evolution
Initially introduced as Matic Network, Polygon evolved into a broader multi-chain ecosystem to tackle Ethereum's scalability problems and functionality challenges. Polygon's creators saw the need for a Layer 2 solution that surpassed a singular method and chose to develop a more inclusive framework.
Technical Perspectives
Employing a mixed Proof-of-Stake (PoS) and Plasma framework, Polygon enables quicker, low-cost transactions. Its sidechains function concurrently with the Ethereum main chain, easing transaction volume and facilitating faster confirmations.
Moreover, Polygon's architecture is crafted to accommodate multiple Layer 2 solutions, guaranteeing adaptability and extensive applicability for diverse use cases.
Implementation and Use Cases
With its powerful scaling solution and conformity with Ethereum's tools and infrastructure, Polygon has drawn an extensive variety of decentralized projects – ranging from DeFi platforms to game applications and NFT marketplaces. Its versatility has made it popular among those seeking scalability without sacrificing security or decentralization.
Arbitrum vs. Polygon
To compare Arbitrum and Polygon accurately, it is vital to comprehend the subtleties that set these Layer 2 powerhouses apart.
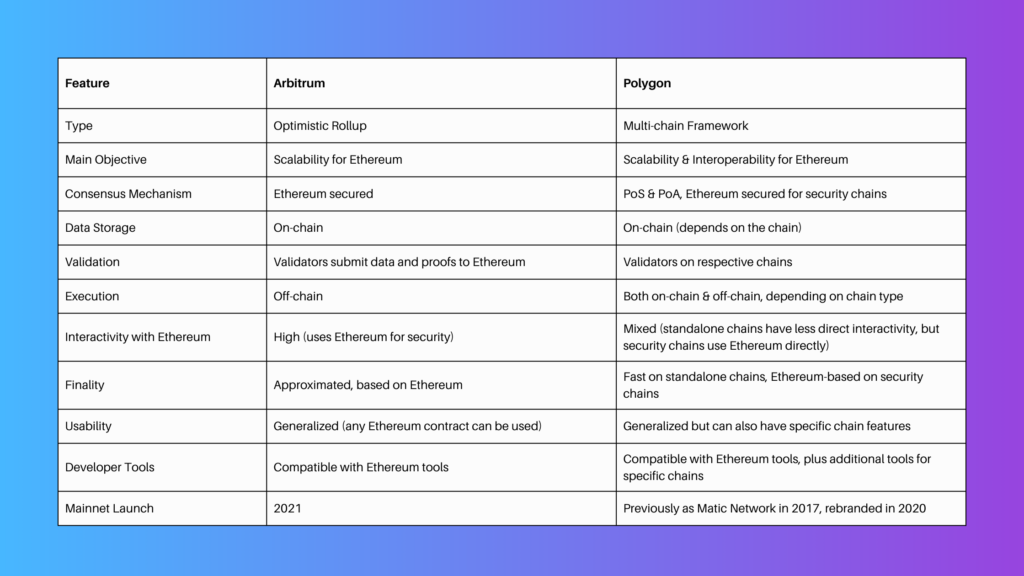
Technical Approaches and Mechanisms
Arbitrum utilizes Optimistic Rollups to primarily bundle multiple off-chain transactions before submitting them onto the chain as one unit. Transactions are assumed valid by default, with on-chain verification needed only if conflicts arise.
In contrast, Polygon implements sidechains that function in tandem with Ethereum's main chain employing a combination of PoS and Plasma to enable speedy transactions at reduced cost. Its structure is created to incorporate numerous Layer 2 solutions, supplying a wider array of tools and techniques.
Adoption and Ecosystem
Despite both platforms witnessing significant adoption, they serve slightly diverse users. Arbitrum attracts projects seeking uncomplicated integration while maintaining a strong connection with Ethereum, primarily reaping the benefits of reduced fees and heightened throughput.
On the other hand, Polygon delivers a more all-encompassing multi-chain environment, appealing to projects that seek an extensive toolset, increased flexibility, and a broad vision of interconnected chains.
Expenses and Fees
Both solutions strive to substantially lower Ethereum transaction costs. That said, specific fee structures may differ based on transaction volume, network congestion, and other factors. Generally, both Arbitrum and Polygon offer substantially lower transaction fees compared to Ethereum Layer 1.
Compatibility and Interoperability
Both Arbitrum and Polygon emphasize Ethereum compatibility, assuring projects can effortlessly migrate or incorporate without significant restructuring. However, Polygon's wider objective of crafting an interconnected multi-chain ecosystem presents a unique aspect of interoperability, aiming to merge various Layer 2 solutions into an integrated network.
Conclusion
Choosing between these solutions is not a matter of which is objectively superior, but rather which aligns more closely with a project's unique needs and goals. Some may favor Arbitrum's streamlined integration with Ethereum, while others might lean towards Polygon's expansive toolkit and vision.
 en
en  pl
pl 











