Introduction
Web3 backend development is essential for building scalable, efficient and decentralized applications (dApps) on EVM-compatible blockchains like Ethereum, Polygon, and Base. A robust Web3 backend enables off-chain computations, efficient data management and better security, ensuring seamless interaction between smart contracts, databases and frontend applications.
Unlike traditional Web2 applications that rely entirely on centralized servers, Web3 applications aim to minimize reliance on centralized entities. However, full decentralization isn’t always possible or practical, especially when it comes to high-performance requirements, user authentication or storing large datasets. A well-structured backend in Web3 ensures that these limitations are addressed, allowing for a seamless user experience while maintaining decentralization where it matters most.
Furthermore, dApps require efficient backend solutions to handle real-time data processing, reduce latency, and provide smooth user interactions. Without a well-integrated backend, users may experience delays in transactions, inconsistencies in data retrieval, and inefficiencies in accessing decentralized services. Consequently, Web3 backend development is a crucial component in ensuring a balance between decentralization, security, and functionality.
This article explores:
- When and why Web3 dApps need a backend
- Why not all applications should be fully on-chain
- Architecture examples of hybrid dApps
- A comparison between APIs and blockchain-based logic
This post kicks off a Web3 backend development series, where we focus on the technical aspects of implementing Web3 backend solutions for decentralized applications.
Why Do Some Web3 Projects Need a Backend?
Web3 applications seek to achieve decentralization, but real-world constraints often necessitate hybrid architectures that include both on-chain and off-chain components. While decentralized smart contracts provide trustless execution, they come with significant limitations, such as high gas fees, slow transaction finality, and the inability to store large amounts of data. A backend helps address these challenges by handling logic and data management more efficiently while still ensuring that core transactions remain secure and verifiable on-chain.
Moreover, Web3 applications must consider user experience. Fully decentralized applications often struggle with slow transaction speeds, which can negatively impact usability. A hybrid backend allows for pre-processing operations off-chain while committing final results to the blockchain. This ensures that users experience fast and responsive interactions without compromising security and transparency.
While decentralization is a core principle of blockchain technology, many dApps still rely on a Web2-style backend for practical reasons:
1. Performance & Scalability in Web3 Backend Development
- Smart contracts are expensive to execute and require gas fees for every interaction.
- Offloading non-essential computations to a backend reduces costs and improves performance.
- Caching and load balancing mechanisms in traditional backends ensure smooth dApp performance and improve response times for dApp users.
- Event-driven architectures using tools like Redis or Kafka can help manage asynchronous data processing efficiently.
2. Web3 APIs for Data Storage and Off-Chain Access
- Storing large amounts of data on-chain is impractical due to high costs.
- APIs allow dApps to store & fetch off-chain data (e.g. user profiles, transaction history).
- Decentralized storage solutions like IPFS, Arweave and Filecoin can be used for storing immutable data (e.g. NFT metadata), but a Web2 backend helps with indexing and querying structured data efficiently.
3. Advanced Logic & Data Aggregation in Web3 Backend
- Some dApps need complex business logic that is inefficient or impossible to implement in a smart contract.
- Backend APIs allow for data aggregation from multiple sources, including oracles (e.g. Chainlink) and off-chain databases.
- Middleware solutions like The Graph help in indexing blockchain data efficiently, reducing the need for on-chain computation.
4. User Authentication & Role Management in Web3 dApps
- Many applications require user logins, permissions or KYC compliance.
- Blockchain does not natively support session-based authentication, requiring a backend for handling this logic.
- Tools like Firebase Auth, Auth0 or Web3Auth can be used to integrate seamless authentication for Web3 applications.
5. Cost Optimization with Web3 APIs
- Every change in a smart contract requires a new audit, costing tens of thousands of dollars.
- By handling logic off-chain where possible, projects can minimize expensive redeployments.
- Using layer 2 solutions like Optimism, Arbitrum and zkSync can significantly reduce gas costs.
Web3 Backend Development: Tools and Technologies
A modern Web3 backend integrates multiple tools to handle smart contract interactions, data storage, and security. Understanding these tools is crucial to developing a scalable and efficient backend for dApps. Without the right stack, developers may face inefficiencies, security risks, and scaling challenges that limit the adoption of their Web3 applications.
Unlike traditional backend development, Web3 requires additional considerations, such as decentralized authentication, smart contract integration, and secure data management across both on-chain and off-chain environments.
Here’s an overview of the essential Web3 backend tech stack:
1. API Development for Web3 Backend Services
- Node.js is the go-to backend runtime good for Web3 applications due to its asynchronous event-driven architecture.
- NestJS is a framework built on top of Node.js, providing modular architecture and TypeScript support for structured backend development.
2. Smart Contract Interaction Libraries for Web3 Backend
- Ethers.js and Web3.js are TypeScript/JavaScript libraries used for interacting with Ethereum-compatible blockchains.
3. Database Solutions for Web3 Backend
- PostgreSQL: Structured database used for storing off-chain transactional data.
- MongoDB: NoSQL database for flexible schema data storage.
- Firebase: A set of tools used, among other things, for user authentication.
- The Graph: Decentralized indexing protocol used to query blockchain data efficiently.
4. Cloud Services and Hosting for Web3 APIs
- AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions: Serverless functions that handle smart contract interactions.
- Infura, Alchemy, QuickNode: Blockchain RPC node providers offering API access to Ethereum, Polygon and other networks.
When It Doesn’t Make Sense to Go Fully On-Chain
Decentralization is valuable, but it comes at a cost. Fully on-chain applications suffer from performance limitations, high costs and slow execution speeds. For many use cases, a hybrid Web3 architecture that utilizes a mix of blockchain-based and off-chain components provides a more scalable and cost-effective solution.
