Raising capital by your tokens issue - blockchain technology may disrupt fundraising as you know it. Thousands of projects have already raised billions of dollars through ICO. Why might yours be next?
What will you find in the article?
- What is the intial coin offering?
- Advatages of ICO
- How do ICOs work?
- Launching ICO step by step
- Different structure models of ICO
- ICO vs IPO
- STO vs ICO
Most technology startups have limited options when it comes to fundraising. They can either raise a seed round from private investors, pitch a VC fund, or start a crowdfunding campaign.
But if your project is blockchain-based, entirely new possibilities emerge, among them, you can find an initial coin offering (ICO). With ICO, you can issue your own utility tokens to be used in the network you want to create. As it grows, the demand for tokens increases, the same as their price, bringing profits to early investors.
An initial coin offering - ICO is a blockchain industry equivalent of IPO (Initial Public Offering). Find why issuing tokens may be the best way to raise funds for your project.

What is the initial coin offering?
Among STO and IDO, initial coin offering is one of the fundraising methods brought to life thanks to Blockchain technology. Essentially, an initial coin offering regards raising funds for a project by issuing new cryptocurrency where new blockchain-based projects mint and sell new tokens in exchange for other digital assets or fiat money.
Eventually, those token will have a specific utility on the platform built for funds raised during the ICO. For example, they may be exchanged for products or services of the company. In other cases, they become governance tokens that allow investors to vote to shape the project’s future.
How did it start?
Everything started in 2013 with Mastercoin’s initial coin offering that raised approximately 5 million dollars. The Mastercoin launch was quickly followed by Ethereum. Yes, that’s right - one of the most influential technology projects of this decade was funded via an initial coin offering. During Ethereum's ICO, creators raised 18 million dollars. To this day, Ethereum remains one of the most successful ICOs.
Yet, those 18 million sounds like nothing, compared to the 4 billion raised by EOS in several rounds during 2018-2019. It was the largest ICO to date.
Democratization of fundraising
But initial coin offering (ICO) isn’t all about big projects with enormous capital for fundraising campaigns. Their main advantage over IPO is allowing also smaller startups to arrange a successful funding round.
Advantages of initial coin offerings
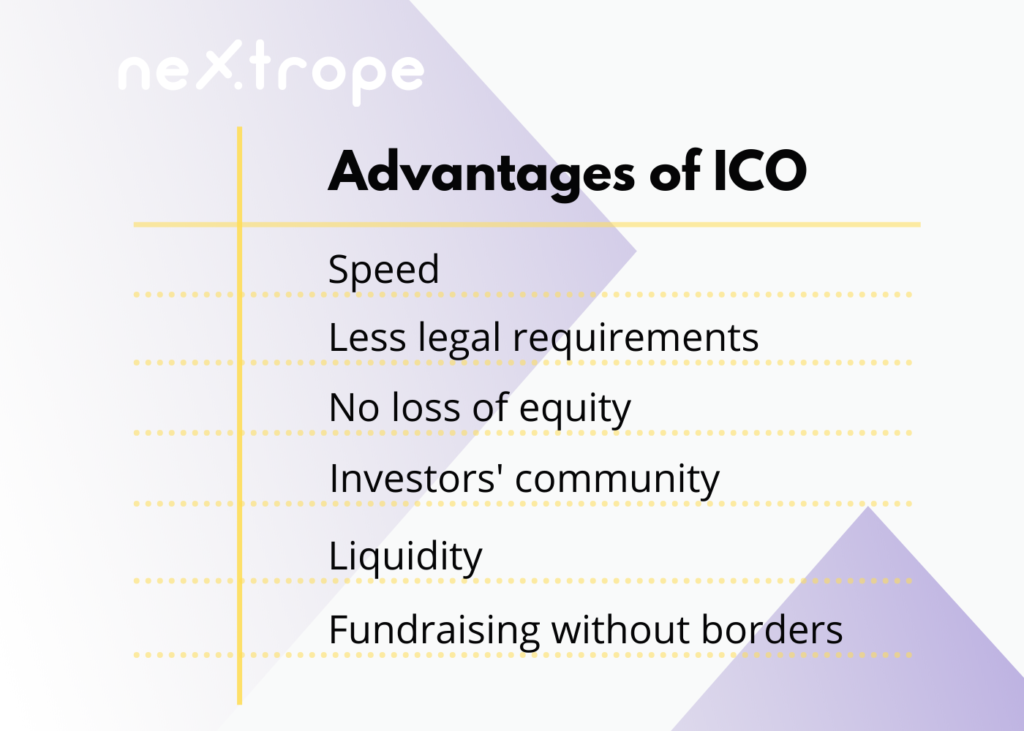
Speed
Quick access to funding at a seed stage. Conducting an ICO campaign can be a matter of just a few weeks.
