What are the differences between DEX and CEX? Which one suits your needs and business assumptions best? Read this article before you make that crucial decision.
In the article you learn about:
- Different types of crypto exchanges
- What is a centralized exchange?
- Pros and cons of centralized exchanges
- How does decentralized exchange work?
- Liquidity pools and Automatic Market Maker
- Pros and cons of decentralized exchanges
Crypto Exchanges
The cryptocurrency exchange is an indispensable part of cryptocurrency trading, which may be considered as one of the most important financial trends of this century. Hence more and more investors are becoming interested in launching their own exchange. The fundamental decision that has to be made at the begging is choosing the model of crypto trading that will meet our requirements.
In this article, we'll take a closer look at centralized and decentralized exchanges, which will hopefully enable you to examine which of them is right for your project in the crypto space.

Centralized Exchange
Most big cryptocurrency exchanges you know are probably centralized. Coinbase, Binance, BKEX, or Upbit - you are familiar with them. Thanks to higher liquidity and lower transaction fees they remained the first choice of crypto traders for a long time.
Times have changed and players such as decentralized exchange Uniswap or Sushi Swap have gained significant importance in the crypto market. Yet, in many cases, centralized exchanges still remain the most suitable solution. What's their backbone?
Centralization of an exchange
Centralization of the exchange essentially means that each trade there takes place with a centralized intermediary. The centralized exchange has its order book, where every order is recorded and validated. All the data is stored and exchanged between exchange servers. Additionally, transactions and user information go through a centralized security process.
To access the exchange, users have to sign up by providing their bank details and personal data. This is the part of KYC and AML practices, which aim to prevent money laundering and have to be followed by every centralized exchange.
Buying cryptocurrencies on a centralized exchange
Trading on centralized exchanges generally seems simple. You just need to choose coins and confirm the transaction. The exchange will show the funds you acquired in your account. Then you can trade them for other digital assets. The price of each coin on the site is based on an order book.
However, users don't really hold their funds. The exchange works here as a custodian of the customer’s funds. Furthermore, trades don't occur on the blockchain. Instead, they take place only within the exchange's database.
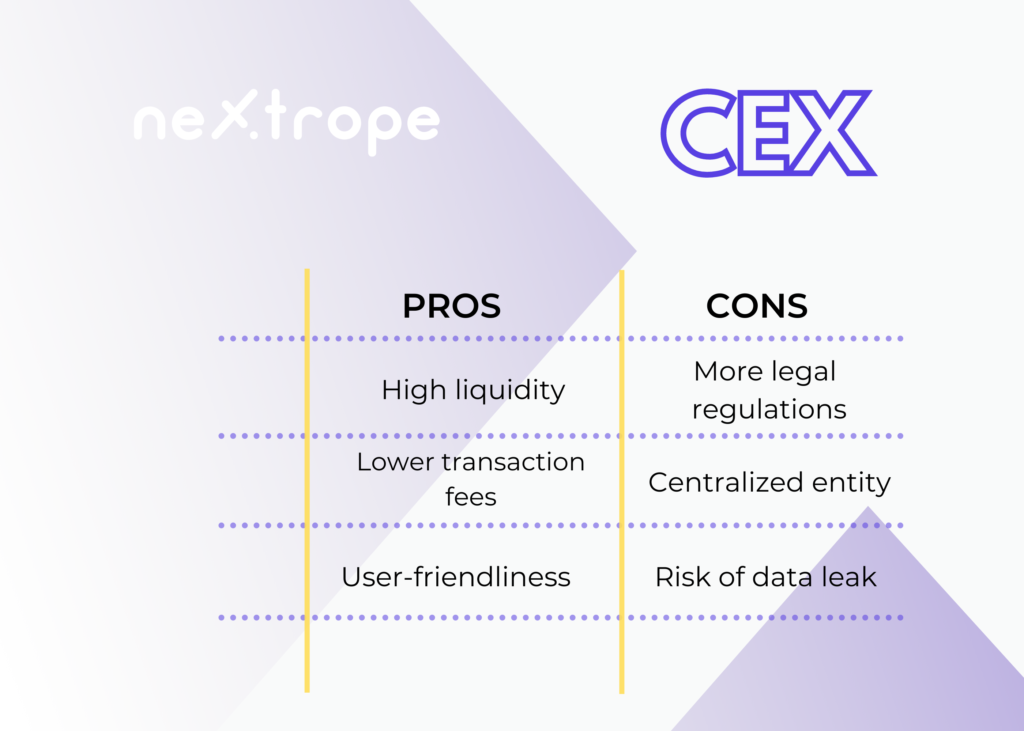
Pros of Centralized Exchanges
User-friendliness
Generally, centralized exchanges have a more user-friendly platform. They give users easy and uncomplicated access to crypto trading. This is especially relevant for crypto newcomers.
