Forget order books, the future of Decentralized Exchanges lies in Automated Market Makers. Automated Market Maker AMM enables traders to earn shares of transactions in exchange for becoming liquidity providers. What does it mean for DEXs?
In this article you will learn:
- What are Automated Market Makers?
- How does Automated Market Maker work?
- AMM vs On-chain / Off-chain order book
- How to implement liquidity pools into your DEXs
- Why are Automated Makers so important for the whole DeFi ecosystem?
Automated Market Makers were first introduced to the public with the release of Uniswap in 2018.
Essentially, they are autonomous trading machines that replace traditional order books with liquidity pools run by algorithms.
What are Automated Market Makers?
As we mentioned in one of our previous articles, a decentralized exchange can handle trading in three ways:
- On-chain order book
- Off-chain order book
- Automated Market Maker AMM
The last one is undoubtedly the most efficient. That's why the vast majority of modern decentralized exchanges are based on it.
Definition:
Automated Market Maker AMM is a decentralized exchange protocol that relies on smart contracts to set the price of digital assets and provide liquidity.
Cryptocurrency assets are priced according to a pricing algorithm and mathematical formula, instead of the order book that is used by traditional exchanges.
The mathematical formula varies from protocol to protocol. Uniswap, for example, uses the following formula:
a * b = k
Where 'a' and 'b' are the number of tokens traded in the liquidity pool. Since 'k' is constant, the total liquidity of the pool must always remain the same. Different AMMS use various formulas. However, all of them set the price algorithmically.
What's important, Automated Market Makers allow almost anyone create a market using blockchain technology.

How Automated Market Makers work?
For trading pairs, for example, BTC/ETH, Automated Market Makers work similarly to order books, which are based on buy and sell orders. However, a vital difference is that a trading pair isn't needed to make a trade. Alternatively, users can interact with a smart contract that will constitute the other side of the trading pair for them. This is what the term “automated market-making” refers to.
P2P and P2C
You are probably familiar with the term “peer-to-peer transactions,” which is crucial to understanding decentralized exchanges. Every transaction that runs between two users without any intermediary can be called P2P.
We can think about Automated Market Makers as peer-to-contract solutions because trades take place between users and a smart contract.

Liquidity pools
Trading pairs, which you know from Centralized Exchange and Decentralized Exchange using order books, are an individual liquidity pool in Automated Market Maker. Therefore, users are essentially trading funds with liquidity pools, rather than with other users.
If you want to trade two tokens, for example, sell BNB for Ether, you need to find the BNB/ETH liquidity pool.
We can imagine a liquidity pool as a large pile of assets. But where do they come from?
Liquidity providers
The answer might sound quite surprising: funds are added to liquidity pools by the users of the exchange. Or, more precisely, liquidity providers.
In exchange for providing liquidity, liquidity providers earn fees on transactions in their pool. Unlike traditional market making with professional market makers, here anyone can become one.

Profits for liquidity
To become a liquidity provider you need to deposit both assets represented in the pool. Adding funds to the liquidity pool is not difficult and rewards are worth considering. The profits of liquidity providers differ depending on the platform. For instance, on Uniswap 0,3% of every transaction goes to liquidity providers.
Slippage on Automated Market Makers
Different Automated Market Makers may encounter different issues. Yet the risk of slippage is something we should always keep in mind while planning our own DEX.
Why does it occur?
As I mentioned earlier, asset pricing is determined by an algorithm and a mathematical formula. We can say that it's determined by the ratio between the assets in the liquidity pool. Or more specifically, it is the change in this ratio that occurs after a trade. The larger the transaction, the wider the margin of change, and the greater the amount of slippage.
Indeed, when a large order is placed in AMMs and a sizable amount of coin is removed or added to a liquidity pool, it can even cause a notable difference between the market price and the pool price.
More liquidity = less slippage
In the Automated Market Maker model, more liquidity means less slippage that large orders may incur. Ultimately, this may attract more volume to your DEX. That's why if you want to use Automated Market Maker on your platform, you need to have a solid strategy for encouraging your users to deposit funds in liquidity pools.

