Ethereum, since its inception, has stood at the forefront of blockchain innovation, introducing concepts that have revolutionized the industry. At its core, Ethereum is not just a cryptocurrency but a platform for decentralized applications (dApps), powered by its native token, Ether. Among the numerous advancements in the Ethereum ecosystem, one concept that is gaining momentum is Account Abstraction. This concept, particularly highlighted in the ERC-4337 standard, presents a paradigm shift in how accounts are managed on the Ethereum blockchain, promising enhanced security and a more seamless user experience.
Account Abstraction, though a technical concept, has far-reaching implications for everyday users, developers, and the broader Ethereum community. It represents a move towards a more flexible and user-friendly blockchain, addressing some of the challenges and limitations of the current account model. As we delve into this topic, we will uncover the intricacies of Account Abstraction and the pivotal role of the ERC-4337 standard in reshaping the Ethereum experience.
Understanding Account Abstraction
Ethereum primarily uses two types of accounts: Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs) and Contract Accounts. EOAs are controlled by private keys and are typically used by individuals to send transactions or interact with smart contracts. In contrast, Contract Accounts are governed by their contract code and are used to deploy and run smart contracts.
The traditional Ethereum account model, centered around EOAs, has its limitations. It often leads to complex management of private keys and lacks flexibility in transaction execution. This is where Account Abstraction comes into play. It proposes a unified account model, blurring the lines between EOAs and Contract Accounts. Under Account Abstraction, user accounts would essentially function like smart contracts, enabling more complex and secure transaction rules beyond the simple private key model.

ERC-4337 Standard: An Overview
The ERC-4337 standard represents a significant milestone in Ethereum’s ongoing evolution, offering a novel approach to implementing Account Abstraction without necessitating extensive changes to the core Ethereum protocol. This standard introduces a framework that enables users to experience the benefits of Account Abstraction, bringing enhanced flexibility and security to account management on the Ethereum blockchain.
The Core Concept of ERC-4337
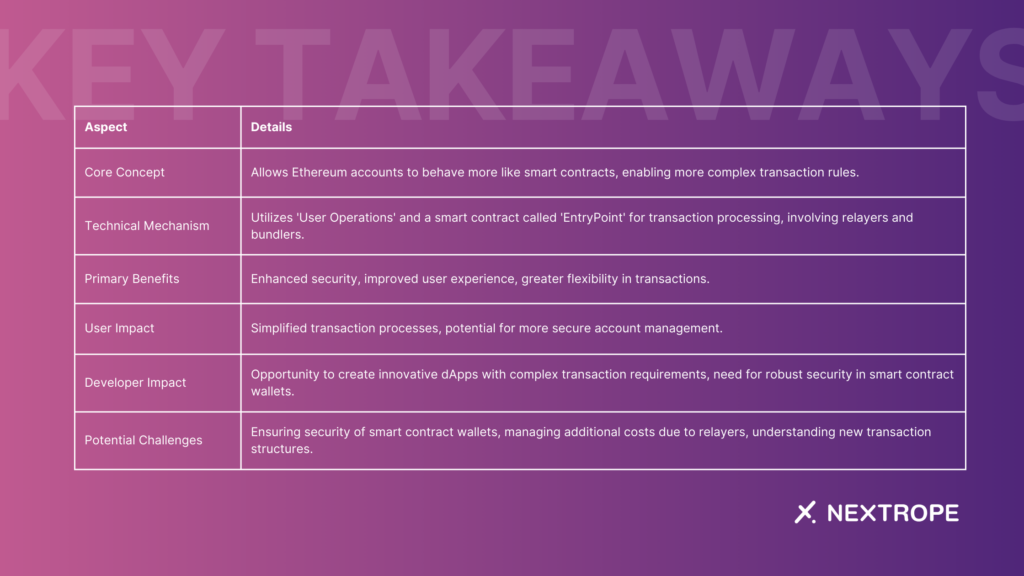
At its heart, the ERC-4337 standard is about enabling accounts on Ethereum to behave more like smart contracts. This shift allows for more sophisticated rules around transaction execution, which traditionally could only be applied to Contract Accounts. The key innovation of ERC-4337 is the introduction of a new entity known as the ‘User Operation.’ These are bundles of transactions that users sign, which are then executed by a new type of account called a ‘Bundler.’ Bundlers are responsible for submitting these operations to the blockchain, ensuring that they conform to the user’s predefined rules.
Technical Mechanisms
ERC-4337 operates through a smart contract, known as the ‘EntryPoint,’ which acts as a hub for User Operations. Users send their signed operations to this contract, which then delegates the execution to the appropriate smart contract wallets. This process is facilitated by relayers who, in exchange for a fee, submit these operations to the EntryPoint. The beauty of this setup is that it does not require any changes to miners’ or validators’ operations in the Ethereum network, making it a less intrusive yet effective solution for Account Abstraction.
Benefits of ERC-4337
The introduction of the ERC-4337 standard brings several key advantages:
Enhanced Security: By allowing accounts to set more complex rules for transaction execution, ERC-4337 provides an additional layer of security. This includes capabilities like multi-signature verification and automated checks before transaction execution.
Improved User Experience: With ERC-4337, users can enjoy a more streamlined and flexible transaction process. For instance, they can execute batch transactions, set up recurring payments, or integrate more sophisticated wallet recovery options.
Greater Flexibility: Developers can create more innovative dApps with complex transaction requirements, thanks to the flexibility offered by ERC-4337. This could lead to new use cases and applications on the Ethereum blockchain.

