DEX is far more than just another DeFi trend in the game. Decentralized exchanges allow crypto traders to swap tokens in a peer-to-peer model. Direct transactions between parties, no need to sign in - these are just some of their advantages over centralized exchanges.
In this article, you will find:
- How does decentralized exchange work?
- Decentralized exchange vs centralized exchange
- Pros and cons of decentralized exchanges
- What do DEXs mean for the world of decentralized finance?
Definition:
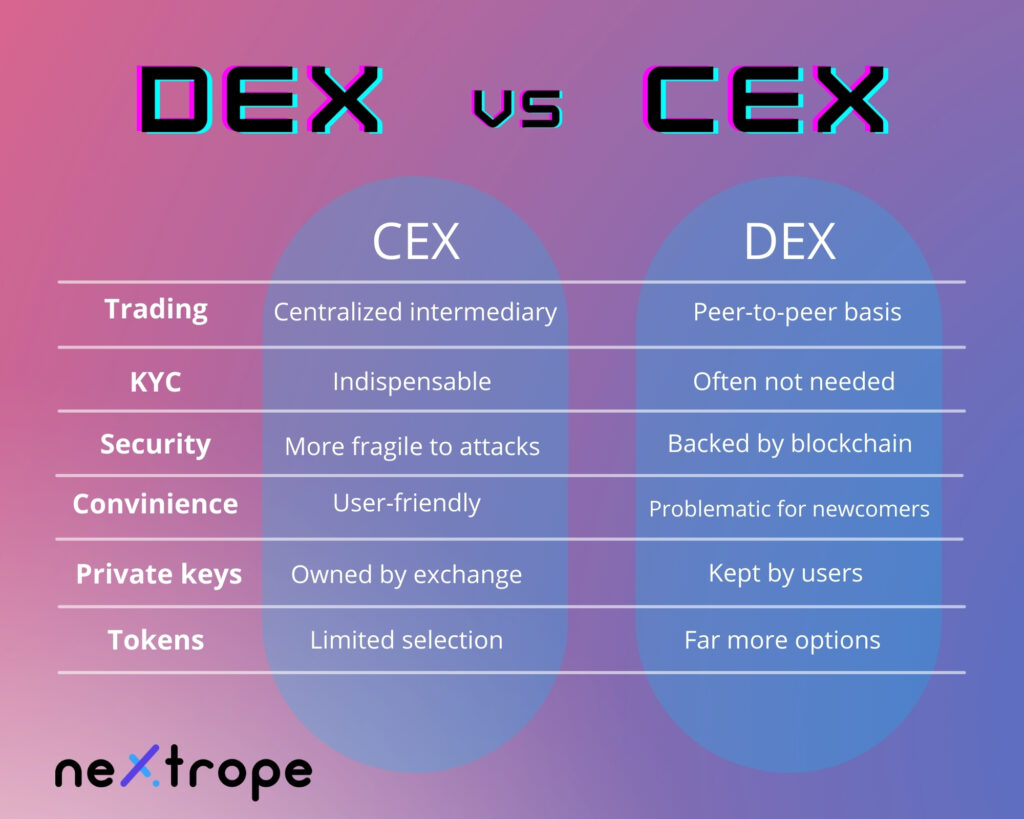
Decentralized exchange, also known as DEX, is a platform where crypto investors can buy and sell cryptocurrencies without intermediaries.
Substantially any exchange working on a peer-to-peer basis could be called decentralized. Yet, in this article, we will focus on those with backend existing on a blockchain.
Thanks to the usage of that technology, no one takes custody of your assets and the safety of transactions is guaranteed by protocol. Therefore, you don't have to give the exchange this amount of trust as in the case of centralized exchanges.

How does centralize exchange work?
Centralized exchanges, for example, Coinbase, are digital markets where people can buy, sell and trade digital assets such as Bitcoin, Ether, or other cryptocurrencies.
To access the site, you have to sign up by providing banking details and identifying personal data. This is the part of KYC and AML practices, which have to be followed by every centralized exchange. Because such data is fragile, it's quite clear that a security dilemma is present even before one starts trading.
