In the ever-changing world of blockchain technology, Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) have risen as influential models for decentralized cooperation and decision-making. By harnessing the transparent and secure nature of blockchain, AI, and cryptocurrencies, DAOs establish self-regulating communities centered around common objectives and values. Tokenomics, which encompasses the creation and application of token-based economic systems within these organizations, lies at the core of DAOs. This article delves into the importance of tokenomics in DAOs and its crucial role in promoting involvement and encouraging cooperation among community members.
Are you interested in DAO security? Be sure to check out our article on The DAO Hack
DAO tokenomics involves using digital tokens to stimulate and reward ecosystem participants for their contributions. These tokens act as both a medium for exchange and a symbol of value, allowing individuals to partake in the governance, decision-making, and development processes within the DAO. By syncing community members’ interests with the organization’s success, tokenomics in DAOs serve as a potent tool for instigating active engagement and collaboration.
Understanding Tokenomics in DAOs
DAO tokenomics is a critical aspect in the functioning and management of decentralized autonomous organizations. In this segment, we study the core principles of DAO tokenomics, commencing with an examination of DAO tokens. Symbolizing ownership or membership within a DAO, the digital assets called DAO tokens are spread among participants and hold considerable worth in their ecosystem. They act as a governance mechanism for DAOs by giving holders specific rights, tasks, and decision-making authority.
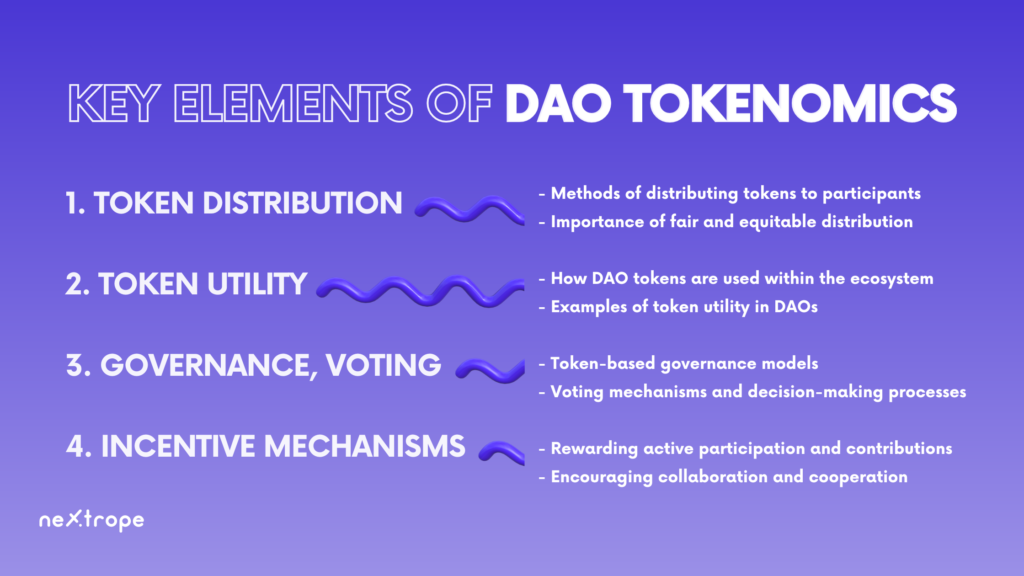
1. Token Distribution
Several crucial factors should be taken into account when discussing DAO tokenomics. Primarily, token distribution is essential. To disseminate tokens among participants, DAOs utilize various techniques such as token sales, airdrops, or reward-based contribution programs. Establishing a fair and inclusive environment hinges on the equitable allocation of tokens, making certain that everyone has equal chances to engage and contribute.
2. Token utility
Token utility is another vital element, pertaining to the use of DAO tokens within their ecosystem. Such tokens can possess multiple functions – they might work as a medium of exchange or provide access to services and features, or they could represent voting rights. By improving the value and usability of tokens, these utility aspects promote their integration into the community.
