In recent years, the blockchain space has experienced a surge in popularity for Decentralized Autonomous Organizations, also known as DAOs. Operating through smart contracts on blockchain networks, these organizations are designed with transparency, decentralization, and autonomy in mind. The potential of DAOs to revolutionize traditional business and organizational models exists, yet it also brings forth distinct legal and regulatory issues. With the growing popularity of DAOs, it has become crucial to establish legal frameworks that regulate their functioning, creating a need for a clear "DAO legal structure."
Legal Framework for DAOs
Nonetheless, the legal aspects concerning DAOs are intricate and demand an in-depth comprehension of both blockchain technology and conventional legal systems. Presently, the prevailing legal frameworks for classic business entities such as limited liability companies and corporations do not directly apply to DAOs. This situation poses a challenge for regulators and DAO operators since there isn't an evident legal precedent concerning DAOs. In the following section, we will delve into the existing legal frameworks for DAOs.
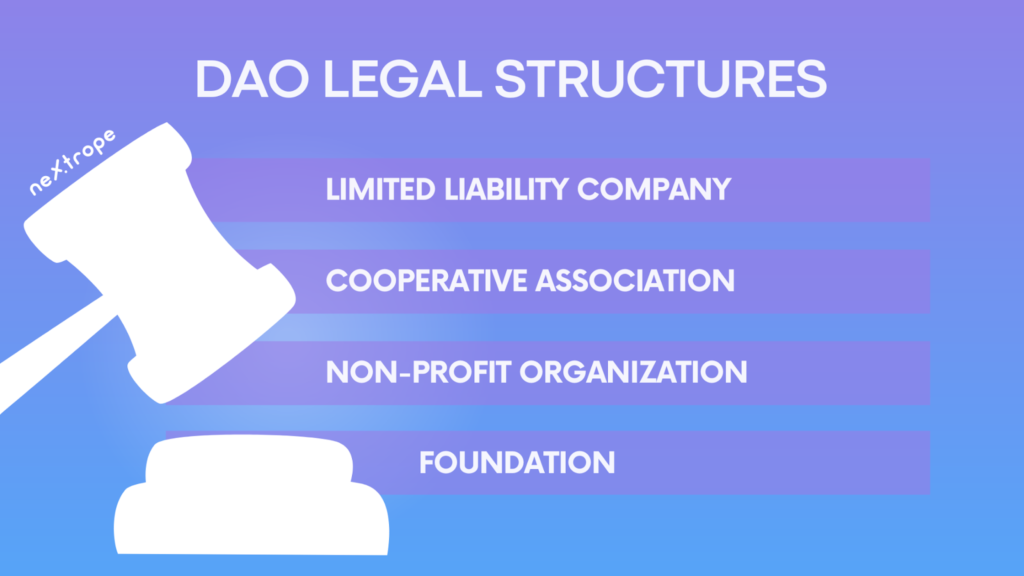
DAO Legal Structures:
DAOs utilize decentralized networks yet often need a legal structure for compliance and traditional system interaction. Various structures are available, each with unique benefits and factors. Common DAO legal structures include:
- Limited Liability Company (LLC): By forming an LLC, a DAO gains a defined legal framework and limited liability for members. It enables participants to establish ownership, roles, and responsibilities while maintaining legal protection.
- Cooperative Association: As another alternative, forming a cooperative association enables members to collectively own and operate the DAO. This model promotes democratic decision-making and profit-sharing, adhering to cooperative principles.
- Non-Profit Organization: Philanthropic or community-focused DAOs may adopt a non-profit structure. This allows them to pursue charitable goals, access tax-exempt status, and use existing non-profit regulations.
- Foundation: Some DAOs choose foundation structures, prevalent in crypto and blockchain fields. Foundations offer governance, resource allocation, and community management frameworks while pursuing specific goals like developing decentralized tech or promoting causes.
It's crucial to understand that each legal structure's suitability for a DAO depends on its objectives, jurisdiction, and operations.
Would you like to read about Smart Contracts Security Audits? Be sure to check out our article!
