
Ethereum Economics is a comprehensive term that encapsulates the economic principles and mechanisms guiding the Ethereum network, touching on everything from its currency, Ether, to its role in facilitating decentralized applications and smart contracts.
Understanding Ethereum Economics
Ethereum’s economic framework is designed to balance scalability, security, and decentralization, often referred to as the blockchain trilemma. The network’s native cryptocurrency, ETH, is not just a medium of exchange but also a vital component of Ethereum’s security protocol, especially with the transition to proof of stake (PoS) in Ethereum 2.0. Ethereum Economics also encompasses the platform’s approach to transaction fees (gas fees), its monetary policy, and the mechanisms for issuing new ETH into the system, which together influence the network’s liquidity, usability, and overall value.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
The supply and demand dynamics within Ethereum Economics are crucial for understanding its market value and the incentives for participation in the network.
Supply Aspects:
- Ether Issuance: The total supply of ETH is influenced by the network’s issuance rate, which has evolved over time. Unlike Bitcoin, Ethereum does not have a hard cap on the total supply of ETH, but various upgrades (notably the London Hard Fork and EIP-1559) have introduced mechanisms to moderate the growth of the supply.
- Ethereum 2.0 and Staking: The transition to Ethereum 2.0 introduces staking, where validators lock up ETH as a security deposit to participate in network consensus. This shift from proof of work (PoW) to proof of stake (PoS) not only changes the security model but also influences the circulating supply of ETH by encouraging the locking up of Ether in staking contracts.
Demand Aspects
- Smart Contracts and dApps: Ethereum’s utility as a platform for deploying smart contracts and dApps creates a fundamental demand for ETH, as it is required to pay for transaction fees and computational services.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and NFTs: The explosive growth of DeFi and the NFT market on the Ethereum platform has significantly increased the demand for ETH. These applications require ETH for transaction fees, collateral, and sometimes as a medium of exchange within their ecosystems.
The interplay between supply and demand is further nuanced by factors such as network upgrades, changes in transaction fees, and the overall adoption rate of Ethereum-based applications. As Ethereum continues to evolve, particularly with the full implementation of Ethereum 2.0, these dynamics are likely to shift, presenting new economic considerations and opportunities for users, investors, and developers alike.
Ethereum’s Monetary Policy
Ethereum’s monetary policy is a critical aspect of its economic model. It focuses on managing the supply of Ether (ETH) to ensure network security and incentivize balanced participation. Unlike traditional monetary systems or even other cryptocurrencies with a fixed supply cap, Ethereum adopts a more dynamic approach.
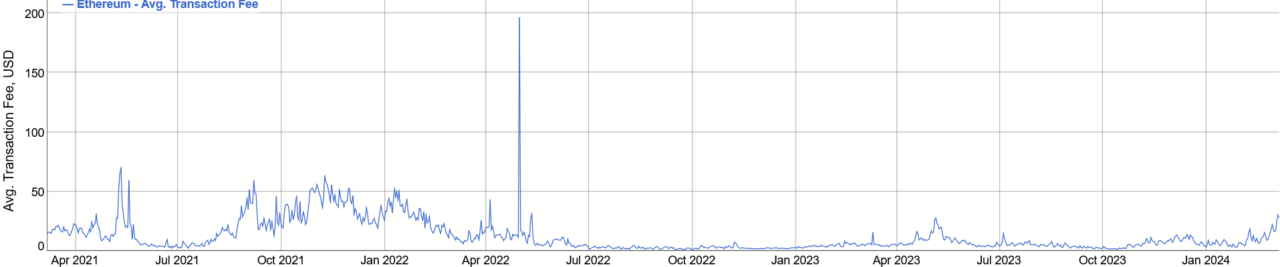
Transaction Fees
EIP-1559, implemented as part of the London Hard Fork in 2021, significantly altered Ethereum’s monetary policy. It introduced new mechanisms in regard to charging transaction fees. Specifically it divided fee into 2 parts. The Base Fee and Priority Fee.
