Bitcointalk.org maintains a crucial role within the blockchain, cryptocurrency, and decentralized technology community as one of the earliest platforms for discussions, announcements, and promotions. Established by the enigmatic creator of Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcointalk has evolved into an indispensable center for blockchain devotees, developers, and crypto investors. The forum facilitates conversations surrounding Bitcoin, cryptocurrencies, and the broader blockchain ecosystem.
Bitcointalk is instrumental in the progression of crypto projects, functioning as a platform for revealing their founding, significant updates, and events. It offers access to a targeted niche audience, generates traffic, and serves as an ideal space for ICO promotions. To effectively capitalize on Bitcointalk for a successful endeavor, comprehending how the platform operates and its available opportunities is necessary. In this article, we will investigate the features, guidelines, and tactics for executing a Bitcointalk campaign efficiently. We'll start by familiarizing ourselves with the platform.
- Understanding Bitcointalk and Its Functionality
- The Features That Made Bitcointalk a Propeller for Crypto Projects Campaigns
- Who Writes and (Most Importantly) Reads on Bitcointalk
- The Hidden Opportunity of Bitcointalk Nobody Talks About
- How Successful Blockchain Companies Secretly Make It in Bitcointalk
- Conclusion - Bitcointalk Campaigns
- Nextrope Tokenization Launchpad Platform
Understanding Bitcointalk and Its Functionality
Launched in 2009 by Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcointalk.org is a renowned cryptocurrency forum that exists as an invaluable resource regarding blockchain, cryptocurrencies, and Bitcoin. Although Satoshi Nakamoto is no longer actively developing, they still manage the domain names bitcointalk.org and bitcoin.org while theymos administers the forum.
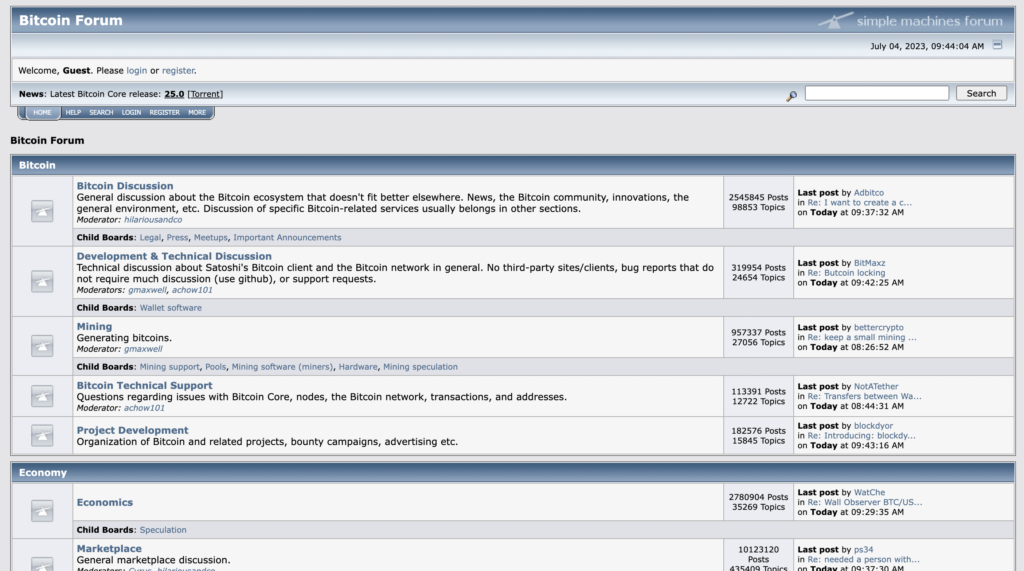
Bitcointalk's structure is founded upon a software package named Simple Machine Forum (SMF), an open-source solution. Its design and functionality have stayed largely consistent since its creation. The forum comprises various sections such as Bitcoin-specific forums, Economy, Other topics, Alternate Cryptocurrencies, and Local discussion boards with sub-forums and threads encompassing an array of cryptocurrency-related subjects.
A significant portion of Bitcointalk is devoted to Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs), where most emerging cryptocurrencies announce their projects and orchestrate bounty campaigns. Possessing a Bitcointalk account has become a standard prerequisite for any project intending to launch an ICO.
The influence of Bitcointalk surpasses being solely a forum, as it holds cultural importance within the crypto sphere, having coined terms like "HODL" (holding a token) and celebrating Bitcoin Pizza Day on May 22, commemorating a user's 10,000 BTC pizza purchase in 2010.
