
Chainlink emerges as the bridge between the real world and the blockchain. On the other side, Avalanche flashes through the blockchain space with a lightning-speed platform that promises scalability without compromise. Both are revolutionaries in their own right, yet their paths are markedly different. Chainlink’s quest to secure the integrity of off-chain data in a decentralized manner contrasts with Avalanche’s mission to redefine blockchain’s scalability and usability. But what happens when these paths intersect?
What is Chainlink?

Overview
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that plays a critical role in bridging the gap between smart contracts on blockchain networks and real-world data. It enables smart contracts to securely interact with external data.
Key Features of Chainlink
- Decentralized Data Oracles. Chainlink’s network of decentralized oracles ensures that data fed into smart contracts is accurate and tamper-proof, mitigating risks associated with relying on a single data source.
- Smart Contract Connectivity to Real-World Data. It facilitates the seamless integration of external data sources, such as financial market data, weather information, and much more, enabling smart contracts to execute based on inputs from the real world.
- Chainlink VRF (Verifiable Random Function). This feature provides a secure and provably fair source of randomness for blockchain applications, crucial for gaming, NFTs, and any application requiring random number generation.
READ: “What is Chainlink“
What is Avalanche?

Overview
Avalanche is a highly scalable blockchain platform designed for decentralized applications (dApps) and custom blockchain networks. It distinguishes itself with its emphasis on scalability, speed, and eco-friendliness.
Key Features of Avalanche
- High Throughput and Low Latency. Avalanche boasts a high transaction output rate with low latency, making it an ideal platform for scaling dApps and financial solutions.
- Eco-friendly Consensus Mechanism. Unlike proof-of-work (PoW) systems that require significant energy expenditure, Avalanche uses a novel consensus mechanism that is energy-efficient, contributing to a more sustainable blockchain ecosystem.
- Scalability and Interoperability. The platform supports the creation of multiple custom blockchains that can interoperate seamlessly, facilitating a diverse and scalable ecosystem of applications.
READ: “Avalanche’s Investment in Real-World Assets Tokenization“
Comparing Chainlink and Avalanche
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, understanding the nuances between different platforms and solutions like Chainlink and Avalanche becomes increasingly important. Here’s how these two blockchain giants stack up against each other:
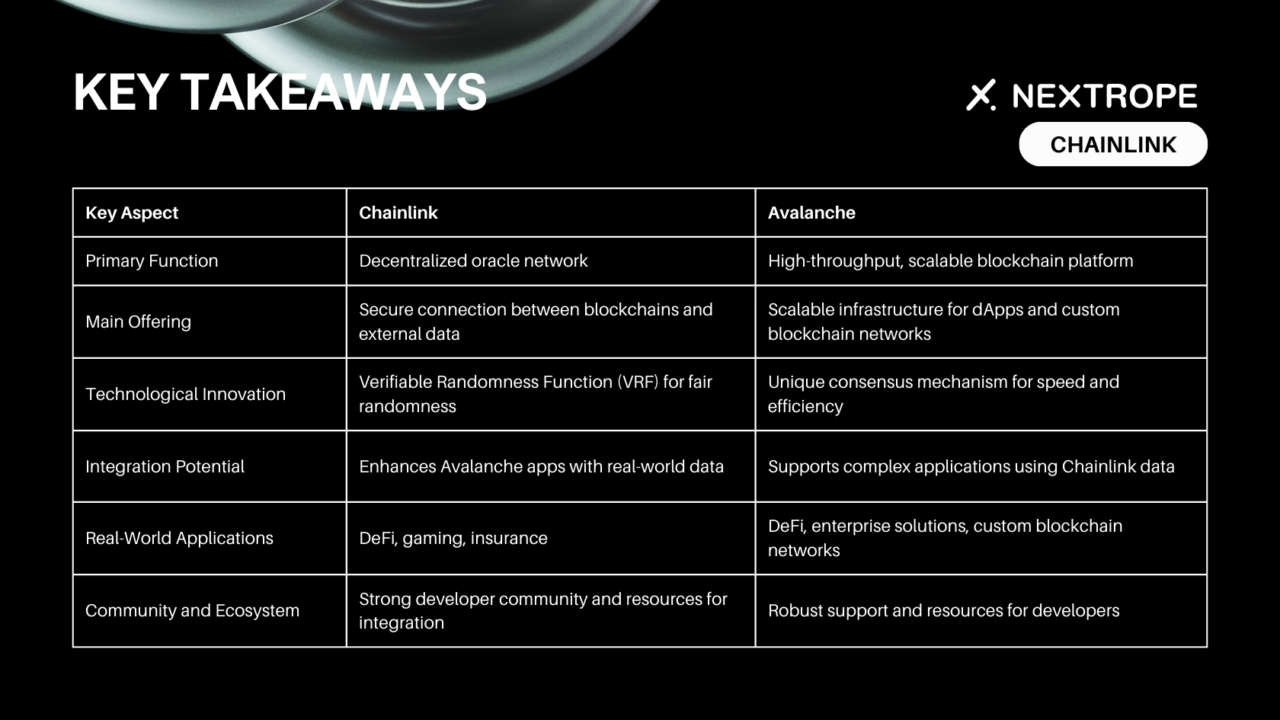
Technological Foundations – Chainlink and Avalanche
Underlying Technologies and Architectures:
- Avalanche utilizes a unique consensus protocol known as Avalanche consensus, combining the benefits of classical consensus algorithms with the decentralized nature of blockchains. This protocol allows for high throughput, quick finality, and energy efficiency.