You need to remember that to stay competitive in the decentralized finance market, you should offer liquidity of at least a sufficient level.
Generally, exchanges decide on sharing profits generated by trading fees with liquidity providers. In some cases (e. g. Uniswap), all the fees go to liquidity providers. If a user's deposit represents 5% of the assets locked in a pool, they will receive an equivalent of 5% of that pool’s accrued trading fees. The profit will be paid out in liquidity provider tokens. When users want to leave the pool, they simply exchange their tokens for their share of transaction fees.
Yield Farming
Yield farming is one of the most important opportunities that can attract new users to your DEX platform. How does it work? What does it even mean?
LP tokens
We often say that liquidity has a pivotal value in the DeFi space. Creating tokens that are awarded in exchange for providing liquidity is a great idea to increase it.
Normally when a token is staked or deposited somehow, it cannot be used or traded, which decreases liquidity in the whole system. In the case of Automated Market Makers, implementing easily convertible liquidity provider tokens solves the problem of locked liquidity. Their mechanism is simple: users get them as proof of owing tokens that they have deposited.
With LP tokens, each token can be used multiple times, despite being invested in one of the liquidity pools. Additionally, we can say that LP tokens open up a new, indirect form of staking. This means that instead of staking tokens themselves we just prove that we own them.
What is Yield Farming?
Yes, on multiple exchanges users can stake their LP tokens and profit from them. Essentially, this is what we call yield farming. The main idea behind it is to maximize profits by moving tokens in and out of different DeFi protocols.
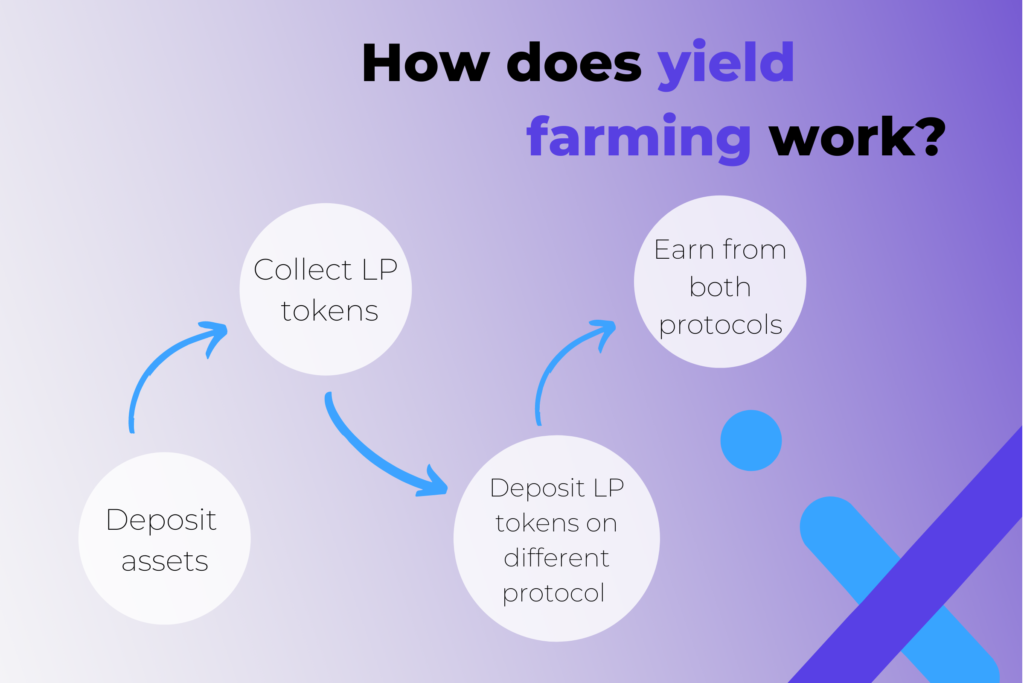
How does it work on DEXs?
Actually, from the user perspective it's quite simple:
- deposit assets into a liquidity pool
- collect LP tokens
- deposit or stake LP tokens into a separate lending protocol
- earn profit from both protocols
Note: You must exchange your LP tokens to withdraw your shares from the initial liquidity pool.
What is impermanent loss?
Impermanent loss occurs when the price ratio of two assets changes after traders deposit them in the pool. The higher the shift in price, the more significant the impermanent loss. Impermanent loss mostly affects liquidity pools with highly volatile assets.
However, this loss is impermanent: there is a probability that the price ratio will revert. Permanent losses can only occur if liquidity providers withdraw their digital assets before the price ratio reverts.
Conclusion
Of all the solutions that we can currently observe on decentralized exchanges, the Automated Market Maker offers the highest liquidity. Today most DEXs are running on AMM or plan to implement it in the nearest future. That's why Automated Market Maker has crucial importance for the DeFi ecosystem.Do you want to know how to apply Automated Market Maker in your project? Don't hesitate to ask our specialists for a free consultation.
 en
en  pl
pl