High liquidity
Since the whole process doesn't take place on a blockchain, the network nodes don't have to be updated in real-time, hence trading speed is usually much higher than on DEX.
Lower transaction fees
The trading fee on CEX is fixed, and they tend to be lower than on decentralized exchanges for the same reason as stated above.
Trading with fiats
Unlike DEXs, centralized exchanges allow users to buy crypto for fiat currencies.
Cons of Centralized Exchanges
More legal regulations
Centralized exchanges are limited by strict government requirements. For example, high standards of the identity verification process have to be respected.
Centralized entity
From a technical point, when you deposit funds on a centralized exchange, you lose control over it. The exchange puts your funds into integrated wallets controlled by it.
Additionally, CEXs extract users' private keys. They will no longer be your keys. Therefore, if you want to withdraw your money, the exchange has to sign the transaction on your behalf.
This is an important reason why many traders migrate to decentralized exchanges.
Risk of leaking private user data
Due to KYC procedures, crypto users provide extensive data. As such information is fragile, a security dilemma is present even before one starts trading. This may lead to the lack of users’ trust, especially when we talk about smaller, less-known exchanges.

Decentralized Exchange
In many ways, decentralized exchanges are similar to centralized ones. However, the differences are more than substantial. In decentralized exchanges, trade essential relies on a blockchain (most often Ethereum or the Binance Smart Chain). Trading between users is conducted using smart contracts - orders are executed on-chain. As a result, the exchange doesn't take control of users' assets during the entire process.
Cross-chain exchanges are a very promising novelty on the DEX market. Yet, most of them operate only on one blockchain - most often Ethereum or the Binance Smart Chain.
How can a decentralized exchange handle trading?
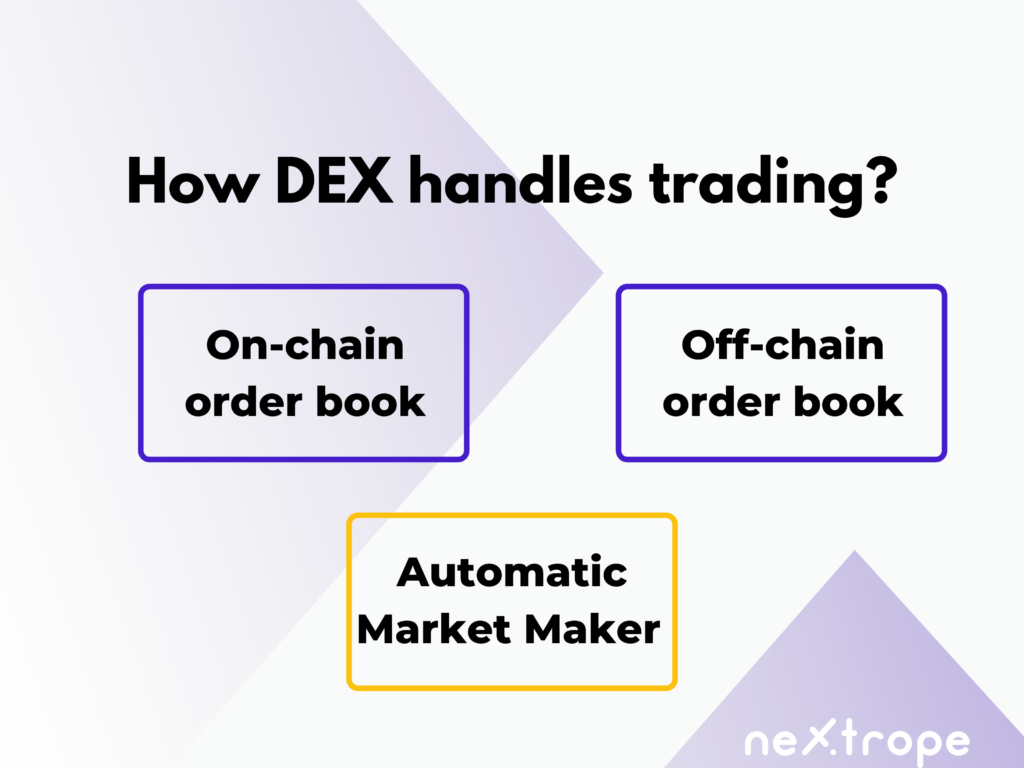
On-chain order book
There are decentralized exchanges where every transaction is written into a blockchain. This means that every order, as well as cancellation or alteration, is handled on-chain.