To effectively harness Bitcointalk for promotional goals, comprehending its features and functions is essential. The platform employs a ranking and merit system that incentivizes high-quality posts and minimizes spam. Members can achieve higher ranks by accumulating merits through valuable input. Higher-ranking members attain additional privileges such as participating in signature and translation campaigns.
With over 2 million community members, Bitcointalk's vast user base renders it an invaluable source of traffic and engagement. It attracts diverse users including cryptocurrency enthusiasts, skilled developers, business proprietors, and support staff who maintain the forum's cleanliness and offer technical assistance.
The Features That Made Bitcointalk a Propeller for Crypto Projects Campaigns

Over the years, Bitcointalk.org has been instrumental in advancing and boosting altcoins and cryptocurrency projects. Its unique qualities make it the perfect platform for unveiling, discussing, and bringing attention to new digital currencies. We will now examine the key aspects that contribute to Bitcointalk's success as an accelerator for altcoin and cryptocurrency initiatives:
1. Well-established Community. A sizable, active community of blockchain aficionados, developers, investors, and experts call Bitcointalk home. This engaged group is passionate about the world of cryptocurrency, making it a prime audience for introducing and exploring new digital assets and projects.
2. Announcement Threads. Crypto projects can develop specialized announcement threads on Bitcointalk to showcase their work, offer updates, and connect with the community. These threads centralize discussion and allow project teams direct communication with potential investors and advocates.
3. Signature Campaigns. Utilizing signature campaigns on Bitcointalk, project teams can engage forum members to endorse their projects by incorporating project-related data and links in their forum signatures.
4. Bounty Campaigns. Crypto initiatives often employ bounty campaigns on Bitcointalk to allocate tokens or rewards to community participants for specific tasks like social media promotion, content generation, bug identification, or translation services.
5. ICOs and Token Sales. The forum has become a premier platform for Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and token sales events. Projects can present their ICOs on Bitcointalk, sharing essential information such as whitepapers or token sales details.
6. Trust System. A trust system on Bitcointalk allows forum users to review and evaluate the reliability of their peers. This feature fosters confidence within the community, making it easier for users to identify dependable projects and contributors.
Who Writes and (Most Importantly) Reads on Bitcointalk
Bitcointalk hosts a myriad of individuals with varied interests, who actively engage in discussions, exchange information, and connect over different subjects related to cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Let's delve into the two primary groups found on Bitcointalk: writers and readers.
Writers

1. Crypto Project Teams. Bitcointalk accommodates active participation from cryptocurrency project teams. They use dedicated announcement threads to present their projects, share updates, respond to inquiries, and interact with the community. Teams typically consist of developers, founders, and marketing representatives focused on raising awareness, nurturing a community, and acquiring investors.
2. Crypto Enthusiasts and Experts. A devoted community of crypto enthusiasts and experts calls Bitcointalk home as they eagerly contribute to discussions about various subjects. They exchange knowledge, perspectives, and ideas regarding cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology, trading, mining, among other related areas. These individuals possess a thorough comprehension of the crypto domain and provide worthwhile information assisting others in making well-informed decisions.
3. Investors and Traders. Investors and traders seeking new investment prospects frequent Bitcointalk to gain insight into market tendencies and perform due diligence on potential endeavors. They actively examine project announcement threads, whitepapers, and discussions to assess credibility, possibilities, and risks tied to different altcoins and cryptocurrency projects.
4. Bounty Hunters. Bounty hunters frequently use Bitcointalk as a platform to partake in bounty campaigns. These individuals actively peruse and engage with bounty threads while carrying out specific undertakings such as social media promotions or content generation in exchange for rewards or tokens. Their activities bolster the visibility and marketing efforts of various crypto projects.
Readers

1. Crypto Enthusiasts and Investors. A diverse group of crypto enthusiasts and investors is drawn to Bitcointalk to read about information related to altcoins, token sales, ICOs, market trends, and general cryptocurrency discussions. They rely on the platform to remain informed about recent developments, project updates, and arising opportunities in the crypto sphere.
2. Researchers and Analysts. Bitcointalk functions as a vital resource for researchers and analysts who investigate specific projects, perform due diligence, and appraise the potential of myriad cryptocurrencies. They study project announcement threads, whitepapers, technical discourses, and community feedback to forge educated opinions and make well-informed decisions.
