
Token Economy is often defined as the study of determining and evaluating the economic characteristics of a cryptographic token.
Today most blockchain projects fund their operations through the sale of tokens. For that reason, founders need to have a good understanding of the tokenomics design process. Surprisingly, studies show that in most cases tokenomics design is unsound and based on intuition. In this article, we approach the topic from a perspective that’s backed by empirical data and shown to work.
Key Tokenomics Considerations
Optimal Tokenomics depends on the specifics of the project. Part of them is deciding what behaviors you want to incentivize (disincentivize) in a way that aligns with the projects’ interests. That’s a tricky task since you need to identify every relevant user behavior and corresponding incentive. You also need to pick quantitative parameters that will ensure the right balance. In the case of DeFi protocols, systemic risk is especially high. Arbitrary parameters and assumptions often lead to death spirals and vulnerability to attacks. For that reason, all tokenomics systems should be stress-tested and validated before release.
Key Principles
There are many good practices that founders should follow when designing tokenomics for their project. We’ll briefly cover the most important ones.
Utility is The Key
This one seems obvious, but let me explain… What matters in the context of tokenomics is the utility of your token – that’s not the same as the utility of your product. Demand for blockchain products doesn’t automatically translate to demand for their native tokens! While users’ adoption of your product is important, it’s not enough. You need to tie the value of your token to the success of the product. This can be done through different Value Capture mechanisms e.g. redistributing profits among holders.
(PS. Governance Rights and Staking are most definitely not enough!)
Look at comparable projects
When designing tokenomics it’s good to look for projects similar to the one you’re creating. The more similar, the better. Read their whitepapers, study their tokenomics, and look at key metrics. Then ask yourself – what are the things they did well, and what are their mistakes? You’re guaranteed to find some inspiration. A key metric you can use when deciding upon the initial valuation of your project is Total Value Locked/market capitalization
Minimize Volatility
As a founder the key metric that will determine whether people call you a genius or a fraud is the price of your token. For that reason, many teams optimize tokenomics for high token price above everything else. This is often done by offering unsustainable APY in exchange for stacking tokens. Other common choices include burning, or buyback programs funded by anything other than revenue. While these mechanisms may be able to drive the hype and price up, they don’t increase the value of the protocol itself. The result is high volatility and a lack of resilience to malicious attacks and adverse market conditions. Ironically, optimizing for high prices usually results in the opposite effect. What you should do instead is focus on minimizing volatility, as it fosters sustainable growth.
Overview of Supply-Side
Supply-side tokenomics relates to all the mechanisms that affect the number of tokens in circulation and its allocation structure.
While supply is important for tokenomics design it’s not as significant as people think. Mechanisms like staking or burning should be designed to support the use of products and aren’t utilities on their own.
Capped or Uncapped Supply
Founders put a lot of attention into choosing between a capped or uncapped supply of the token. It’s a common belief that capping supply at some maximum level increases the value of currently circulating tokens. Research shows that it doesn’t really matter, but tokens without capped supply, statistically perform slightly better.
