As the blockchain ecosystem continues to evolve, one of the key challenges it must overcome is scalability. The underlying technology of the blockchain is capable of disrupting various industries, but its potential is often bottlenecked by scalability issues. Layer 2 scaling solutions have emerged as a promising approach to overcome these challenges. In this section, we will delve into the specifics of three main Layer 2 scaling solutions: Lightning Network, Plasma, and Rollups.
Lightning Network
The Lightning Network is a Layer 2 payment protocol that operates on top of a blockchain-based cryptocurrency like Bitcoin. Its main goal is to enable fast, low-cost transactions between participating nodes.
How Lightning Network works:
The Lightning Network relies on off-chain state channels. A state channel is essentially a private two-way route opened between two parties. These parties can conduct an unlimited number of transactions between themselves, off the main blockchain. Only when the channel is closed does the final state of these transactions get recorded on the blockchain. This approach significantly reduces the load on the blockchain, allowing for faster and cheaper transactions.
Use cases and benefits of Lightning Network:
Quick micro-transactions: The Lightning Network allows for instant, high-volume transactions, making it suitable for micro-transactions and instant payments.
Lower fees: Since transactions occur off-chain, the cost associated with transactions is significantly reduced.
Challenges and limitations of Lightning Network:
While the Lightning Network does offer compelling benefits, there are also challenges associated with its use. These include complexity of use, the requirement for nodes to be online for transactions, and potential privacy issues.
Plasma
Plasma is a Layer 2 scaling solution proposed for the Ethereum blockchain. It aims to enable the processing of smart contracts on a large scale by creating off-chain channels.
How Plasma works:
Plasma works by creating a series of child chains (smaller blockchains) that branch off from the main Ethereum blockchain. These child chains can handle a significant amount of computational work that would otherwise slow down the main chain.
Use cases and benefits of Plasma:
High throughput: Plasma can handle a large number of transactions per second, which is critical for applications requiring high throughput.
Scalable smart contracts: By handling smart contracts off the main chain, Plasma enables scalable decentralized applications (dApps) on Ethereum.
Challenges and limitations of Plasma:
Just like the Lightning Network, Plasma also faces several challenges. These include the complexity of the Plasma architecture, difficulty in handling mass exits from child chains, and the fact that it’s still largely theoretical and not widely adopted.
Rollups
Rollups are another Layer 2 solution primarily designed for the Ethereum network. They boost the network’s capacity by rolling multiple transactions into a single transaction on the blockchain.
How Rollups work:
There are two main types of Rollups: zk-Rollups and Optimistic Rollups. Both types essentially bundle or “roll up” multiple transactions into one, but they use different methods for verifying the validity of transactions.
Use cases and benefits of Rollups:
Greater scalability: Rollups can significantly increase the transaction throughput of the Ethereum network.
Lower fees: By bundling multiple transactions, Rollups can reduce the cost per transaction.
Challenges and limitations of Rollups:
As with any technology, Rollups come with their own set of challenges. These include the complexity of the technology, the reliance on relayers to bundle transactions, and potential centralization risks.
Each of these Layer 2 solutions offers unique approaches to solving the scalability issue, and they each come with their own set of trade-offs. Understanding these technologies is crucial as we continue to innovate and improve upon the existing blockchain infrastructure.
Comparing Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
As we have explored, each Layer 2 scaling solution – Lightning Network, Plasma, and Rollups – offers unique benefits and faces distinct challenges. These solutions aren’t one-size-fits-all; their effectiveness can vary greatly depending on the specific requirements and constraints of the blockchain network they are applied to. In this section, we will compare these solutions on various key aspects such as speed, security, complexity, and current adoption rates.
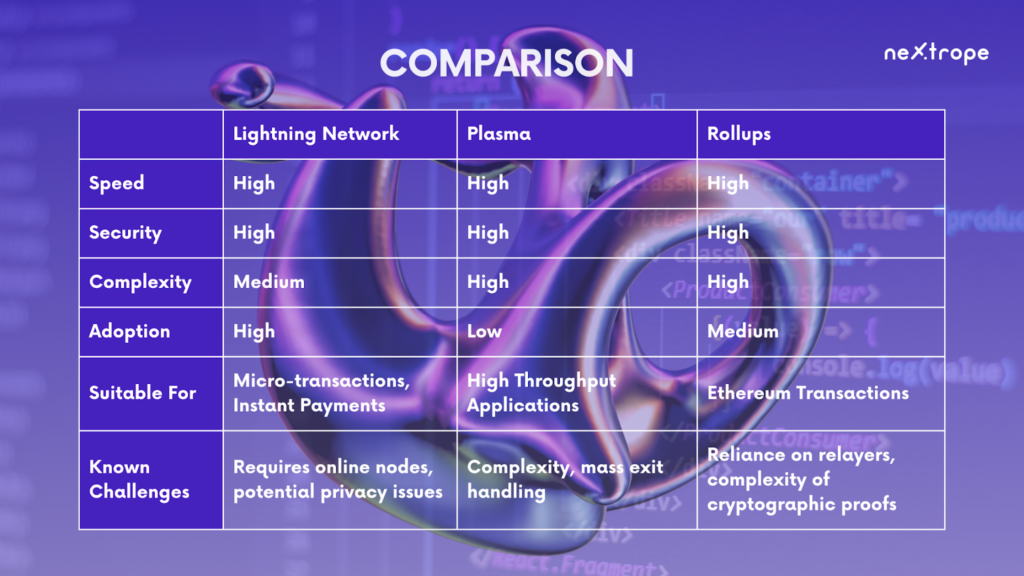
Speed
Lightning Network: The Lightning Network provides instant, high-volume transactions, making it extremely fast for applicable use cases, particularly micro-transactions and instant payments.