Global Adoption of DAOs: A legal overview
The advent of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) has been met with varying legal responses across the globe. Wyoming led the charge in the United States by recognizing DAOs as limited liability companies (LLCs) in 2021. This ground-breaking move has since inspired other states like Tennessee to revise their corporate codes to include provisions for decentralized organizations.
Switzerland, known for its forward-thinking approach to cryptocurrency and blockchain regulation, has also considered recognizing DAOs as legal entities. The Swiss Federal Council has pondered creating a unique legal entity specifically for DAOs, which could help integrate them within the purview of Swiss law.
Meanwhile, the Island of Jersey has introduced a hybrid entity – the Jersey Limited Liability Company (LLC), inspired by the LLC models of Cayman and Delaware. These LLCs are increasingly being used as legal wrappers for DAOs, effectively merging conventional legal structures with decentralized organization models. This innovative approach allows DAOs to benefit from the well-established legal structure of LLCs while simultaneously leveraging the advantages of blockchain technology and smart contracts.
In the United Kingdom, the government has tasked the Law Commission with the responsibility of studying DAOs. Given their growing relevance in the crypto-token and decentralized finance sectors, understanding DAOs' unique characteristics and potential legal implications is critical. The 15-month study aims to understand DAOs' legal treatment under English and Welsh law, their structure, and operation, along with potential legal barriers. The project aligns with the UK's broader ambition of becoming a global hub for crypto-asset technology, and clarifying the legal status of DAOs within the UK is an integral part of this vision.
For more on the legal aspects of Dao, read this
Questions to help pick a DAO legal entity
Are you wondering what legal structure to give your DAO? Read these questions, they may help you think through important issues
Should you form a DAO? If your project doesn't require blockchain and decentralization, creating a DAO may not be beneficial, and another organizational structure could be more appropriate.
Is a legal entity structure necessary for your DAO? Legal entities often possess greater capabilities than those without entities. Some benefits include: managing community-controlled treasuries with ease, owning assets and intellectual property, employing people and generating income, and collaborating with external organizations. Essentially, legal entity status grants a DAO legal existence, reduces participant liability, and assists in determining and fulfilling tax obligations. Although no perfect legal entity structure exists for the majority of DAOs, selecting an appropriate one can help reduce risks.
What kind of DAO are you creating? The DAO's purpose will frequently direct the most fitting legal structure; however, no universal solution exists. A network/protocol overseeing DAO may not be adequate for other types of DAOs. Investment-focused DAOs might fare well as LLCs, similarly to numerous existing investment clubs. Collector, social or charitable DAOs could function better as LLCs or UNAs based on their specific circumstances. Meanwhile, cooperative and collective DAOs might find LCAs suitable—a format utilized by many existing co-ops. When determining a DAO's legal entity, referring to frameworks for existing analogues can be helpful.
In the case of network/protocol DAOs, consider the following: does significant U.S. membership or activity exist? Does the DAO control network/protocol income or a treasury? If none of these factors apply, an Entityless structure might be a suitable choice. However, if any one of these conditions is met, the DAO's activities may lead to U.S. tax obligations for the DAO or its members. Opting for U.S. entity structures is recommended as the most straightforward method of satisfying these obligations.
For the visually oriented, here’s guide in the form of a decision tree made by a16zcrypto
Conclusion
The global adoption of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) has begun to impact existing legal frameworks. As DAOs gain popularity, it becomes increasingly essential to establish clear legal structures that accommodate their unique characteristics. Although the traditional legal frameworks for business entities do not directly apply to DAOs, multiple legal structures such as LLCs, cooperative associations, non-profit organizations, and foundations can still provide some compliance and interaction with conventional systems. Innovations in legislation, like those seen in Wyoming and Jersey, demonstrate growing efforts to integrate decentralized organizations into existing legal contexts. While countries like Switzerland and the United Kingdom explore the possibility of new legal entities or study existing laws' adaptability, it is evident that DAO's legal and regulatory landscape is constantly evolving. Stakeholders must remain informed of these developments to navigate the uncharted territory of DAO legal structure and regulatory challenges successfully.
 en
en  pl
pl