Buying cryptocurrencies on a centralized exchange
The price of each coin on the site is based on an "order book" - consisting of orders to buy and sell.
Trading on centralized exchanges generally seems simple. You just need to choose coins and confirm a transaction. The exchange will show the funds you acquired in your account. Then you can trade them for other digital assets.
Yet, users don't really hold their funds. Exchange work here as a custodian of customer funds. Furthermore, trades don't occur on the blockchain. Instead, they take place only within the exchange's database.
Disadvantages of central authority
From a technical point, when you deposit funds on a centralized exchange, you lose control over it. Exchange puts your funds into wallets controlled by it.
Additionally, it owns your private keys. Therefore, if you want to withdraw your money, the exchange has to sign the transaction on your behalf.
Security
With CEXs come some vital security questions.
Firstly, exchanges can limit user access to their assets or even restrict the ability to trade them. Secondly, the risk of a hacker attack is always present. Exchanges work very hard to avoid it, yet as the example of Mt. Gox shows, they are still vulnerable.
Advantages of centralized exchanges
Generally, this type of cryptocurrency exchange is easier and more convenient to use than decentralized exchanges. Especially for the newcomers.
Moreover, trading there is often faster because the whole process doesn't take place on a blockchain. Additionally, trading fees can be lower as well.
How do decentralized exchanges work?
In many ways, decentralized exchanges are similar to centralized ones. However, differences are more than substantial. Essentially in decentralized exchanges, trade rely on a blockchain (most often Ethereum or Binance Smart Chain). Trading between users is conducted using smart contracts - orders are executed on-chain. Thanks to that, during the whole process exchange, doesn't take control of users' assets.
Cross-chain exchanges are a very promising novelty on the DEX market. Yet, most of the popular decentralized exchanges operate only on one blockchain - most often Ethereum or Binance Smart Chain.
There are three ways in which decentralized exchanges operate trading:
- On-chain order book
- Off-chain order book
- Automated Market Maker
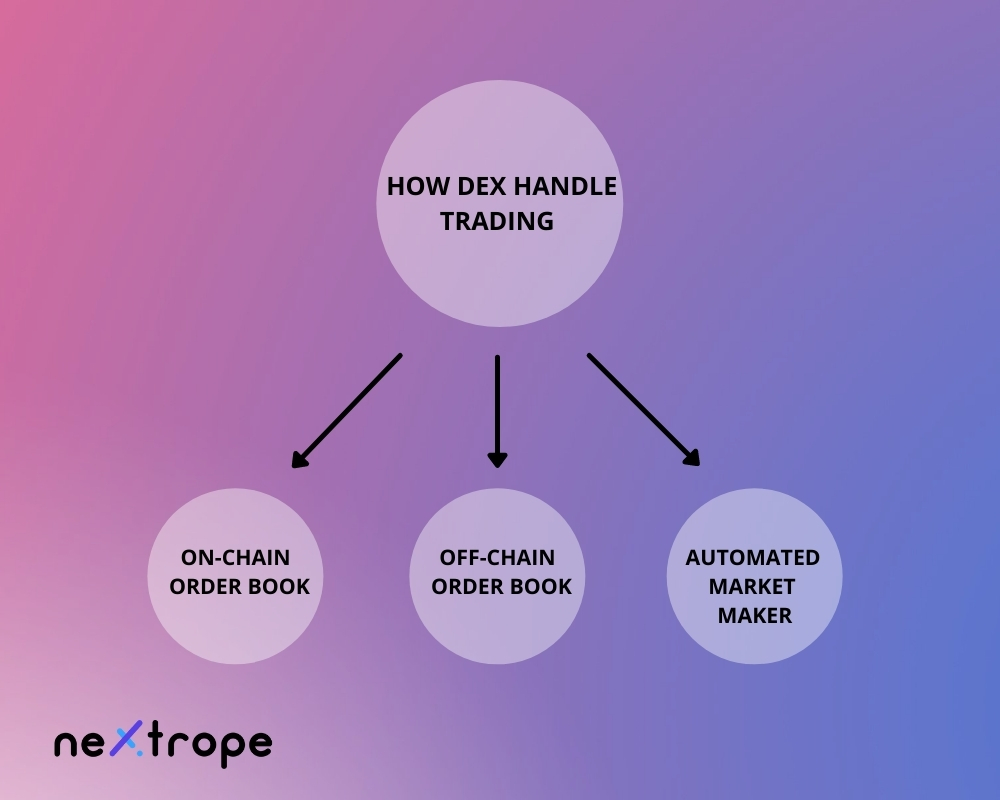
On-chain order book
There are decentralized exchanges where every transaction is written to a blockchain. It means that every order, as well as cancellation or alteration, is handled on-chain.
