The financial landscape has been revolutionized by decentralized finance (DeFi), which utilizes blockchain technology, artificial intelligence (AI), and cryptocurrencies to develop innovative and transparent financial solutions. One crucial element driving the future of DeFi is interoperability and cross-chain solutions, as the space experiences rapid growth. This article will discuss the importance of interoperability within the DeFi ecosystem and examine cross-chain solutions, concentrating on their impact on the future of decentralized finance.
Understanding Interoperability in DeFi
Often known as DeFi, decentralized finance signifies a fundamental shift in our understanding and engagement with conventional financial systems. DeFi, built upon blockchain technology, seeks to democratize finance by removing intermediaries, facilitating peer-to-peer transactions, and granting open and transparent financial services to anyone with internet access. The DeFi ecosystem has experienced tremendous growth in recent years, encompassing lending and borrowing platforms, decentralized exchanges, and yield farming, consequently attracting billions of dollars in investments and garnering interest from both institutional and retail investors.
Nonetheless, as the DeFi landscape grows more expansive and numerous blockchain networks are established, the demand for interoperability becomes increasingly vital. Interoperability denotes the capacity for various blockchain networks and decentralized applications (dApps) to communicate and seamlessly interact with each other. This interconnectedness is essential for DeFi's future because it enables efficient asset, data, and value transfers across diverse blockchain networks, opening up a realm of possibilities and promoting collaboration among distinct projects.
Check out our article about the future of DeFi!
The Promise of Cross-Chain Solutions
Cross-Chain Solutions are rapidly emerging as the linchpin of future decentralized finance, promising to overcome one of the most significant barriers in the space - the lack of interoperability. At its core, a Cross-Chain Solution allows different blockchain platforms to communicate and interact with each other, enabling the seamless exchange of information and assets. This is a game-changer for DeFi as it could potentially unlock massive liquidity pools trapped within isolated blockchain ecosystems.
In addition, Cross-Chain Solutions also bring the potential for enhanced scalability, security, and efficiency. They provide the means for DeFi applications to leverage the strengths of multiple blockchain networks, bypassing the constraints tied to a single blockchain. This could lead to the creation of more robust and versatile DeFi services, opening up a myriad of opportunities for both developers and users.
Furthermore, Cross-Chain Solutions can foster a more inclusive and interconnected DeFi landscape. By allowing different blockchain networks to interoperate, they eliminate the barriers between disparate communities, bringing together diverse participants under a unified financial ecosystem. In essence, Cross-Chain Solutions hold the promise of creating a truly global and decentralized financial system, thus taking us one step closer to the original vision of blockchain technology.
Use Cases of Cross-Chain Solutions in DeFi
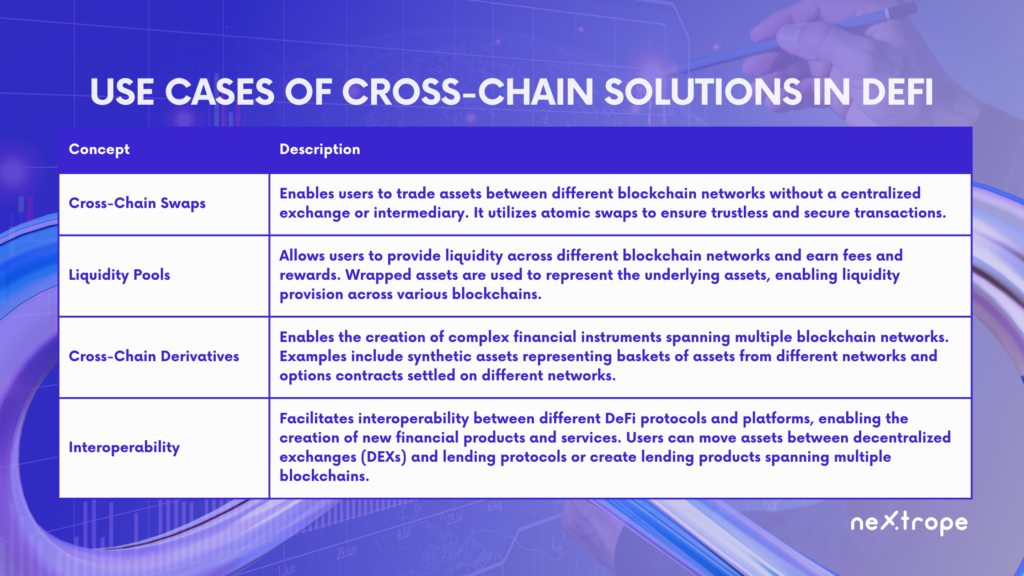
Cross-chain solutions are already playing a crucial role in the DeFi space by enabling the creation of innovative financial products and services that were previously impossible. Here are some real-world use cases of how cross-chain technology is being used in DeFi today:
- Cross-Chain Swaps: Cross-chain swaps allow users to trade assets between different blockchain networks without the need for a centralized exchange or intermediary. These swaps use atomic swaps to ensure the transaction is trustless and secure.