Plasma: Plasma can handle a large number of transactions per second by offloading the computational work to child chains, providing high throughput for applications.
Rollups: Rollups, both zk-Rollups and Optimistic Rollups, can significantly increase the transaction throughput of the Ethereum network by bundling multiple transactions into one.
Security
Lightning Network: The security of the Lightning Network relies on the security of the underlying blockchain. However, issues can arise if nodes aren’t online, and potential privacy issues exist.
Plasma: Plasma inherits the security of the main Ethereum chain. However, it faces potential issues in the event of mass exits from child chains.
Rollups: Rollups also inherit the security of the underlying Ethereum blockchain. zk-Rollups provide more immediate finality and security, while Optimistic Rollups rely on a challenge period for transaction validation.
Complexity
Lightning Network: The Lightning Network requires a good understanding of channel management and liquidity provision, which adds to its complexity.
Plasma: The architecture of Plasma is complex, involving the management of multiple child chains branching off from the main chain.
Rollups: Rollups, especially zk-Rollups, involve complex cryptographic proofs, making them complex to understand and implement.
Adoption
Lightning Network: The Lightning Network has seen significant adoption, especially in the Bitcoin ecosystem, for micro-transactions and instant payments.
Plasma: Plasma, while promising, is still largely theoretical and has seen limited adoption due to its complexity and the challenges it faces.
Rollups: Rollups are gaining traction in the Ethereum community. Notably, the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade roadmap includes the use of Rollups for scalability.
In conclusion, each Layer 2 solution has its own strengths and weaknesses. The choice between Lightning Network, Plasma, and Rollups depends on various factors such as the specific use case, the underlying blockchain, and the trade-offs that are acceptable for the desired application. As the blockchain space continues to evolve, we can expect these solutions to mature and new ones to emerge, providing ever more efficient ways to scale blockchain networks.
The Future of Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
The blockchain ecosystem continues to evolve at a rapid pace. As we’ve seen, Layer 2 scaling solutions are instrumental in helping the technology overcome its inherent limitations and reach its full potential. As we look ahead, several key trends emerge that hint at the future direction of Layer 2 technologies.
Continued Innovation and Development
As with any emerging technology, we can expect continued innovation and development in the field of Layer 2 solutions. This could mean the refinement of existing technologies, such as Lightning Network, Plasma, and Rollups, but it could also mean the introduction of entirely new solutions as developers identify new approaches and techniques.
Widespread Adoption and Use
Currently, Layer 2 solutions are being adopted and implemented across a number of blockchain networks. As the benefits of these solutions become more widely recognized and understood, we can expect to see an increase in their adoption. This could mean more businesses and users utilizing these solutions, leading to an overall increase in the efficiency and scalability of blockchain networks.
Integration with Layer 1
Layer 2 solutions will likely become increasingly integrated with Layer 1, the underlying blockchain protocol. This could mean a closer integration between the two layers, allowing for smoother and more efficient transactions. In fact, in the Ethereum community, there is already talk of “Layer 1.5” solutions that blend elements of both layers.
Increased Interoperability
As more Layer 2 solutions are developed, there will be a need for increased interoperability between them. This could mean the development of protocols or standards that allow for different Layer 2 solutions to interact and work together, providing users with more flexibility and choice.
Regulatory Challenges
As Layer 2 solutions become more widespread, they will likely face increased scrutiny and regulation. This could pose challenges for the development and adoption of these solutions, but it could also lead to greater transparency and trust in the technology.
You want to read more? Read this article!
Conclusion
In conclusion, the future of Layer 2 scaling solutions is exciting and full of potential. While challenges remain, the ongoing development and increasing adoption of these technologies are a positive sign for the future of blockchain technology. As we continue to innovate and push the boundaries of what’s possible, Layer 2 solutions will undoubtedly play a critical role in the evolution of the blockchain ecosystem.