Without a doubt, this is the purest approach to decentralization. There is absolutely no third party involved at any stage of trading. Everything is extremely transparent. Unfortunately, there are vital downsides as well.
The on-chain order book is far less practical than the other two options. Firstly, because every node on the blockchain records the order, placing it requires paying a fee. Furthermore, users have to wait until the miner adds necessary data to the chain. This translates to high costs and poor liquidity.
Off-chain order book
Off-chain order books are a bit more centralized than their counterparts. But they are also far more practical. In this model, orders are hosted elsewhere and only the final transaction is settled on the blockchain. Moreover, you can still benefit from non-custodial storage.
As orders aren't stored on-chain, this approach is faster and less costly. Furthermore, it helps a better liquidity of trades to be achieved. However, it can encounter some of the security issues typical for CEXs.
Trading pairs
Let’s use the example of Ether and Bitcoin to describe how trading pairs work in the order book model on DEX.
If users want to trade their ETH for BTC, they need to find another trader willing to sell BTC for ETH. Furthermore, they need to agree on the same price.
While in the case of popular cryptocurrencies and tokens, finding a trading pair shouldn’t be a problem, things get a bit more complicated when we want to trade more alternative assets.
The vital difference between order books and automatic market makers is that the second one doesn’t require the existence of trading pairs to facilitate trade.
Automatic Market Maker AMM
Automated Market Maker (AMM) is a decentralized exchange protocol that relies on smart contracts to set the price of tokens and provide liquidity. In an automated market makers' model, assets are priced according to a pricing algorithm and mathematical formula instead of the order book used by traditional exchanges.
Essentially, they are autonomous trading machines that replace traditional order books with liquidity pools run by algorithms. According to many, it was the development of AMM that enabled the mass adoption of decentralized exchanges.
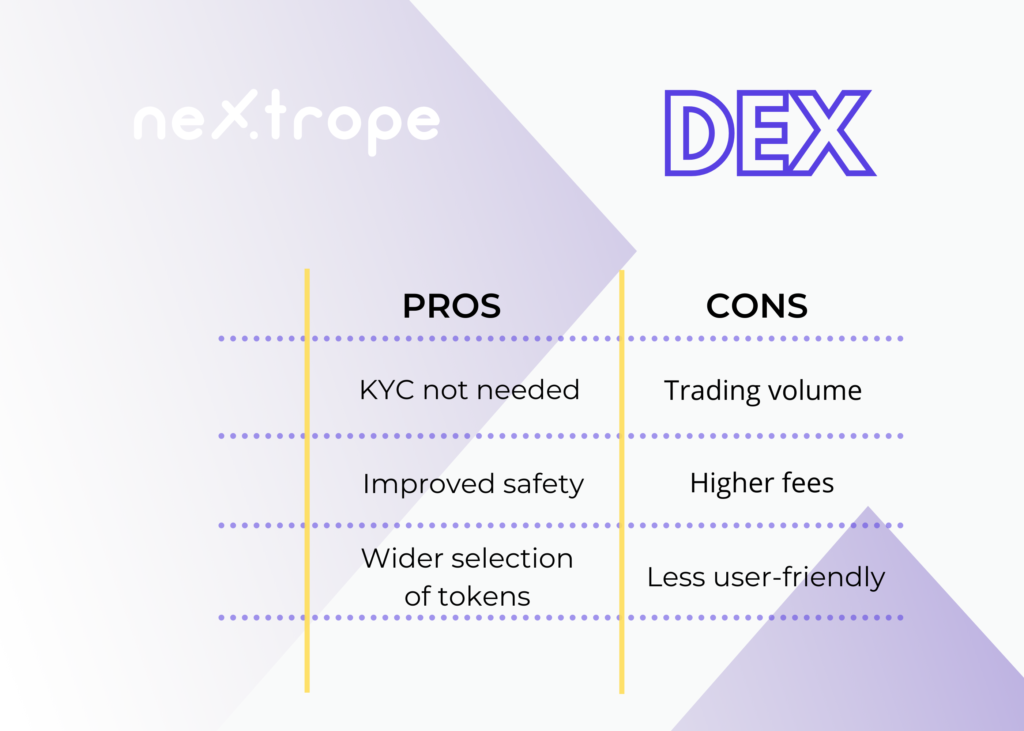
Pros of Decentralized Exchanges
No KYC
Most of the DEXs don’t have to follow KYC and AML requirements, because they don’t intermediate in transactions between parties. That’s why it’s often more convenient to build your own DEX than CEX.