Fewer legal requirements
ICOs are far less regulated than any other fundraising method. Hence they require minimal bureaucracy.
Your project, your equity
During ICO, you can raise funds without loss of equity.
Community
Your ICO investors will create a strong community, willing to test and even promote the project.
Liquidity
Global markets, where your tokens will be sold, operate 24/7.
Fundraising without borders
Contrary to a public offering, your tokens will be sold on a global market, which means that the campaign doesn’t have to be restricted to one jurisdiction. Anyone with a crypto wallet can buy them.
How do ICOs work?
Essentially, launching initial coin offerings means issuing your own tokens that will have a specific utility in your project. That’s why they are named Utility Tokens. You can read more about different token types in this article. Contrary to a securities offering, ICO doesn’t grant investors shares of the company. Instead, they distribute tokens with a specific utility in the project that will be built for raised funds.
To raise money through initial coin offering, startups usually start with creating a white paper. This is a document that describes the project and its goals, providing investors with information that may help them decide whether they want to participate.
During the ICO process, investors buy tokens with other cryptocurrencies or fiat money. If the funding requirements are met, raised capital will support the creation of the project. If they aren’t, they may be returned to investors. It depends on chosen structure model.
Different structure models of ICO
Initial coin offerings may be structured in various ways. In some examples, tokens sold during ICO have a fixed price and specified limited supply. In contrast, others limit the supply but leave the token price dynamic, which means that fundraising will depend on the amount of raised funds.
There are also initial coin offerings that set a static price of token and dynamic token supply that depends on the amount of funding received.
ICO and federal securities laws
It’s important to note that currently, in the majority of jurisdictions, ICOs remain largely unregulated. This means that they are far less restricted than IPOs or even STOs.
Essentially, most tokens issued during ICO aren’t treated as securities because they don’t represent any equity in the project. Instead, they have a certain utility in their network.
How to raise capital via ICO?
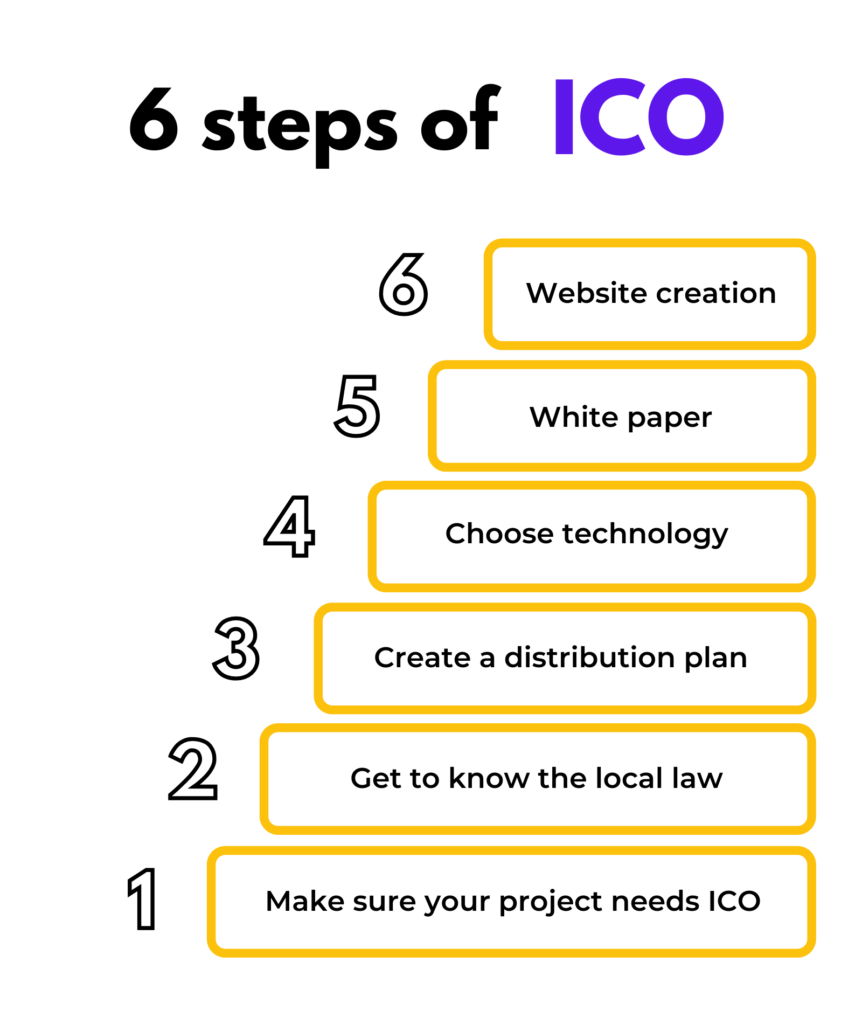
In the whole initial coin offering process, the following stages can be distinguished:
Make sure your project needs ICO
A brief disclaimer: not every company qualifies for ICO. And even if it does, there may be better alternatives.