- Chainlink, on the other hand, is not a blockchain but a decentralized network of nodes that provide data to blockchain networks. It uses a network of independent node operators who are incentivized to provide accurate data to smart contracts.
Consensus Mechanisms:
- Avalanche employs a Proof of Stake (PoS) model designed to be lightweight and energy-efficient. Validators participate in reaching consensus by staking AVAX tokens, contributing to the network’s security and governance.
- Chainlink does not use a consensus mechanism in the same way a blockchain network like Avalanche does. Instead, it relies on a decentralized network of oracles to validate and relay data, ensuring the integrity of information provided to smart contracts.
Use Cases and Applications – Chainlink and Avalanche
Chainlink is best suited for applications that require secure, reliable, and tamper-proof data inputs from the real world. This includes:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi) applications needing accurate price feeds.
- Gaming platforms requiring verifiable randomness.
- Insurance contracts dependent on real-world data for claim verification.
Avalanche is optimized for a wide range of blockchain applications needing high throughput, quick finality, and scalable infrastructure, such as:
- Scalable DeFi platforms and DEXes.
- Enterprise blockchain solutions.
- Custom blockchain networks (subnets).
Examples of Real-World Applications and Partnerships:
- Chainlink has partnered with Google Cloud for cloud data integration and with numerous DeFi platforms like Synthetix and Aave for price feeds and randomness.
- Avalanche has formed partnerships with Deloitte for enhancing security and speed in disaster relief platforms and with top DeFi protocols to build on its highly scalable network.
Ecosystem and Community
Development Community and Ecosystem Support:
- Both Chainlink and Avalanche boast robust and active communities. Chainlink’s community is highly engaged in developing external adapters and securing data for smart contracts. Avalanche’s community focuses on developing dApps and custom blockchain networks.
Tools, Resources, and Support:
- Chainlink offers extensive documentation, a vibrant developer community, and grants for projects integrating Chainlink’s technology.
- Avalanche provides developers with comprehensive resources, including tutorials, technical documentation, and funding for ecosystem growth through the Avalanche Foundation.