No third parties involved
The basic idea behind decentralized trading is removing third-party providers. All transactions take place in a peer-to-peer or peer-to-contract model.
Full control of your assets
A decentralized exchange doesn't hold the user's assets or private keys. Therefore funds are under the user's control at every stage of trading.
More diversified crypto assets
On the DEX platform, trades of tokens that aren’t listed on CEXs are possible.
Cons of Decentralized Exchanges
Trading volume
The volume traded on CEXs is still much higher than that on DEXs. Liquidity is lower as well.
Higher fees
This is not an absolute standard, but when it comes to trading fees CEXs often offer better prices.
Convenience
A decentralized exchange is less user-friendly than a traditional one.
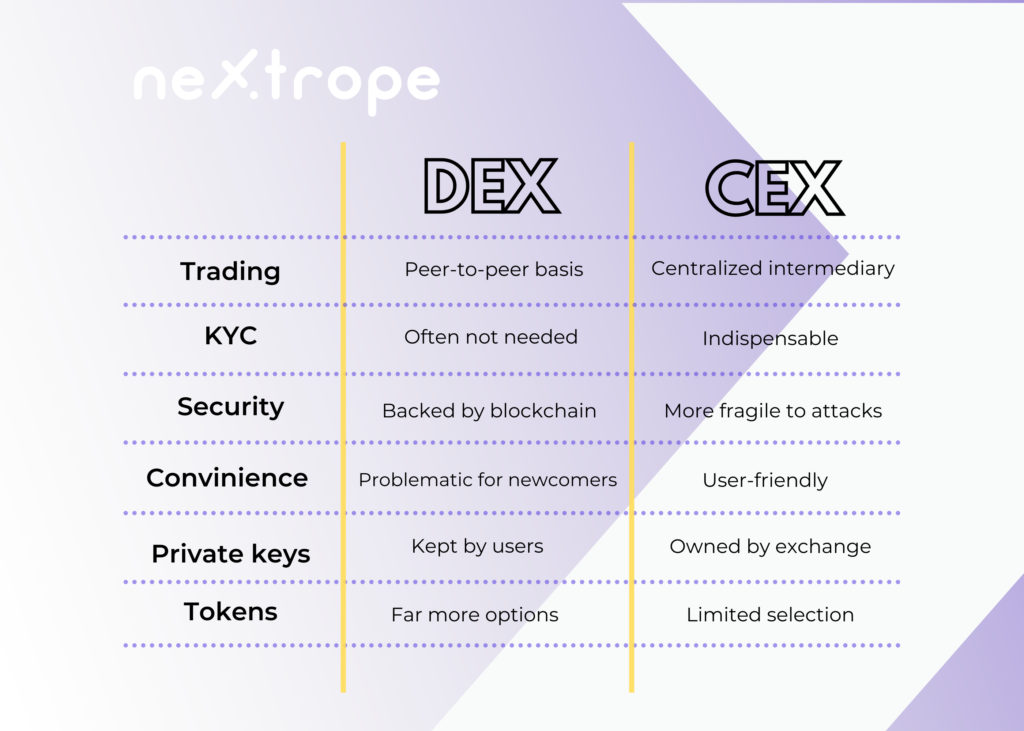
Developing DEX vs CEX
Crypto space develops at a tremendous speed, continuously bringing new possibilities. The number of people interested in crypto investments increases every day; hence the popularity of both decentralized and centralized exchanges has recently grown significantly. You need to bear this in mind when deciding to launch your crypto exchange.
Launching a crypto exchange requires not only experience of blockchain developers’ fluently using blockchain protocols but also a solid and well-planned business strategy. That's why choosing a technology partner with previous experience with both blockchain development and business consulting in the crypto field might be the optimal solution.
Do you want to gain more first-hand knowledge regarding building crypto exchanges? Don't hesitate to ask our professionals who will be happy to answer your questions.
 en
en  pl
pl