ICO isn’t a universal solution that will suit every project. Many factors should be taken into consideration before choosing it.
First of all, initial coin offerings work best for blockchain-based projects. There are many good ICOs out right now; hence the competition for the attention of investors is high. If your project uses unnecessary tokens and doesn’t back them with attractive utility, investors probably won’t be interested in putting their funds into it.
Yet, the crypto industry offers more solutions that support fundraising. Some of them, as STO, are also suitable for non-blockchain projects.
Get to know the local law
ICOs are a relatively new fundraising solution. Hence many countries still haven’t developed a clear legal framework for them.
So far, only China and South Korea have banned ICOs. Yet, you have to be aware that in some jurisdictions launching your private ICO will be much easier than in others. You can find more information regarding this issue in our article: The 5 most popular jurisdictions for your company’s tokenization.
Create a distribution plan
The plan will depend on your primary requirements and assumptions. For instance, there may be different stages of the token sale before you get to the actual initial coin offering. For example, Telegram managed to raise $850 million during the pre-sale only.
At this stage, you have to decide which of the previously mentioned models you will choose? Is the price going to be stable or rather dynamic? What about the supply? Moreover, you should determine how many of them will be sold at each stage of the token sale.
Choose the right technology
This may sound trivial, but the right technology solutions are the backbone of your ICO’s success. There are several universally required technologies, among them blockchain, smart contracts, tokens, and solid back-end and security infrastructure.
When it comes to blockchain, the majority of the companies decide to use established, well-known protocols. In most cases, it’s Ethereum. Launching an ICO on your own blockchain is possible and can sometimes be observed in the industry. Yet, it’s time and cost-consuming. Additionally, for the majority of projects, there is no need to do so.
White paper
A white paper is a document that describes the project and explains its goals in almost every possible detail. It’s aimed to provide potential investors with the information needed to decide whether they want to participate. This includes:
- Vision
- Market analysis
- Goals
- Available resources
- Development strategy
- Legal frames
- Details regarding token and its distribution
- Description of the team
Not sure how to write a proper white paper? Our consultants will gladly guide you through the whole process.
Website creation
You need to face that your project will be judged mainly by the content and appearance of its website. It has to contain clear information about your team, aims, and measures to protect investors’ interests.
Before ICO launch, the website should also feature a token sale landing page. Remember about approachable UX here.
ICO vs. IPO

The main difference between IPO and ICO lies in equity. During ICO, owners don’t have to give up a part of their equity in exchange for funds, as they do with shares in the case of IPO. Instead, they issue tokens that will have a utility in their project. Therefore, ICO is mainly used for blockchain-based projects.
Because during the ICO no equities are sold, there are fewer restrictions regarding ICOs than IPOs. For example, most ICOs don't fall under securities law. Thus, they require less bureaucracy and are more suitable for seed-stage startups. Furthermore, investing in ICO tokens isn't restricted to accredited investors, as it happens with IPO.
ICO vs. STO: main differences
There are different types of token offerings out there. One of the most important is the slightly younger STO - security token offering. Here instead of utility tokens, security tokens are issued. This means that their value is backed by real assets - for example, shares in the company or real estate. You can read more about security tokens in this article.
The main advantage of STO is that they are suitable for various projects, not only blockchain-based ones. In this way, you can even tokenize alternative assets, such as cars or precious metals.
On the other hand, because tokens represent specific equity, they are treated as securities. And this means far more legal restrictions.
What is ICO? - Conclusion
Initial coin offerings are an excellent opportunity for seed-stage startups to raise capital for further development. During the past 6 years, billions of dollars have been raised using ICO, funding such projects as Telegram or Ethereum. At the same time investing in ICO gained tremendous popularity, even outside the crypto community.
Yet as with every solution, they aren’t free from limitations. While from a technology perspective process is getting easier every year, more and more legal restrictions emerge. Furthermore, because of several ICO projects, reaching investors now requires a well-planned marketing strategy.
Are you interested in launching your own ICO, but you are not sure if your team will manage to fulfill all the requirements? After conducting one of the first tokenizations globally and many other ICOs, we may say that we know the ropes of successful tokenization. Hence, if you have any questions, don’t hesitate to ask.
 en
en  pl
pl