Base Fee
Base Fee is dynamically determined based on network congestion and burned. It increases are based on two factors: how congested the network is, and for how long it’s been congested. This means that the base fee will keep increasing until activity on the network goes back to targeted average level. Because that base fee is burned it also means that ETH is deflationary when the network’s activity is high.
Priority Fee
Priority Fee is an additional fee which serves as a tip for validators. It’s set by a user, to encourage validators to process his transaction. Higher fee means that transaction will be validated before other transactions. Priority fee should be above 0, because validators must have some incentive to include transaction in a block.
Staking and Ethereum 2.0
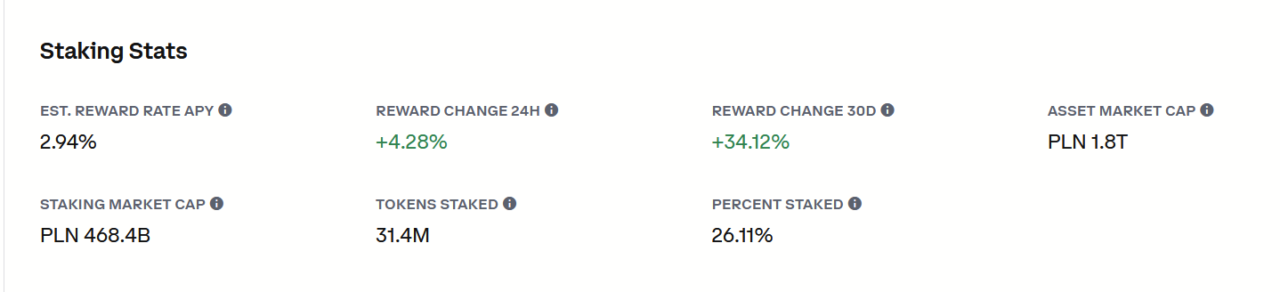
The transition to Ethereum 2.0 and its proof of stake (PoS) consensus mechanism introduces staking rewards as a new form of issuance. Validators stake a minimum of 32 ETH to participate in the network’s security and consensus mechanism. High entry barrier contributes to a fact that only 26% of total supply is staked. This is lower value than in some other blockchains like Cardano (64% staked).
Penalties
Ethereum ensures that validators act in the best interest of the network by introducing a set of penalties.
Slashing
Slashing is a penalty for violating protocol’s rules and engaging in dishonest behavior. Portion of validator’s ETH is taken away if he tries to
- Propose two different blocks
- Attesting conflicting versions of the blockchain (attesting means voting in favor of validator’s view of the chain.
Inactivity Leaks
If validator is inactive and doesn’t participate in e.g. block attestations, he gradually loses some of his ETH. This ensures that stakers actively participate in securing the network. This prevent a situation when a number of validators would regularly ignore their duties, and contribute to destabilizing the nework.
Conclusion
The exploration of Ethereum Economics makes one appreciate it’s complexity. It’s impressive how precise Ethereum developers had to be. They found parameters that balance its ecosystem very well (e.g. how did they choose that staking precisely 32ETH is better than 28ETH). Besides quantitative parameters the logic behind the fees structure, penalties, and others is interesting as well. All this, makes Ethereum Economics an excellent case study for token engineers and blockchain developers.
If you’re looking to design a sustainable tokenomics model for your DeFi project, please reach out to contact@nextrope.com. Our team is ready to help you create a tokenomics structure that aligns with your project’s long-term growth and market resilience.
FAQ
What role does Ether (ETH) play in Ethereum’s economy?
- ETH is not only a medium of exchange but it’s also crucial for the network’s security. In PoS model what prevents validators from harming the network is the fact that they might lose their ETH stake.
How did EIP-1559 change Ethereum’s fee market?
- EIP-1559 introduced a two-part fee structure with a base fee and priority fee. Base fee gets burned, contributing to Ethereum being potentially deflationary under high activity. Priority fee incentivizes miners to include transactions in a block.
What is Ethereum’s strategy for scaling and addressing network congestion?
- Ethereum’s strategy is to make use of Layer 2 Solutions, with Ethereum blockchain serving as a secure settlement layer.


