The energy sector is undergoing a transformation with the emergence of peer-to-peer energy trading, facilitated by blockchain technology, which allows for direct energy exchanges between individuals and businesses. This decentralized method yields advantages such as increased efficiency, cost reductions, improved grid resiliency, and the incorporation of renewable energy sources. In this article, we examine the impact of peer-to-peer energy trading and how blockchain plays a crucial role in revolutionizing the way energy is generated, used, and traded.
Understanding the Energy Sector and its Current Challenges
The energy sector is a vast and complex network responsible for the production and distribution of energy in various forms to consumers around the globe. It encompasses a range of industries including oil and gas, electricity, renewables, and more, each playing a crucial role in powering our everyday lives. Traditionally, the sector has been dominated by a few large players who generate power and distribute it across their network, a centralized system that has been in place for many years. These players include public and private utilities, oil and gas companies, and government entities, who control the supply and price of energy to a large extent.
However, this traditional energy sector is fraught with numerous challenges. One of the most significant is the environmental impact of non-renewable energy sources such as coal, oil, and natural gas, which contribute to air pollution and climate change. The sector also struggles with issues of inefficiency and waste in energy production and distribution.
Moreover, the centralized nature of the energy sector often leads to disparities in energy access and affordability. In many regions, consumers have little choice when it comes to their energy provider, leading to monopolies or oligopolies and a lack of competition. This can result in high prices for consumers and businesses, making energy a significant cost burden. Additionally, in some parts of the world, particularly rural and remote areas, access to reliable energy sources is still a significant challenge.
The Role of Blockchain in Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading
Blockchain technology, a decentralized ledger system originally conceptualized for cryptocurrencies, is now making waves in various sectors, including energy. Its inherent characteristics – transparency, security, and immutability – make it an ideal choice for transforming traditional energy systems into more democratic and efficient models.
In the context of the energy sector, blockchain can offer a radical shift from a centralized system to a decentralized one. The technology enables peer-to-peer energy trading, a model where energy consumers can become prosumers – both producing and consuming energy. They can generate their own energy from renewable sources like solar panels and sell excess energy directly to their neighbors or back to the grid. Transactions in this model are recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency, traceability, and trust among users.
Blockchain technology also simplifies transactions by eliminating the need for intermediaries. Traditional energy transactions often involve multiple parties including energy providers, grid operators, and financial institutions, each adding a layer of complexity and cost. With blockchain, energy transactions can be automated using smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. This leads to faster, cheaper, and more efficient energy transactions.
Moreover, blockchain could help resolve some of the grid management challenges associated with integrating a large number of small-scale, decentralized energy resources. Blockchain-based systems can facilitate real-time monitoring, grid balancing, and demand response – all crucial for maintaining grid stability in a decentralized energy model.
Finally, the use of blockchain in peer-to-peer energy trading can empower consumers, giving them greater control over their energy usage and costs. It can democratize the energy sector by providing consumers with more choices and fostering competition among energy producers, potentially leading to lower energy prices.
