In the realm of blockchain technology, decentralized oracles play a crucial role by facilitating secure and trustworthy connections between real-world data and blockchain networks. Acting as a conduit, these oracles enable the seamless integration of off-chain information into decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts. Utilizing such oracles allows developers to expand on the potential of blockchain technology by tapping into verifiable and resistant data from a variety of sources. We will delve into the complexities of constructing decentralized oracles in this guide, addressing their advantages, obstacles, recommended approaches, and available frameworks for crafting inventive blockchain solutions.
Understanding Oracles in the Blockchain Context
Understanding Oracles
Specialized systems known as oracles facilitate the connection between blockchain networks and external data sources. Serving as intermediaries, they supply off-chain data to on-chain applications like smart contracts and DApps, allowing blockchain applications to access real-world information, events, and data feeds securely and reliably.
Types of Oracles
Centralized Oracles:
When it comes to providing data inputs for blockchains, centralized oracles depend on a single authority or entity. Though their implementation is relatively simple, they create a single point of failure and potential vulnerabilities, which can compromise the data’s trustworthiness and security.
Decentralized Oracles:
In contrast, decentralized oracles use the principles of blockchain technology to offer a more secure and dependable method. They distribute the tasks of data retrieval, validation, and aggregation among multiple participants to ensure consensus while minimizing manipulation or tampering risks. Decentralized oracles enhance trust and verifiability in blockchain applications.
Decentralized oracles are prominent due to their capability to deliver reliable and tamper-proof data inputs that align with the core concepts of decentralization and trustlessness in blockchain technology. By comprehending the various oracle types and their implications, developers can make well-informed decisions when incorporating oracles into their blockchain endeavors.
Components of a Decentralized Oracle
A decentralized oracle is not a simple, single entity, but rather a combination of several components that work together to connect blockchain-based smart contracts with the external world. Understanding these components is vital for any developer who wishes to construct a decentralized oracle. Let’s delve into the core components:
Oracle Node
Oracle nodes are the workhorses of a decentralized oracle network. They are responsible for retrieving and validating real-world data from external data sources. Oracle nodes are also responsible for reporting the retrieved data back to the blockchain. A decentralized oracle network includes multiple oracle nodes to ensure data accuracy and prevent manipulation.
Data Providers
Data providers are the external sources from which oracle nodes retrieve the necessary real-world information. They can be anything from APIs of web services, data feeds, databases, to IoT devices. The choice of data providers is critical as they directly affect the accuracy and reliability of the data used in smart contracts.
Aggregation Contract
Once oracle nodes retrieve and validate data, it must be processed and formatted in a way that’s useful for the smart contract requesting the data. This is where the aggregation contract comes in. It takes the data from multiple oracle nodes, processes it (often by calculating a median or average), and then feeds the aggregated data to the requesting smart contract.
Reputation System
In a decentralized oracle network, a reputation system is typically used to incentivize honest behavior and discourage malicious activity. Oracle nodes are rewarded or penalized based on their performance. Nodes that consistently provide accurate and timely data are rewarded, while those found to be unreliable or dishonest are penalized.
Request and Response Model
The request and response model is a core component of how a decentralized oracle functions. When a smart contract needs data from the outside world, it sends a request to the oracle. The oracle nodes then fetch the required data from the chosen data providers, validate it, and send it back to the smart contract.
Security Mechanisms
Security is a paramount concern for any component interfacing with a blockchain. Decentralized oracles often incorporate various security measures to protect against attacks. These might include cryptographic proofs for data integrity, multi-signature confirmations for critical transactions, and secure data transmission protocols.
In summary, building a decentralized oracle involves constructing and connecting these components in a way that ensures the reliable, secure, and timely delivery of real-world data to smart contracts. Each component plays a crucial role in the overall functioning of the decentralized oracle. Understanding these components and their interactions is a prerequisite for creating a robust decentralized oracle.
Building a Decentralized Oracle – The Process
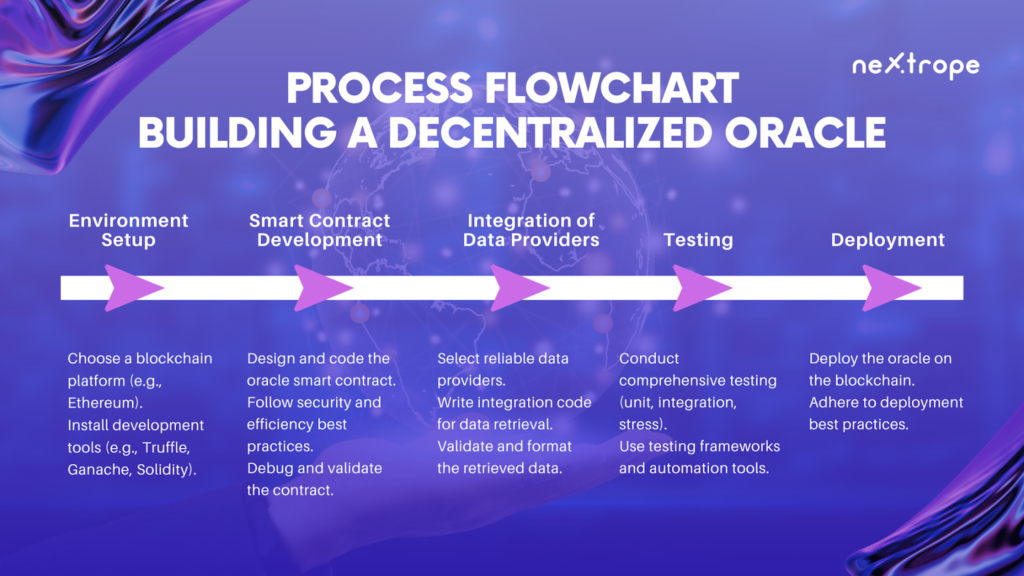
Creating a decentralized oracle is a challenging but rewarding process. It involves careful planning, thoughtful design, meticulous coding, rigorous testing, and effective deployment. Here is a step-by-step guide to building a decentralized oracle.
