
In the rapidly evolving world of blockchain and cryptocurrencies, one technological advancement stands out for its potential to revolutionize user interaction and operational efficiency: Account Abstraction (AA). This concept, although technical in nature, offers a gateway to a more accessible and versatile experience in the realm of digital assets and decentralized applications.
In this article, we delve into the intricacies of Account Abstraction, exploring its practical applications through various case studies and potential future implementations. Our journey into the world of AA not only highlights its current capabilities but also sheds light on its promising future in shaping the landscape of blockchain technology and cryptocurrency usage.
What is Account Abstraction?
Account Abstraction, at its core, is a concept that seeks to simplify and unify the user experience in the blockchain ecosystem. Traditionally, blockchain accounts are differentiated into two primary types: externally owned accounts (EOAs), controlled by private keys, and contract accounts, governed by their contract code. Account Abstraction blurs this distinction, proposing a more flexible framework where the functionalities of contract accounts can be integrated into user accounts.
The idea of Account Abstraction is not new; it has roots tracing back to the early days of Ethereum, with co-founder Vitalik Buterin being a prominent advocate. The primary goal of AA is to enhance the user experience by providing more control and flexibility, while also bolstering security measures. In a typical blockchain environment, users often face challenges related to key management, transaction complexities, and limited operational functionalities. Account Abstraction addresses these issues by enabling users to execute transactions that are more versatile, secure, and user-friendly.
MUST READ: What is Account Abstraction?
The Timeline of Account Abstraction Adoption
(from Binance Report)
Source: A Primer on Account Abstraction August 2023 https://research.binance.com/static/pdf/a-primer-on-account-abstraction.pdf
Case Studies of Account Abstraction
Visa’s Paymaster Contracts
Experiment with Paymaster Contracts. Visa explored the use of Paymaster contracts to abstract away basic blockchain interactions, improving the on-chain payment experience through a self-custodial smart contract wallet. This proof of concept aimed to reduce friction and unlock the potential of digital transactions.
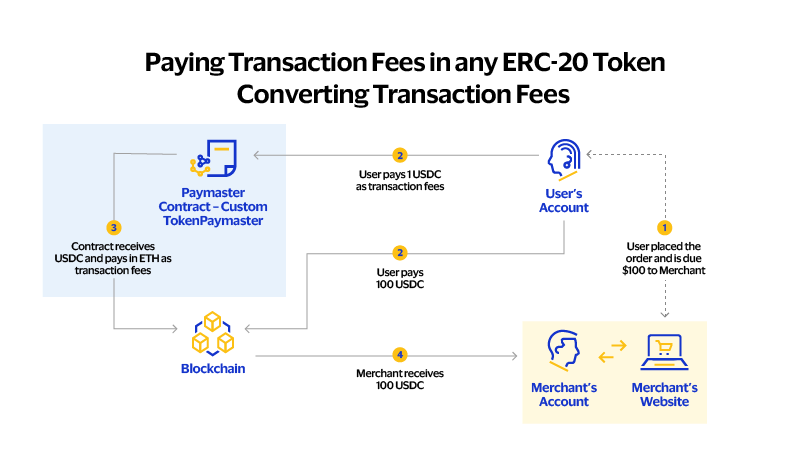
Implementation. The Paymaster contract acts as an intermediary currency conversion service, allowing users to pay in various digital currencies, which are then converted to the blockchain’s native token for gas fees. Alternatively, it can cover the gas fees, offering free transactions through their wallet platform.
Safe (Formerly Gnosis Safe)
Multi-Signature Scheme. Safe stands out for its multi-signature scheme, requiring multiple entities to sign transactions, reducing the risk of malicious attacks.
Integration of AA. Safe has integrated the ERC-4337 standard, allowing users to create smart contract wallets with customizable rules for transaction authorization, such as setting spending limits for enhanced security.
Argent on StarkNet
Social Recovery Feature. Argent, a leading wallet provider on StarkNet, introduced the concept of social recovery, allowing users to recover lost or forgotten private keys.
Innovative Wallet Recovery. Users can nominate “guardians” to help access the wallet if the seed phrase is forgotten, or use their email and phone number for off-chain recovery, introducing a familiar two-factor authentication mechanism.
MUST READ: Account Abstraction on Starknet
Braavos Wallet
Signature Abstraction. Braavos, another wallet provider on StarkNet, has adopted a form of signature abstraction, allowing users to customize their transaction verification process.
Biometric Identity Authentication. Users can access their wallet using their phone’s biometric features, like facial or fingerprint recognition, providing a secure and user-friendly experience.
Visa’s Delegable Accounts for Automatic Payments
Auto Payments for Self-Custodial Wallets. Visa demonstrated a solution for automatic payments in self-custodial wallets, enabling recurring payments based on predetermined conditions without manual user approval each time.