3. Newcomers and Learners. Bitcointalk also caters to novices exploring the realm of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. These individuals peruse educational threads, beginner's guides, and pose questions to acquire a more profound comprehension of the principles, terminology, and practical facets of cryptocurrencies. They depend on the knowledge and experience imparted by community members to traverse the intricate crypto terrain.
The Hidden Opportunity of Bitcointalk Nobody Talks About
1. Connecting with Industry Professionals. Bitcointalk draws a multitude of professionals from various fields such as developers, entrepreneurs, marketers, and investors. Joining discussions related to specific projects or subjects allows connections with these professionals. Active participation helps establish relationships, expand your network, and uncover new possibilities in the cryptocurrency world.
2. Collaborating on Projects. Bitcointalk is an assembly point for individuals possessing diverse skills and experience. Capitalizing on this platform can aid in finding potential collaboration partners for your projects or discovering ventures aligning with your abilities and interests. Delving into discussions, browsing project announcement threads, and connecting with like-minded individuals may lead to productive partnerships.
3. Learning from the Community's Experienced Members. Bitcointalk houses an active community of knowledgeable experts and enthusiasts who openly impart their wisdom and insights. Engaging in conversations lets you learn from these experienced members while staying up-to-date on crypto trends, best practices, and emerging opportunities.
How Successful Blockchain Companies Secretly Make It in Bitcointalk
To establish a notable presence as a blockchain company on Bitcointalk, using a strategic plan that extends past mere project promotion is crucial. Here are some essential tactics employed by successful blockchain companies in making their mark on Bitcointalk:
1. Establishing a Solid Reputation
For any blockchain company aiming to succeed on Bitcointalk, creating a robust reputation is vital. Active community involvement, offering useful insights, and professionally addressing queries and concerns transparently are indispensable. Consistently showcasing your knowledge, expertise, and dedication to the project will help you gain the trust and respect of the Bitcointalk community.
2. Presenting Incentives
Plenty of prosperous blockchain companies give incentives to Bitcointalk users to boost engagement and involvement. Offering airdrops, bounties, or exclusive rewards to active contributors of discussions, project promoters, or valuable feedback providers can help. By providing incentives, companies can garner more attention, enhance engagement, and establish a devoted community around their project.
3. Engaging in Signature Campaigns
Blockchain companies often use signature campaigns as a way to raise their projects' visibility and promotion on Bitcointalk. Participation in these campaigns allows company representatives to showcase their project's logo and links in their forum signatures. As they contribute to discussions, this results in increased exposure, improved brand recognition, and attraction of potential investors or users.
4. Sharing Updates and Achievements
Dedicated announcement threads on Bitcointalk allow blockchain projects to communicate updates, milestones, and news items. Successful firms capitalize on these threads to deliver regular project-related updates about developments, partnerships, and accomplishments. Consistently publicizing positive news generates anticipation and sustains the interest of the Bitcointalk community in the project.
5. Connecting with Prominent Community Members
Influential members with an extensive following and significant respect within the community exist on Bitcointalk. Networking with these individuals and cultivating their support can substantially elevate a company's profile and trustworthiness. Companies can deploy their influence in promoting their projects by interacting with these influential community members, participating in their dialogues, and addressing their doubts.
6. Exploiting the Bounty and Altcoin Announcements Sections
Bitcointalk's Bounty section offers a platform for rewarding users for accomplishing specific tasks like social media promotion, content creation, or bug reporting. Successful firms harness this section to foster engagement and raise awareness. In addition, the Altcoin Announcements section enables companies to generate dedicated threads for project introductions and to disclose crucial details to prospective investors or users.
Conclusion - Bitcointalk Campaigns
In conclusion, Bitcointalk serves as a propeller for altcoins and crypto projects, offering them visibility and community support. By understanding how to effectively engage with the platform and leverage its features, blockchain companies can position themselves for success. It is important to approach Bitcointalk with authenticity and a commitment to adding value to the community. By capitalizing on the hidden opportunities it presents, companies can establish a strong foundation for long-term success in the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology.
Nextrope Tokenization Launchpad Platform
Nextrope Launchpad Platform is a White Label solution in a Software-as-a-Service model that helps you launch your project within a month and fundraise with Initial Coin Offering (ICO) or Security Token Offering (STO).
 en
en  pl
pl