Step 1: Setting up the Environment
The first step in building a decentralized oracle is setting up the development environment. This typically involves:
- Choosing a blockchain platform: The choice of blockchain platform depends on various factors like the target audience, security requirements, scalability needs, and the type of data to be handled. Ethereum is a popular choice due to its extensive developer support and robust smart contract capabilities, but other platforms like Binance Smart Chain, Polkadot, or Cosmos might be more suitable depending on your specific needs.
- Setting up the development tools: Depending on the chosen blockchain platform, you will need to install and configure the appropriate development tools. For Ethereum, this would include tools like Truffle, Ganache, and the Solidity programming language.
Step 2: Developing the Oracle Smart Contract
The next step is to write the oracle smart contract. This contract will handle requests from other contracts, fetch data from the external world, and return the retrieved data. This process involves:
- Designing the contract: Before you start coding, you should design the contract’s interface and determine how it will interact with other contracts and external data sources.
- Writing the contract: Using your chosen programming language (such as Solidity for Ethereum), write the smart contract code. Be sure to follow best practices for security and efficiency.
- Debugging: Debugging is a critical part of the development process. Test your contract thoroughly to ensure it behaves as expected and doesn’t contain any vulnerabilities.
Step 3: Integrating Data Providers
Once your oracle smart contract is ready, you’ll need to connect it to external data providers. This involves:
- Selecting data providers: Choose reliable and accurate data providers that can supply the type of data you need. This could be anything from financial data feeds, weather APIs, IoT devices, or other web services.
- Writing the integration code: Write the necessary code to fetch data from your chosen data providers and feed it into your oracle contract.
Step 4: Testing and Deploying the Oracle
The final step is to test your oracle thoroughly and then deploy it on your chosen blockchain. This includes:
- Testing: Conduct thorough testing to ensure that your oracle works correctly and securely. This should include unit tests, integration tests, and stress tests. Consider using testing frameworks and tools to automate this process.
- Deployment: Once you’re confident that your oracle is ready, deploy it on the blockchain. Be sure to follow best practices for contract deployment, and consider using a deployment tool to make the process easier and more reliable.
- Building a decentralized oracle is a complex but rewarding process. By following these steps, you’ll be well on your way to creating a powerful tool that can bridge the gap between the blockchain and the outside world.
Popular Platforms for Building Decentralized Oracles
While it’s entirely possible to build a decentralized oracle from scratch, leveraging existing oracle platforms can significantly ease the development process. These platforms offer tools, services, and frameworks that simplify the creation of secure, reliable, and efficient decentralized oracles. Let’s explore some popular platforms:
Chainlink
Chainlink is one of the most well-known and widely used decentralized oracle platforms. It provides a flexible framework for connecting smart contracts with real-world data, APIs, and other off-chain resources. Developers can use Chainlink to create custom oracle networks, choose their own data sources, and define aggregation strategies.
Band Protocol
Band Protocol offers a decentralized data oracle that allows smart contracts to access external data in a secure and scalable manner. The Band Protocol is known for its efficient design, which reduces the amount of data stored on-chain, leading to faster transactions and lower costs.
Provable (formerly Oraclize)
Provable provides reliable oracle services for various blockchains, including Ethereum, Bitcoin, and EOS. It focuses on data transport, authenticity proofs, and easy integration. Provable’s technology allows developers to fetch data from any web API, ensuring a wide range of potential use cases.
Challenges and Potential Solutions
Building decentralized oracles comes with a set of unique challenges. Here are some of the most common ones, along with potential solutions:
Data Accuracy and Reliability
Challenge: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data from external sources
Solution: Using multiple data sources for cross-verification and choosing reputable and reliable data providers. Implementing a consensus mechanism for data validation can also help.
Timeliness of Data
Challenge: Providing real-time or near-real-time data to smart contracts, as fetching data from external sources can introduce latency
Solution: Optimizing the data retrieval process, using fast and reliable data providers, and implementing predictive algorithms to anticipate future data needs.
Security
Challenge: Protecting against potential attacks such as man-in-the-middle attacks, Sybil attacks, or direct attacks on the data source
Solution: Implementing robust security measures like cryptographic proofs for data integrity, secure data transmission protocols, and utilizing additional security services from oracle platforms, if available.
Complexity of Development
Challenge: Navigating the complex process of building a decentralized oracle, which requires deep knowledge of blockchain technology and the specific oracle platform
Solution: Leveraging existing oracle platforms that offer tools and frameworks to simplify the development process, and utilizing educational resources and developer communities around these platforms.
Despite these challenges, with the right approach and tools, it’s entirely possible to build effective and secure decentralized oracles to bridge the gap between blockchain networks and the real world.
Conclusion
Decentralized oracles play a crucial role in connecting blockchain networks with real-world data, facilitating secure and dependable interactions. By leveraging these oracles, developers can tap into verified data from diverse sources, extending blockchain technology’s reach across numerous sectors. In this exhaustive guide, we have delved into the concept of oracles, making a distinction between centralized and decentralized varieties while shedding light on their advantages and drawbacks. Additionally, we have explored the fundamental elements of a decentralized oracle, the procedure for constructing one, and well-known platforms that streamline oracle development. Equipped with this information, developers can seamlessly incorporate decentralized oracles into their blockchain ventures, uncovering new potential and transforming how blockchain engages with the real world.