Ease of Transaction. This setup allows users to set up programmable payment instructions, highlighting the potential for real-world applications and convenience.
Lens Protocol’s Social Media Integration
Dispatcher Wallet. Lens Protocol implemented AA to delegate signing privileges to a dispatcher wallet for functions like posting, commenting, and changing profile metadata.
User-Friendly Interactions. This enables seamless interactions with dApps without constant approval and the dispatcher wallet also covers gas fees, removing the need for users to hold native tokens for in-app interactions.
ERC-6551: Token-Bound Accounts
Enhanced NFT Utility. ERC-6551 empowers NFTs to function as smart contract accounts, enhancing their utility by allowing them to hold assets, manage identities, and participate more actively in the on-chain landscape.
Sapienz Project
Digital Street Culture. The Sapienz project by Stapelverse incorporates ERC-6551, offering customizable characters based on owned NFTs, with various cosmetics attached to the TBA of the characters.
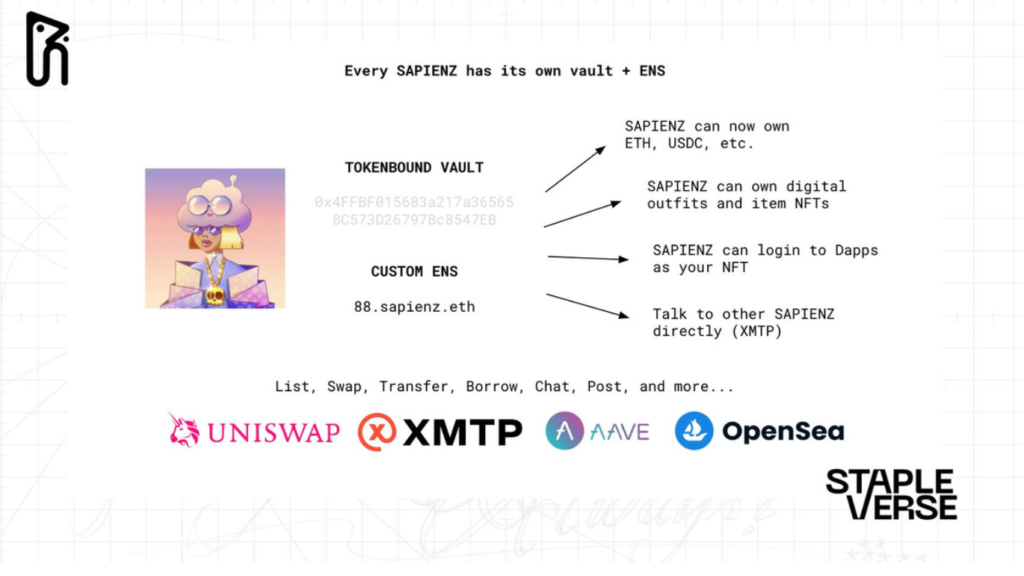
Source: @stapleverse
Conclusion – Account Abstraction Case Studies
| Case Study / Implementation | Key Features | Impact / Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Visa’s Paymaster Contracts | Paymaster contracts for self-custodial wallets; intermediary for currency conversion and gas fee coverage. | Enhances on-chain payment experience, reduces friction, and unlocks digital transaction potential. |
| Safe (Formerly Gnosis Safe) | Multi-signature scheme integrated with ERC-4337 for customizable transaction authorization. | Increases security and operational flexibility in wallet transactions. |
| Argent on StarkNet | Social recovery feature allowing wallet recovery through nominated ‘guardians’ or off-chain methods. | Improves wallet security and user experience through innovative recovery options. |
| Braavos Wallet | Signature abstraction enabling customized transaction verification; biometric identity authentication. | Provides secure and user-friendly access to wallet functions. |
| Visa’s Delegable Accounts for Automatic Payments | Automated payments in self-custodial wallets with programmable payment instructions. | Facilitates real-world application of blockchain for convenient, automated transactions. |
| Lens Protocol’s Social Media Integration | Dispatcher wallet for delegating signing privileges; seamless interactions with dApps, covering gas fees. | Enhances user experience in social media and dApp interactions. |
| ERC-6551: Token-Bound Accounts | NFTs as smart contract accounts; enhanced utility in holding assets and managing identities. | Expands the functionalities and applications of NFTs in the blockchain ecosystem. |
| Sapienz Project | ERC-6551 utilization for customizable NFT-based characters in digital street culture context. | Innovates in digital culture by merging NFTs with character customization and interaction. |
These case studies showcase the diverse and impactful applications of Account Abstraction across various sectors. They highlight AA’s potential in simplifying user experience, enhancing security, and expanding the functionalities of blockchain technology.