Implementing Account Abstraction with ERC-4337
The implementation of Account Abstraction using the ERC-4337 standard marks a pivotal moment in Ethereum’s development. This process involves several critical steps and considerations for both developers and users.
Implementation
- Smart Contract Wallet Deployment: The first step involves deploying a smart contract wallet compatible with the ERC-4337 standard. This wallet will manage the user’s assets and execute transactions based on predefined rules.
- Setting Up User Operations: Users need to define their transaction rules and parameters within these smart contract wallets, known as User Operations.
- Utilizing Relayers and Bundlers: To execute transactions, users interact with relayers who submit their operations to the EntryPoint contract. Bundlers then include these operations in the blockchain.
Considerations for Developers and Users
- Security: While ERC-4337 enhances security, developers must ensure that the smart contract wallets and User Operations are robust against potential vulnerabilities.
- User Experience: Developers should focus on creating intuitive interfaces for setting up and managing User Operations, making the process user-friendly.
- Cost Implications: Implementing ERC-4337 may involve additional costs, such as fees for relayers. Users and developers need to consider these financial implications.

Impact on the Ethereum Ecosystem
Increased Security and Trust: With more robust account security features, Ethereum can attract a broader audience, including those previously wary of blockchain’s security aspects.
Enhanced User Accessibility: Simplified transaction processes and user-friendly interfaces will lower the barrier to entry, potentially leading to increased adoption of Ethereum-based applications.
Innovation in dApps Development: Developers will have more freedom to experiment with complex transaction mechanisms, leading to innovative dApps that could redefine the blockchain landscape.
Long-Term Implications
Standardization and Interoperability: Account Abstraction could become a standard feature in future blockchain platforms, enhancing interoperability across different networks.
Influence on Other Blockchains: Ethereum’s move towards Account Abstraction may inspire similar developments in other blockchain ecosystems, fostering a new wave of blockchain innovation.
Conclusion

The introduction of Account Abstraction, particularly through the ERC-4337 standard, is a landmark development in Ethereum’s history. It represents a significant stride towards a more flexible, secure, and user-friendly blockchain platform. As we venture into this new era, the potential of Ethereum to revolutionize not just finance but various sectors of the economy becomes increasingly evident. The ERC-4337 standard is not just an enhancement of Ethereum’s technical capabilities but a step towards realizing the broader vision of blockchain technology – a more open, secure, and accessible digital future for all.
Key Takeaways