Without a doubt, this is the purest approach to decentralization. There is absolutely no third party involved at any stage of trading. Everything is extremely transparent. Unfortunately, there are vital downsides as well.
The on-chain order book is far less practical than the other two options. Firstly, because every node on the blockchain record the order, placing it requires paying a fee. Furthermore, users have to wait until the miner adds necessary data to the chain. It translates to high costs and poor liquidity.
Front running
Front running refers to a situation when some insider posses information about a pending transaction and uses this knowledge to place an order before the transaction is completed. Because he benefits from the fact that is inaccessible to the public, it’s illegal. Some believe that’s a serious threat in the on-chain model.
It can't occur in the traditional way, since everything is recorded on the global ledger. Yet, a miner can observe the order before it's added to the blockchain, and add their order first.
Off-chain order book
Off-chain order books are a bit more centralized than their counterparts. But they are also far more practical. In this model, orders are hosted elsewhere and only the final transaction is settled on the blockchain. Moreover, you can still benefit from non-custodial storage.
Because orders aren't stored on-chain, this approach is faster and less costly. Furthermore, it helps to achieve better liquidity of trades. However, it can encounter some of the security issues typical for CEXs.
Automated Market Maker (AMM)
Automated Market Maker, sometimes called Proactive Market Maker, has some serious advantages over the previous two solutions.
In order books model, if you have Bitcoin and want to trade it for Ether, you need someone who wants to buy Bitcoin and have Ether. Moreover, they have to be willing to trade at an agreed-upon price.
AMM simply removes counter-parties and applies algorithms that deal with asset pricing. With Automative Market Maker, you can trade Ether regardless of whether there’s someone who wants it for Bitcoin.
To achieve it, AMMs typically use liquidity pools. We'll explain this term in another article.
Decentralized margin trading
Margin trading refers to the practice of borrowing funds from a broker to trade a financial asset, which forms the collateral in lending from the broker. Usually, a broker in DeFi is one of the AMMs.

Pros of decentralized exchange
Lower risk
Decentralized cryptocurrency exchange doesn't hold users' assets. Because they are held in a private wallet, and you have the keys, they are immune to hacks.
No KYC needed
Most of DEXs doesn’t have to follow KYC and AML requirements, because they don’t intermediate in transactions between parties. That’s why it’s often more convenient to build your own DEX than CEX.
More options
On the DEX platform, trades of tokens that aren’t listed on CEXs are possible.
Cons of decentralized exchange
Trading volume
The volume traded on CEXs is still much higher than that on DEXs. Liquidity is lower as well.
Higher fees
It's not an absolute norm, but when it comes to fees CEXs often offer the best price.
Convenience
Decentralized exchange is less user-friendly than a traditional one.
Conclusion
Decentralized Exchanges can be considered as one of the key factors in the current Defi boom. That’s why we mentioned them among the top DeFi trends for 2021. To this point, everything indicates we were right. Just look at the success of projects like Uniswap or PancakeSwap. 2021 definitely belongs to DEXs. Apparently, today crypto traders value high security, privacy, and the wide range of options that they bring.
Yet, DEXs are still a relatively new branch of the crypto world. Therefore, there is still much space for innovation. That’s why more and more investors become interested in building their own Decentralized Exchange. With the high speed of blockchain technology development and the growing popularity of alternative crypto assets, circumstances are more than promising.
 en
en  pl
pl