- Liquidity Pools: Cross-chain liquidity pools enable users to provide liquidity across different blockchain networks. This means that users can earn fees and rewards for their participation. Liquidity pools use wrapped assets to represent the underlying assets, making it possible for users to provide liquidity across different blockchain networks.
- Cross-Chain Derivatives: Cross-chain derivatives make it possible for users to create complex financial instruments that span multiple blockchain networks. For example, users can create synthetic assets that represent a basket of assets from different blockchain networks, or they can create options contracts that are settled on a different blockchain network.
- Interoperability: Cross-chain technology facilitates interoperability between different DeFi protocols and platforms. This makes it possible to create new financial products and services that leverage the strengths of different platforms. For instance, users can use cross-chain technology to move assets between decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and lending protocols, or to create new lending products that span multiple blockchain networks.
Challenges and Considerations
The immense potential of cross-chain solutions in DeFi comes with several challenges and considerations that need attention. One significant obstacle is regulatory concerns and compliance requirements, given that multiple jurisdictions and regulatory frameworks are involved in cross-chain transactions. It is a complicated task to ensure compliance with these varied regulations while preserving DeFi's decentralized essence, necessitating inventive solutions and cooperation with regulatory authorities.
Moreover, addressing security and trust issues is crucial since the effortless transfer of assets and data across various chains creates new attack vectors and vulnerabilities. To safeguard user funds and uphold trust within the DeFi ecosystem, stringent security measures such as advanced cryptographic methods and smart contract audits are imperative.
Furthermore, attaining standardization and governance for cross-chain interoperability is vital to guarantee compatibility and smooth communication between different blockchain networks. The establishment of shared protocols, norms, and governance structures will encourage interoperability and promote the extensive adoption of cross-chain solutions in DeFi.
Finally, tackling user experience and adoption challenges is essential for achieving mainstream acceptance. Simplification of user interfaces, improved accessibility, and user education about the merits and functionalities of cross-chain solutions are all crucial elements for expanding the user base and realizing the full potential of DeFi interoperability.
The future with Cross-Chain Solutions
One of the key trends to watch out for is the rise of multi-chain DeFi platforms. With the advent of cross-chain technology, we are likely to see an explosion of platforms that operate seamlessly across multiple blockchain networks. This will open up new opportunities for users, allowing them to take advantage of the unique strengths and features of different blockchains. For example, users might be able to earn higher yields on one platform, enjoy lower transaction fees on another, and access unique financial products on a third, all without leaving the comfort of a single, unified platform.
Additionally, Cross-Chain Solutions will likely drive the development of more advanced and complex financial instruments. As demonstrated by the rise of cross-chain derivatives, there is significant potential for the creation of innovative financial products that leverage the interoperability of different blockchains. This could usher in a new era of financial sophistication and accessibility, in line with the ethos of DeFi.
Finally, Cross-Chain Solutions could play a key role in the mass adoption of DeFi. By breaking down the barriers between different blockchain networks, they could help bring about a truly global and inclusive financial system. Users from all corners of the world, irrespective of their local financial infrastructure, might be able to access a plethora of financial services, from basic savings and lending to advanced trading and investment opportunities.
In essence, the future of DeFi with Cross-Chain Solutions looks promising. The combination of interoperability, efficiency, and inclusivity brought about by this technology has the potential to redefine the financial landscape, making it more democratic, accessible, and resilient. The vision of a truly decentralized financial system might not be too far off.
Conclusion
Cross-chain solutions are revolutionizing the future of decentralized finance (DeFi). Interoperability, facilitated by cross-chain technology, is becoming increasingly crucial as the DeFi ecosystem expands. It enables seamless communication and interaction between blockchain networks and decentralized applications (dApps), opening up new possibilities and promoting collaboration. Cross-chain solutions offer significant advantages, including unlocking liquidity, enhancing scalability and security, and fostering inclusivity. They enable cross-chain swaps, liquidity pools, and derivatives, while facilitating interoperability between DeFi protocols and platforms. However, challenges such as regulatory compliance, security, standardization, and user experience must be addressed. The future with cross-chain solutions holds the promise of multi-chain DeFi platforms, advanced financial instruments, and mass adoption, ultimately reshaping the financial landscape into a more democratic, accessible, and resilient system.
 en
en  pl
pl