More about this topic
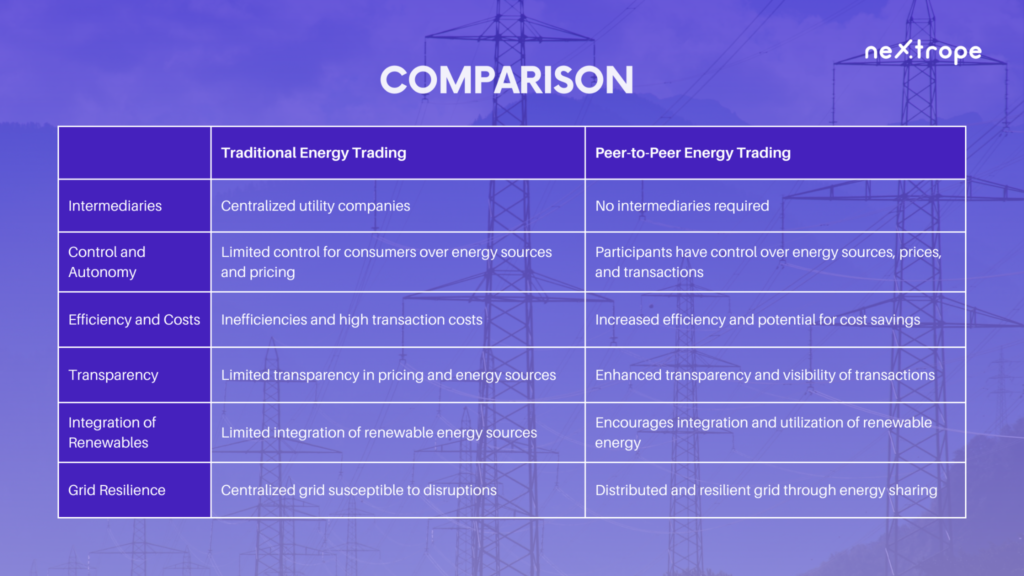
Traditional Energy Trading Model vs. Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading
Centralized utility companies are at the core of the traditional energy trading model, serving as intermediaries between energy producers and end-users. This hierarchy-based system generates and distributes energy, offering consumers limited control over their energy sources and prices. Consequently, this model is often plagued with inefficiency, elevated transaction costs, and a lack of transparency.
Contrastingly, peer-to-peer energy trading revolutionizes this conventional model by enabling direct energy transactions among participants. Utilizing blockchain technology, both individuals and businesses can participate in decentralized energy trading and enjoy increased flexibility, transparency, and autonomy. As a result, network users can select their preferred energy sources, negotiate pricing, and trade surplus energy with others directly. Peer-to-peer energy trading not only empowers consumers but also promotes renewable energy usage and fosters a more resilient, sustainable energy ecosystem.
Future Outlook and Potential of Blockchain in Energy Trading
As we continue to grapple with the complexities and challenges of the current energy sector, blockchain technology, particularly in its application to peer-to-peer energy trading, presents an intriguing and promising path forward.
The potential of blockchain in the energy sector is vast. Its ability to facilitate efficient, transparent, and secure transactions could revolutionize the way we produce, distribute, and consume energy. With an increasing number of renewable energy installations – particularly decentralized ones like home solar panels – the need for a system like blockchain, which can handle numerous small transactions efficiently, is likely to grow.
In the realm of peer-to-peer energy trading, blockchain could empower consumers to become active participants in the energy market, rather than passive users. The democratization of the energy sector could lead to increased competition, potentially driving down energy costs and promoting the adoption of renewable energy sources. This would not only benefit consumers but also contribute significantly to global efforts to combat climate change.
However, the road to this future is not without obstacles. Regulatory hurdles, technological challenges, and the need for further testing and development all stand in the way of widespread adoption of blockchain in the energy sector. It will be important for stakeholders – including regulators, energy providers, and technology developers – to work together to address these challenges and create a supportive environment for the growth of blockchain in the energy sector.
Looking ahead, we can anticipate a future where blockchain technology plays a fundamental role in a decentralized, democratic, and green energy system. The journey towards this future will require continued innovation, collaboration, and a willingness to embrace change. With the right approach and resources, blockchain could indeed transform the energy sector, making peer-to-peer energy trading not just a possibility, but a reality.
Conclusion
The energy sector could be radically transformed by blockchain technology, as it facilitates decentralized energy grids and enables peer-to-peer energy trading. Through secure and transparent transactions, blockchain allows individuals and businesses to exchange energy directly, leading to enhanced efficiency, cost reduction, better grid resilience, and the incorporation of renewable energy sources. Despite facing obstacles like regulation and scalability, the prospects for blockchain in the energy sector remain optimistic. Ongoing innovation and collaboration could propel blockchain towards establishing a decentralized, democratic, and eco-friendly energy system.
Check out how blockchain can revolutionize the real estate market!
 en
en  pl
pl