Imagine a world where the complexities of finance and the ingenuity of blockchain technology converge harmoniously. ERC-1400, a standard that has established rules around securities offerings, and on the other side, ERC-3643 – versatile in broadening technology utilization and tokenization horizons. They are keystones of modern funds management, each with its unique flair and profound implications. As we navigate their nuances, we’ll shed light on their roles, differences, and analogies.
Understanding ERC-1400
Origins and Purpose of ERC-1400
ERC-1400 introduces a standard for security tokens on the Ethereum blockchain. Security tokens, which illustrate digital forms of traditional investment contracts like stocks, bonds, and company shares require a token standard capable of navigating this intricate regulatory environment. The intent was to bring clarity and purified structure to the tokenization of securities, ensuring the process is compliant with existing laws and regulations. Such instruments, in particular, demand a future-thinking approach sticking to the thorough financial legal framework and its progressive traits.
Key Features of ERC-1400
ERC-1400 is characterized by several features that serve the specific needs of security tokens:
Compliance with Financial Regulations
Embeds legal governance directly into the token’s lifecycle. This weaves advanced protocols for identity verification, investor qualification, and conformity with securities regulation. Focusing on shareholders’ protection and regulatory alignment, it presents controlled token transfers or detailed reporting features that enhance credibility.
Control and Transparency
Granular Oversight of Transactions empowers issuers with monitored access to token operations, essential for financial compliance and investor trust. The standard enables rules enforcement and qualifications for each transfer. That means all movements of the token adhere to platform operational criteria. The level of legitimacy provided by ERC-1400 supports the credibility of security token offerings, both in the eyes of regulators and institutional investors.
Comparative Analysis: ERC-1400 vs ERC-3643
ERC-1400 and ERC-3643 cater to distinct needs and scenarios. This analysis aims to contrast features, applications, and the different problems they address.
Wondering what is ERC-3643 all about and how it works? Click to learn more in our latest article.
Table 1: Core Characteristics and Use Cases
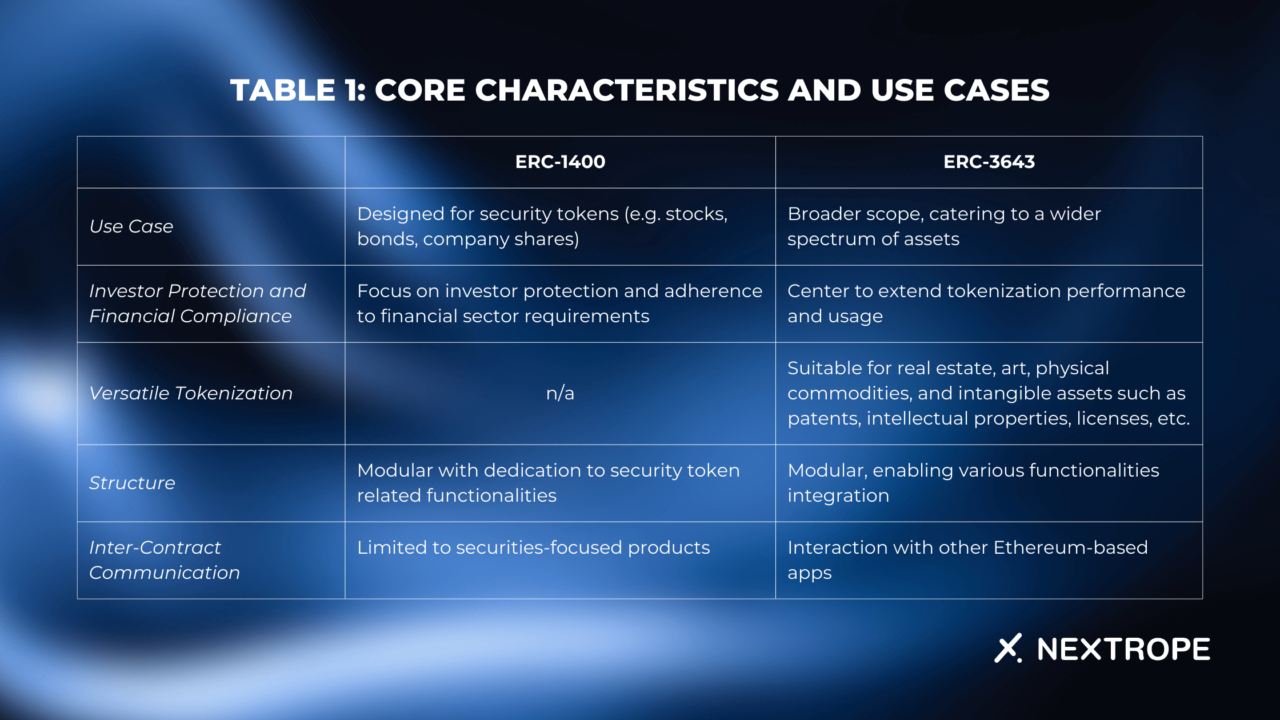
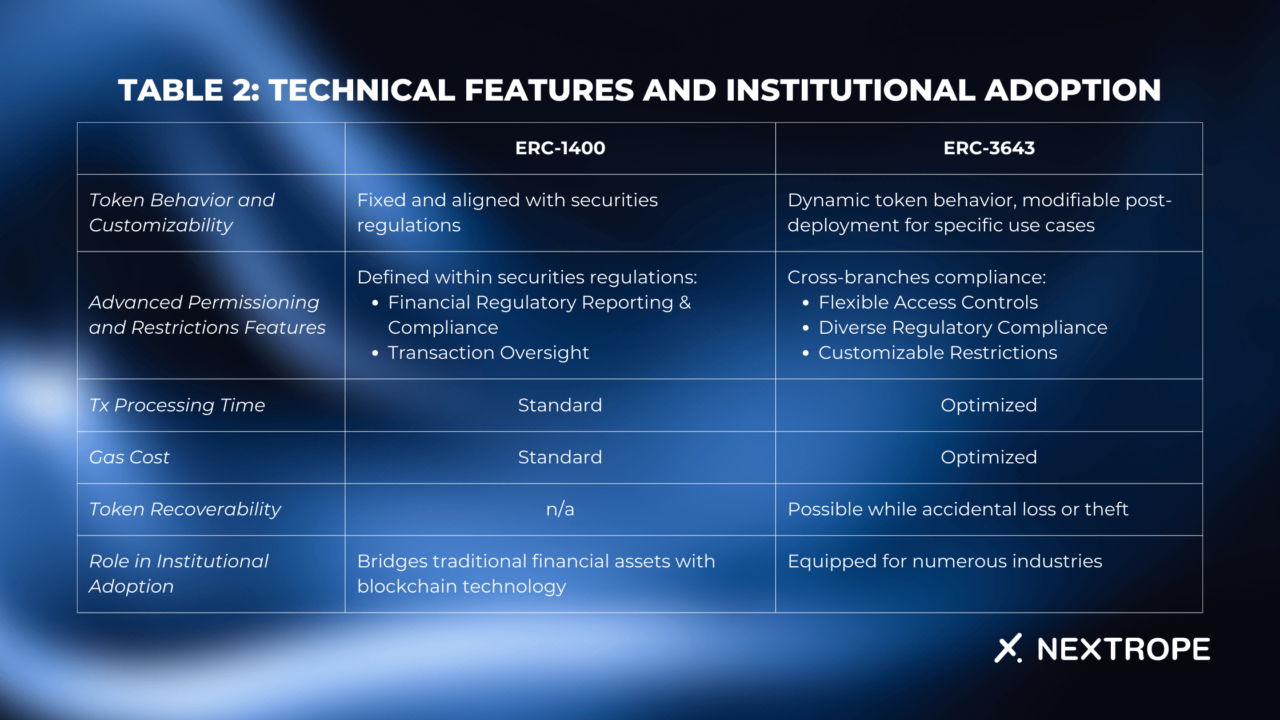
Table 2: Technical Features and Institutional Adoption
Unifying the Standards
Before exploring the differing attributes, it’s important to recognize the familiar ground shared by ERC-1400 and ERC-3643:
Regulatory Compliance Focus
- Common Goal for Ordinances Implementation: Both standards supervise legal regulatory alignment;
- Bridging Traditional Finance and Blockchain: They facilitate wider use of blockchain in traditional economic sectors.