3. Governance and Voting
Tokenomics also heavily influences governance and voting mechanisms in DAOs. Token-driven governance models permit holders to partake in decision-making procedures, suggest and vote for proposals, and affect the course of the DAO. Different voting systems and decision-making methods can come into play – from straightforward majority votes to delegated voting setups – based on a specific DAO’s layout and goals.
4. Incentive Mechanisms
Moreover, incentive structures are central components of DAO tokenomics that encourage active involvement and cooperation within the community. Those who devote their time, resources, or knowledge to a DAO are often rewarded accordingly. Incentivizing active engagement results in a dynamic ecosystem where members are inclined to collaborate and strive toward shared objectives.
Benefits of Effective Tokenomics in DAOs
A variety of advantages arise from efficient tokenomics in DAOs, contributing to the flourishing and expansion of these decentralized entities. Enhanced community involvement and engagement is a notable benefit. DAOs can cultivate a feeling of membership and responsibility among individuals by developing tokenomics that reward substantial contributions and active participation. This encourages members to actively offer their talents, expertise, and assets, knowing they will be acknowledged and compensated. Such intensified involvement results in a thriving and energetic ecosystem where community members join forces, exchange thoughts, and strive towards shared objectives. Moreover, DAO tokenomics allows for effective resource distribution. Moreover, through utilizing tokens as a means for funding and managing resources, DAOs can allocate resources in a transparent, decentralized manner. This guarantees the best use of funds and input, enabling the DAO to carry out projects adeptly, create new features, and foster innovation.
Successful DAO Tokenomics Models
1. MakerDAO
One of the most prominent DAOs in existence, MakerDAO, employs a unique dual-token model that has contributed to its success. The system includes the Maker (MKR) token and the DAI stablecoin.
MKR tokens serve governance purposes, enabling holders to cast votes on proposals, such as adjustments to the system’s parameters. Additionally, the tokenomics of MKR aims to promote responsible governance. As the system operates efficiently, MKR holders reap benefits due to a decrease in MKR’s total supply through a process known as “burning.” Conversely, during times when the system
DAI, on the other hand, is a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar. It’s generated by locking up collateral in the form of other crypto assets. This dual-token model has proven successful, ensuring stability in the system and encouraging active participation from its members.
2. Aragon
Aragon is a platform that allows users to create and manage their DAOs. It uses the Aragon Network Token (ANT), a utility token that provides holders with voting rights within the Aragon network.
Aragon’s tokenomics model is centered around the concept of decentralization and democracy. ANT token holders can vote on various aspects, such as changes to the network’s settings and dispute resolution. This creates a self-sustainable ecosystem where the community directly influences the platform’s direction and future development.
3. Compound
Compound is a decentralized lending platform governed by its users through the COMP token. In this DAO, users earn COMP tokens as they interact with the platform, borrowing, or lending assets.
The Compound’s tokenomics model has been designed to distribute governance power proportionally to those who use the platform the most. COMP tokens give holders the right to propose and vote on changes to the Compound protocol. This model has been successful because it ensures that those who are most invested in and knowledgeable about the platform have the most significant say in its operation and future direction.
4. Yearn.Finance
Yearn.Finance represents a paradigm shift in the way DAO tokenomics models are structured. This platform aims to simplify the ever-growing DeFi space for investors by automating yield farming strategies. At the core of its governance is the YFI token.
Yearn.Finance’s success lies in its unique approach to token distribution, incentives for holding tokens, active community participation, and a founder committed to the platform’s success. Its tokenomics model ensures that the platform remains decentralized, democratic, and in the best interest of its most active users. This case study highlights how an innovative approach to DAO tokenomics can lead to a successful, thriving ecosystem in the DeFi space.
Conclusion
To sum up, DAO tokenomics is critical in motivating engagement and cooperation within decentralized autonomous organizations. Through the usage of tokens for value exchange, governance, and incentive structures, DAOs can foster dynamic communities in which members actively participate and pursue shared objectives. The core components of successful DAO tokenomics include token distribution, token utility, governance and voting systems, and incentives. Nevertheless, ongoing challenges such as decentralization, sustainability, and legal concerns must be tackled as this field continues to progress.
Do you need the help of specialists to create a tokenomy? Contact us!