Tokenomics and Market Performance
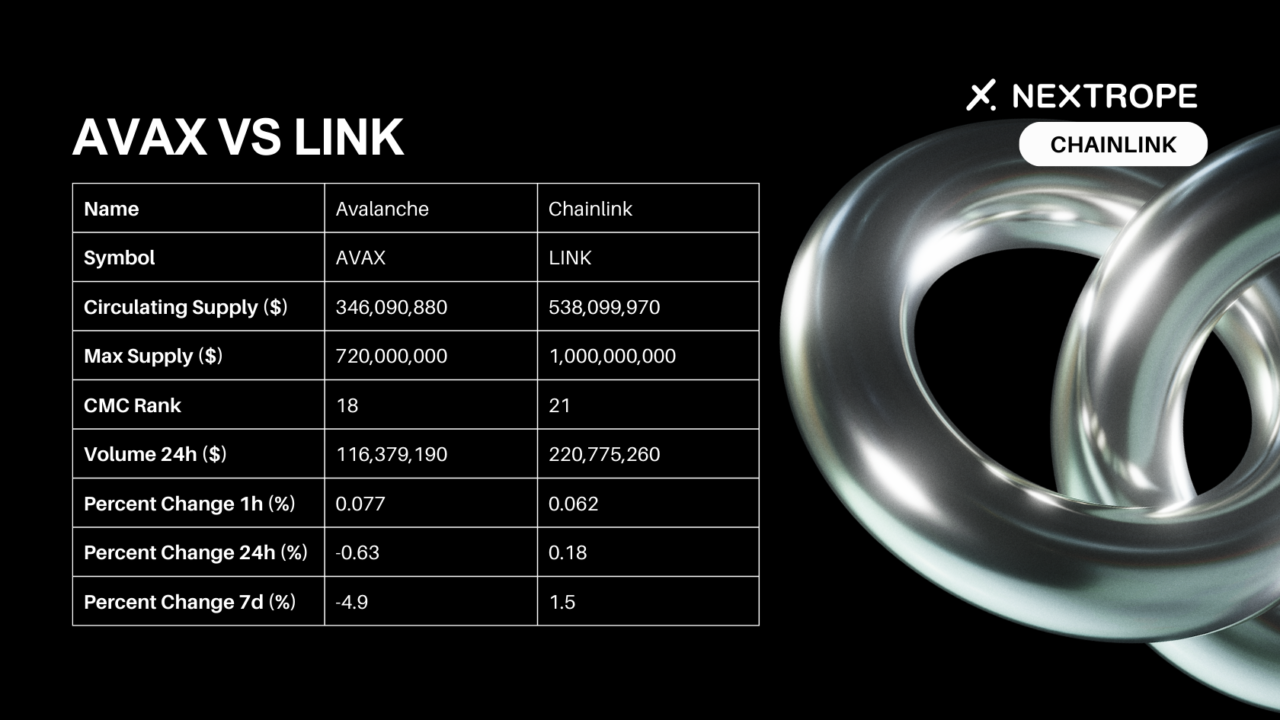
- LINK (Chainlink’s token) is used to pay for services within the Chainlink network, including data requests to oracles. It incentivizes node operators to provide accurate data.
- AVAX (Avalanche’s token) serves as the native currency within the Avalanche network, used for transaction fees, staking, and governance.
- In terms of market performance, both LINK and AVAX have shown significant growth and adoption, reflecting their utility and the demand for their respective network’s services. However, their performance can vary based on overall market trends, technological advancements, and adoption rates in their specific use cases.
Synergies Between Chainlink and Avalanche
Potential for Integration
The potential for integration between oracles and Avalanche’s blockchain platform is substantial. Chainlink’s decentralized oracles can provide Avalanche-based applications with secure and reliable real-world data, enhancing the functionality and scope of Avalanche’s already fast and scalable blockchain. This integration can benefit a wide range of applications, from DeFi and insurance to gaming and prediction markets, by providing them with the essential data needed to operate effectively and transparently.
Conclusion
Chainlink and Avalanche, while serving distinct purposes within the blockchain ecosystem, demonstrate a powerful synergy when combined. Chainlink’s ability to provide secure, reliable, and decentralized data complements Avalanche’s high-throughput, scalable blockchain platform, enabling developers to build more complex, useful, and transparent applications.
READ ALSO: “Chainlink vs Polkadot“
If you are interested in utilizing Chainlink or other blockchain-based solutions for your project, please reach out to contact@nextrope.com
FAQ
What are the fundamental differences between Chainlink and Avalanche?
- Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network providing real-world data to blockchains, while Avalanche is a blockchain platform focusing on high throughput, low latency, and eco-friendliness.
How do Chainlink and Avalanche contribute to the blockchain ecosystem?
- Chainlink secures off-chain data integrity for smart contracts, while Avalanche enhances blockchain scalability and usability with its unique consensus mechanism.
What are the key use cases for Chainlink and Avalanche?
- Chainlink is suited for applications requiring secure, reliable external data, such as DeFi, while Avalanche targets scalable dApps and custom blockchain networks.
How does the developer community and support compare between Chainlink and Avalanche?
- Interested in the size, resources, and support available to developers within each ecosystem, which influences the ease of development and innovation.