Modular Architecture
- Flexibility and Customization: The solutions inherent in ERC-1400 and ERC-3643 allow developers to influence certain details of the token or adapt features to meet specific needs, from top-down legislation to highly advanced technological refinements;
- Adaptability for Future Enhancements: This is not only about meeting current essentials but also about paving the way for future enhancement. As per their modular structure, changes can be made without the need for system overhauling, thereby future-proofing the token standards.
Distinctive Features and Differences
While ERC-1400 and ERC-3643 allocate these foundational similarities, they diverge in their purpose, scope, and technical implementations.
ERC-1400: Specialized for Security Tokens
Targeted Use Case
- ERC-1400 serves the domain of security tokens, which are digital versions of aforementioned stocks or bonds. This standard addresses applicable and potential regulatory challenges associated with their tokenization.
Investor Protection and Financial Compliance
- It commits to investor protection guaranteeing detailed party verification, and the proper maintenance of holders’ rights.
ERC-3643: Broader Scope for Asset Tokenization
Versatile Tokenization
- Unlike ERC-1400, ERC-3643 accommodates a wide range of assets beyond securities.
Reinforced Token Control
- Advanced token behavior patterns provide issuers with a higher degree of customization and control;
- Optimized gas cost and streamlined contract processes also make it well-suited for high transaction volume and large-scale applications.
Conclusion
The comparative journey through ERC-1400 vs ERC-3643 reveals a harmonious standards coexistence. Together, despite a different purpose, they reflect the dynamic nature of blockchain technology. ERC-1400 and ERC-3643 shape the future of technology, and accordingly, with their introduction, the community has been equipped with a solid fundament to actively participate in any asset digitization.
If you are interested in utilizing ERC-3643 or other blockchain-based solutions for your project, please reach out to contact@nextrope.com
FAQ
What are the key features of ERC-1400?
- ERC-1400 embeds legal governance into the token lifecycle, ensuring compliance with securities regulations, and provides granular oversight of transactions, enhancing control and transparency.
How do ERC-1400 and ERC-3643 unify standards?
- Both standards focus on regulatory compliance and bridging traditional finance with blockchain technology. They feature modular architecture, offering flexibility for customization and adaptability for future enhancements.
What is the purpose of ERC-1400 and ERC-3643?
- ERC-1400 specializes in security tokens, addressing regulatory challenges and ensuring investor protection. ERC-3643 has a broader scope for asset tokenization, providing advanced token control and optimization for high transaction volume applications.