Inflation Rate
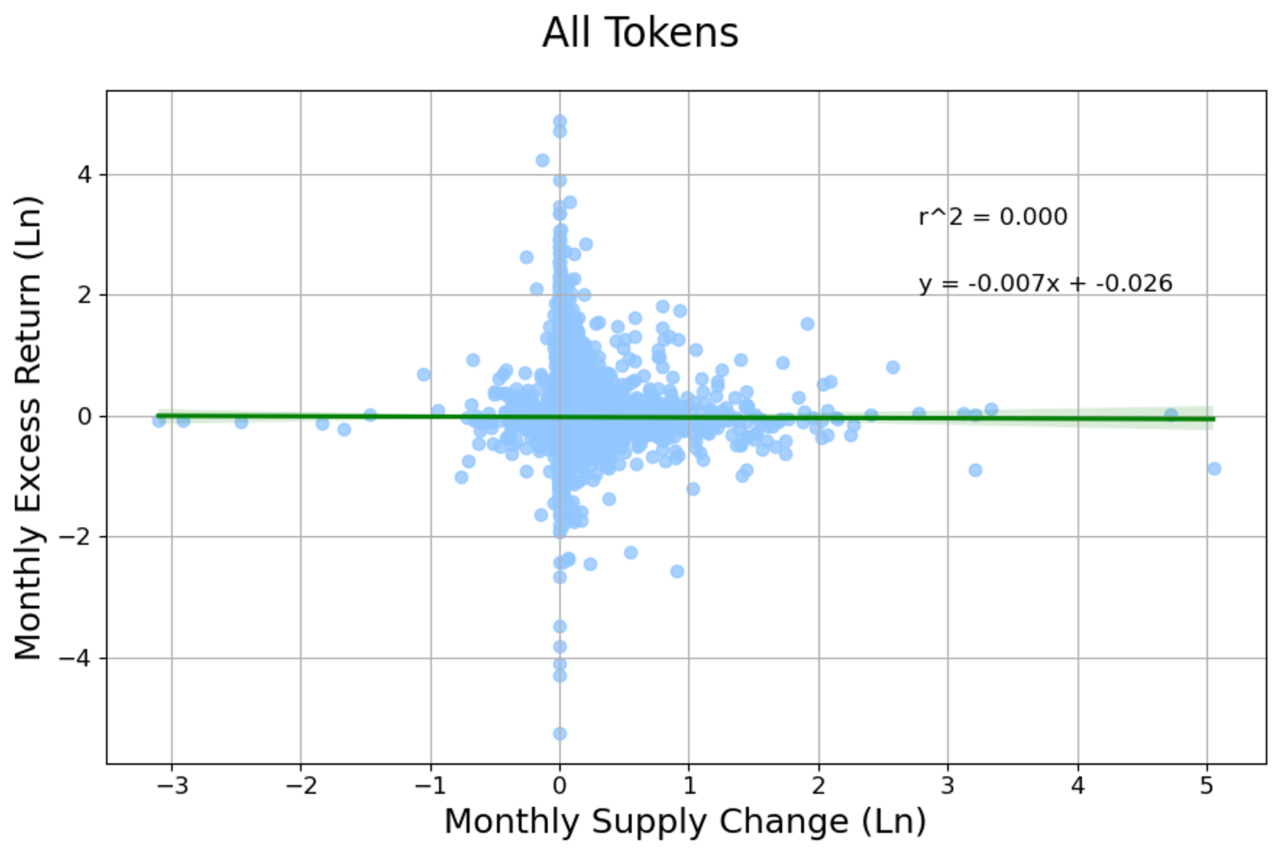
Projects should aim for low, stable inflation. Unless the annualized inflation rate is above 100%, there’s very little correlation between the rate of supply changes and the price of token. For that reason, it’s recommended to adjust token emissions in a way that fosters activity on the network. A reasonable inflation rate that won’t affect the price is between 1-5% monthly.
Allocation:
The industry standards are more or less like the following.
Overview of Demand-Side
Demand-side concerns people’s subjective willingness to buy the tokens. Reasons can be different. It may be due to the utility of your tokens, speculation, or economic incentives provided by your protocol. Sometimes people act irrationally, so token demand has to be considered in the context of behavioral economics.
Role of incentives
The primary incentive that drives the demand for your token should be its utility. Utility is its real-world application or a way in which it captures value generated by the use of your product. Staking, liquidity providing, deflationary policy, and other supply-control mechanisms may support tokens’ value accrual. A common way to do that is through revenue-funded buybacks. Projects may use collected fees to buy their tokens on DEXs. Then burn them, or put them into a treasury fund.
How to design incentives?
- Make them tangible. If you want to promote desired behaviors within the ecosystem you need to provide real rewards. People don’t care about governance rights, because these rights don’t translate to any monetary value. On the other hand, they care about staking rewards, which can be sold for profits.
- Make them easy to understand. If you want to incentivize or disincentivize user behavior, then you should make it clear how the mechanism works. Users often have no time to dive into your whitepaper. If they don’t understand how your product works then they won’t use it.
- Test, test, test. If you don’t test how different incentives balance the tokenomy of your product, then you’re setting yourself up for a terra-luna style collapse.
Conclusion
Proper design of projects’ tokenomics is not easy. Even though it may seem like choosing different parameters and incentives intuitively will work, it’s a reason why the value of projects’ tokens often goes to 0. There are however sound and tested design practices. Stick with us, and get to know them!
If you’re looking to design a sustainable tokenomics model for your DeFi project, please reach out to contact@nextrope.com. Our team is ready to help you create a tokenomics structure that aligns with your project’s long-term growth and market resilience.
FAQ
What is a token economy?
- A token economy refers to the study and analysis of a cryptographic token’s economic characteristics, crucial for blockchain projects’ funding and success.
What are the key principles of designing a token economy?
- Essential principles include ensuring the utility of tokens, analyzing comparable projects, and aiming to minimize volatility to foster sustainable growth.
How does supply and demand affect token economy?
- The supply side involves mechanisms like capping token supply or adjusting inflation rates, while the demand side focuses on creating genuine utility and incentives for token holders.
What are the common pitfalls in designing a token economy?
- The most common problems occur when token’s main function is the transfer of value, rather than supporting the creation of value. (e.g. you can stake useless token to get more of that useless token)
How can token economies be tested and validated before launch?
- Tokenomics can be tested by constructing a mathematical model and running a large number of randomized simulations.