In some cases, forcing full decentralization is unnecessary and inefficient. A hybrid Web3 architecture balances decentralization and practicality by allowing non-essential logic and data storage to be handled off-chain while maintaining trustless and verifiable interactions on-chain.
The key challenge when designing a hybrid Web3 backend is ensuring that off-chain computations remain auditable and transparent. This can be achieved through cryptographic proofs, hash commitments and off-chain data attestations that anchor trust into the blockchain while improving efficiency.
For example, Optimistic Rollups and ZK-Rollups allow computations to happen off-chain while only submitting finalized data to Ethereum, reducing fees and increasing throughput. Similarly, state channels enable fast, low-cost transactions that only require occasional settlement on-chain.
A well-balanced Web3 backend architecture ensures that critical dApp functionalities remain decentralized while offloading resource-intensive tasks to off-chain systems. This makes applications cheaper, faster and more user-friendly while still adhering to blockchain’s principles of transparency and security.
Example: NFT-based Game with Off-Chain Logic
Imagine a Web3 game where users buy, trade and battle NFT-based characters. While asset ownership should be on-chain, other elements like:
- Game logic (e.g., matchmaking, leaderboard calculations)
- User profiles & stats
- Off-chain notifications
can be handled off-chain to improve speed and cost-effectiveness.
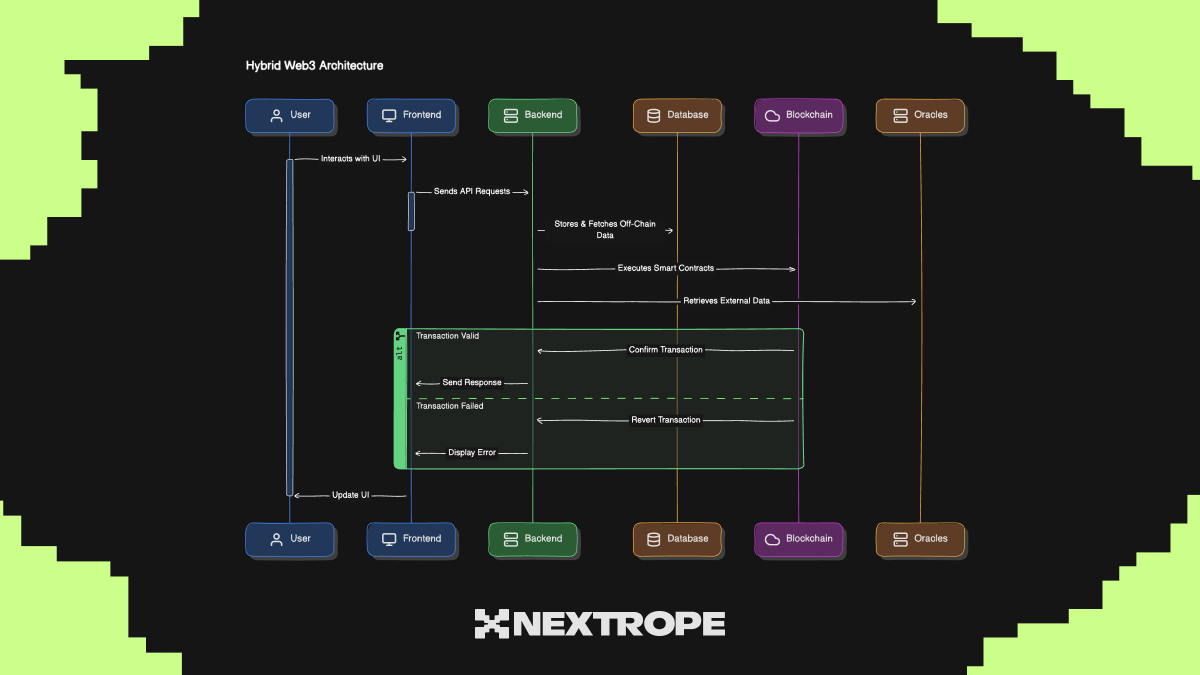
Architecture Diagram
Below is an example diagram showing how a hybrid Web3 application splits responsibilities between backend and blockchain components.
Comparing Web3 Backend APIs vs. Blockchain-Based Logic
| Feature | Web3 Backend (API) | Blockchain (Smart Contracts) |
|---|---|---|
| Change Management | Can be updated easily | Every change requires a new contract deployment |
| Cost | Traditional hosting fees | High gas fees + costly audits |
| Data Storage | Can store large datasets | Limited and expensive storage |
| Security | Secure but relies on centralized infrastructure | Fully decentralized & trustless |
| Performance | Fast response times | Limited by blockchain throughput |
Reducing Web3 Costs with AI Smart Contract Audit
One of the biggest pain points in Web3 development is the cost of smart contract audits. Each change to the contract code requires a new audit, often costing tens of thousands of dollars.
To address this issue, Nextrope is developing an AI-powered smart contract auditing tool, which:
- Reduces audit costs by automating code analysis.
- Speeds up development cycles by catching vulnerabilities early.
- Improves security by providing quick feedback.
This AI-powered solution will be a game-changer for the industry, making smart contract development more cost-effective and accessible.
Conclusion
Web3 backend development plays a crucial role in scalable and efficient dApps. While full decentralization is ideal in some cases, many projects benefit from a hybrid architecture, where off-chain components optimize performance, reduce costs and improve user experience.
In future posts in this Web3 backend series, we’ll explore specific implementation details, including:
- How to design a Web3 API for dApps
- Best practices for integrating backend services
- Security challenges and solutions
Stay tuned for the next article in this series!



